Georgia Department of Education Study Guide Domain III Genetic
... Define genetics Define traits. Define nucleic acid. What are the components of a DNA nucleotide? (3 parts) What are the 4 nitrogen bases found in DNA? Define double helix. Why is DNA called a double helix? The two strands of nucleotides are held together by what? The “sides of the ladder” of DNA con ...
... Define genetics Define traits. Define nucleic acid. What are the components of a DNA nucleotide? (3 parts) What are the 4 nitrogen bases found in DNA? Define double helix. Why is DNA called a double helix? The two strands of nucleotides are held together by what? The “sides of the ladder” of DNA con ...
Unique Human Subjects Concerns for j Genetic Research
... Genetic Information Non-discrimination Act of 2008 (plus prior HIPAA) Genetic information is defined as: Genetic tests on individual (including those done for research): analysis of DNA, RNA, chromosomes, proteins or metabolites to detect genotypes, mutations, or chromosomal changes Genetic tests o ...
... Genetic Information Non-discrimination Act of 2008 (plus prior HIPAA) Genetic information is defined as: Genetic tests on individual (including those done for research): analysis of DNA, RNA, chromosomes, proteins or metabolites to detect genotypes, mutations, or chromosomal changes Genetic tests o ...
6-6 Study Guide
... Refer to your cell sketch in the last box on the previous page. Also refer to Figure 2.3 if necessary. 1. In the first box below, show what your cell would look like at the end of meiosis I. Remember, the result will be two cells that have one duplicated chromosome from each homologous pair. 2. In t ...
... Refer to your cell sketch in the last box on the previous page. Also refer to Figure 2.3 if necessary. 1. In the first box below, show what your cell would look like at the end of meiosis I. Remember, the result will be two cells that have one duplicated chromosome from each homologous pair. 2. In t ...
H_Pylori_MicroArray_Data_Analysis
... • Under the control of the RpoN there is an increase in transcription of genes ...
... • Under the control of the RpoN there is an increase in transcription of genes ...
Cell Cycle DNA Structure and Replication Student PPT Nts
... • ______________________: when a chunk of DNA (usually large) is removed from 1 chromosome and attached to another ...
... • ______________________: when a chunk of DNA (usually large) is removed from 1 chromosome and attached to another ...
Hutchinson Gilford Progeria Syndrome: A
... potentiality for its use in gene therapy. In fact, it permits to manipulate the site of pathogenic mutations using transient viral vectors such as the adenoviral-derived vectors or other non-integrating vectors. The great advantage is that even if the vector cannot integrate within the host, the con ...
... potentiality for its use in gene therapy. In fact, it permits to manipulate the site of pathogenic mutations using transient viral vectors such as the adenoviral-derived vectors or other non-integrating vectors. The great advantage is that even if the vector cannot integrate within the host, the con ...
Document
... Double Crossovers • More than one crossover event can occur in a single tetrad between non-sister chromatids, – if recombination occurs between genes A and B 30% of the time, • (p = 0.3), • then the probability of the event occurring twice is 0.3 x 0.3 = 0.09, or nearly 10 map units. ...
... Double Crossovers • More than one crossover event can occur in a single tetrad between non-sister chromatids, – if recombination occurs between genes A and B 30% of the time, • (p = 0.3), • then the probability of the event occurring twice is 0.3 x 0.3 = 0.09, or nearly 10 map units. ...
mutations
... replication DNA replication is very accurate The enzyme DNA polymerase “proofreads” the copied DNA & repairs most mutations Mutations can be harmful, beneficial or have no effect at all ...
... replication DNA replication is very accurate The enzyme DNA polymerase “proofreads” the copied DNA & repairs most mutations Mutations can be harmful, beneficial or have no effect at all ...
NCEA Level 2 Biology (91157) 2012 Assessment Schedule
... Gene pool is (all) the genes or alleles (held by the individuals) in a population. Mutation can be defined as a (permanent) change in the DNA. Somatic mutations occur in any cells of the body other than in the gametes Gametic mutations only occur in sex cells, eg, sperm /eggs (accept pollen). Explan ...
... Gene pool is (all) the genes or alleles (held by the individuals) in a population. Mutation can be defined as a (permanent) change in the DNA. Somatic mutations occur in any cells of the body other than in the gametes Gametic mutations only occur in sex cells, eg, sperm /eggs (accept pollen). Explan ...
Unit 5: Genetics
... because they make proteins that help prevent the cells from forming tumors. If one of these genes is changed through a mutation, the protein may not do its job, making it easier for a tumor to develop. Women who inherit a mutated copy of either the BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene have an increased chance of dev ...
... because they make proteins that help prevent the cells from forming tumors. If one of these genes is changed through a mutation, the protein may not do its job, making it easier for a tumor to develop. Women who inherit a mutated copy of either the BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene have an increased chance of dev ...
EOC Study Guide Template with answers
... In Diploid the cell contains two sets of chromosomes. Most cells in the body are diploid. The diploid number of chromosomes in a human somatic (body) cell is 46. Haploid means that the cell contains one set of chromosomes, half of a diploid cell. The haploid number of chromosomes in a human body cel ...
... In Diploid the cell contains two sets of chromosomes. Most cells in the body are diploid. The diploid number of chromosomes in a human somatic (body) cell is 46. Haploid means that the cell contains one set of chromosomes, half of a diploid cell. The haploid number of chromosomes in a human body cel ...
Genome Organization
... • Typically a circular, double-stranded DNA molecule. • Linear in yeast and some other fungi. • In animals, typically 16-18 kb. ...
... • Typically a circular, double-stranded DNA molecule. • Linear in yeast and some other fungi. • In animals, typically 16-18 kb. ...
Genetics Terms
... crossed with contrasting traits, all offspring will show the dominant trait. • Law of Segregation – during egg/sperm formation, the pair of genes/alleles for a trait separate so that each gamete has only one of the genes for the trait. ...
... crossed with contrasting traits, all offspring will show the dominant trait. • Law of Segregation – during egg/sperm formation, the pair of genes/alleles for a trait separate so that each gamete has only one of the genes for the trait. ...
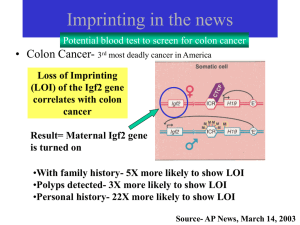
Imprinting
... • Igf2 (paternally expressed)-if defective=40% reduction in growth • Igf2r (Igf2 receptor)- if defective=increase growth • Igf2-/Igf2r- = normal Another test- Ask if imprinting fails to occur in a monogomous ...
... • Igf2 (paternally expressed)-if defective=40% reduction in growth • Igf2r (Igf2 receptor)- if defective=increase growth • Igf2-/Igf2r- = normal Another test- Ask if imprinting fails to occur in a monogomous ...
A-4 Notes
... This ratio of 60/40 is also true (roughly) for your personality type. • Some people feel that this will give employers an excuse to fire people if they don’t have the ‘right’ genetics. • The bottom line is that there is a lot that we do not yet know about genetics. ...
... This ratio of 60/40 is also true (roughly) for your personality type. • Some people feel that this will give employers an excuse to fire people if they don’t have the ‘right’ genetics. • The bottom line is that there is a lot that we do not yet know about genetics. ...
X-inactivation
... Active chromatin – central position in nucleus, it allows maximal efficiency of replication and transcription 2. Centromeric heterochromatin - role in centromeric function – in cohesion of sister chromatids and normal disjunction of chromatids 3. Role in epigenetic regulation of gene expression duri ...
... Active chromatin – central position in nucleus, it allows maximal efficiency of replication and transcription 2. Centromeric heterochromatin - role in centromeric function – in cohesion of sister chromatids and normal disjunction of chromatids 3. Role in epigenetic regulation of gene expression duri ...
Protocol: Kinetic Reporter Gene Assay using the
... Reporter gene assays continue to be one of the simplest, most robust ways to analyze the activation of transcription factors and their associated signaling pathways. This generic protocol is intended to provide a framework around which one could plan reporter assays that fit any application. In addi ...
... Reporter gene assays continue to be one of the simplest, most robust ways to analyze the activation of transcription factors and their associated signaling pathways. This generic protocol is intended to provide a framework around which one could plan reporter assays that fit any application. In addi ...
Omics and Overview tutorial script
... Can zoom in and out Semantic zooming means that information appears and disappears Highlighting and other display tools Can show / hide links between transported compounds and those same compounds inside the metabolic diagram Can highlight reactions and pathways Show highlight all by class Show clea ...
... Can zoom in and out Semantic zooming means that information appears and disappears Highlighting and other display tools Can show / hide links between transported compounds and those same compounds inside the metabolic diagram Can highlight reactions and pathways Show highlight all by class Show clea ...
X-inactivation
... Active chromatin – central position in nucleus, it allows maximal efficiency of replication and transcription 2. Centromeric heterochromatin - role in centromeric function – in cohesion of sister chromatids and normal disjunction of chromatids 3. Role in epigenetic regulation of gene expression duri ...
... Active chromatin – central position in nucleus, it allows maximal efficiency of replication and transcription 2. Centromeric heterochromatin - role in centromeric function – in cohesion of sister chromatids and normal disjunction of chromatids 3. Role in epigenetic regulation of gene expression duri ...
Chromosomal rearrangements in Salmonella spp. s2-2
... mologous recombination, resulting in deletions29; site-specific recombination at the dif-site in the TER region, due to activity of two related recombinases XerC and XerD of the lambda integrase family30. 11 is likely that these types of recombination are responsible for inversion in wild type strai ...
... mologous recombination, resulting in deletions29; site-specific recombination at the dif-site in the TER region, due to activity of two related recombinases XerC and XerD of the lambda integrase family30. 11 is likely that these types of recombination are responsible for inversion in wild type strai ...
No Slide Title
... If there were several resistance genes, the disease organism would take very much longer to overcome all resistance genes (in fact it is ...
... If there were several resistance genes, the disease organism would take very much longer to overcome all resistance genes (in fact it is ...
Vertebrate DNA Transposon as a Natural Mutator
... radiation. At present, the trigger for the germ line transposition of the Tol2 element is not clear. Our speculation is that some specific conditions regarding the genetic conformation are required for the high transposition activity of the Tol2 element, and these were fulfilled in the particular ma ...
... radiation. At present, the trigger for the germ line transposition of the Tol2 element is not clear. Our speculation is that some specific conditions regarding the genetic conformation are required for the high transposition activity of the Tol2 element, and these were fulfilled in the particular ma ...
Genetic Disorder Template
... blue eyes you need a blue eye gene from both parents to have blue eyes so if both parents have blue eyes you will just like if both parents have Cystic Fibrosis their child will. ...
... blue eyes you need a blue eye gene from both parents to have blue eyes so if both parents have blue eyes you will just like if both parents have Cystic Fibrosis their child will. ...
FOXP2 and Speech
... The story goes like this: In 1990, scientists became interested in the KE family in London, half of whose family members have speech disorders. ...
... The story goes like this: In 1990, scientists became interested in the KE family in London, half of whose family members have speech disorders. ...
Site-specific recombinase technology

Nearly every human gene has a counterpart in the mouse (regardless of the fact that a minor set of orthologues had to follow species specific selection routes). This made the mouse the major model for elucidating the ways in which our genetic material encodes information. In the late 1980s gene targeting in murine embryonic stem (ES-)cells enabled the transmission of mutations into the mouse germ line and emerged as a novel option to study the genetic basis of regulatory networks as they exist in the genome. Still, classical gene targeting proved to be limited in several ways as gene functions became irreversibly destroyed by the marker gene that had to be introduced for selecting recombinant ES cells. These early steps led to animals in which the mutation was present in all cells of the body from the beginning leading to complex phenotypes and/or early lethality. There was a clear need for methods to restrict these mutations to specific points in development and specific cell types. This dream became reality when groups in the USA were able to introduce bacteriophage and yeast-derived site-specific recombination (SSR-) systems into mammalian cells as well as into the mouse