An Evaluation of Gene Selection Methods for Multi
... • Although SVM-RFE shows an excellent performance in general, there is no clear winner. The performance of feature selection methods seems to be problem-dependent; ...
... • Although SVM-RFE shows an excellent performance in general, there is no clear winner. The performance of feature selection methods seems to be problem-dependent; ...
Genes without frontiers?
... Gene flow across distantly related bacterial groups (horizontal gene transfer) is a major feature of bacterial evolution (Maynard Smith et al, 1991; Campbell, 2000; Ochman et al, 2000; Gogarten et al, 2002). This evolution need not be slow. The intense selection pressure imposed on microbial communi ...
... Gene flow across distantly related bacterial groups (horizontal gene transfer) is a major feature of bacterial evolution (Maynard Smith et al, 1991; Campbell, 2000; Ochman et al, 2000; Gogarten et al, 2002). This evolution need not be slow. The intense selection pressure imposed on microbial communi ...
Incomplete dominance and Codominance Note
... . This means that the phenotype clearly shows both variations of that trait (it is NOT a blended trait). ...
... . This means that the phenotype clearly shows both variations of that trait (it is NOT a blended trait). ...
Alteration of the target site
... Whether in the presence of antibiotics or not, mutations are always spontaneous. Often these mutations are fatal to the bacterium. However, occasionally mutations can produce genes coding for advantageous phenotypes such as alternative penicillin binding proteins. The susceptible cells are rapidly c ...
... Whether in the presence of antibiotics or not, mutations are always spontaneous. Often these mutations are fatal to the bacterium. However, occasionally mutations can produce genes coding for advantageous phenotypes such as alternative penicillin binding proteins. The susceptible cells are rapidly c ...
Quantitative Genetic Perspectives on Loss of Diversity in
... Implications for Elite x Exotic Crosses • Genetic variance within a single population is due mostly to genes of large effect • Linkage disequilibrium within the cross may reduce genetic variance • Any new alleles from the exotic parent are preferentially lost if: – Linked to negative alleles at phy ...
... Implications for Elite x Exotic Crosses • Genetic variance within a single population is due mostly to genes of large effect • Linkage disequilibrium within the cross may reduce genetic variance • Any new alleles from the exotic parent are preferentially lost if: – Linked to negative alleles at phy ...
The Function and Potential of MicroRNAs
... complex, miRNAs base pair with their partially complementary target mRNA and block its translation into proteins, thereby reducing specific gene expression (Bernstein, 2001). To perform its function of gene regulation in the cell, miRNA is complementary to a part of one or more mRNAs. In animals, t ...
... complex, miRNAs base pair with their partially complementary target mRNA and block its translation into proteins, thereby reducing specific gene expression (Bernstein, 2001). To perform its function of gene regulation in the cell, miRNA is complementary to a part of one or more mRNAs. In animals, t ...
Lecture -18 Modification of food plant taste and appearance
... Monellin is a dimer with an A chain of 45 amino acid residues and a B chain of 50 residues; the chains are held together by weak noncovalent bonds. Unfortunately, the fact that monellin is composed of two separate polypeptide chains limits its usefulness as a sweetener because it is readily dissoci ...
... Monellin is a dimer with an A chain of 45 amino acid residues and a B chain of 50 residues; the chains are held together by weak noncovalent bonds. Unfortunately, the fact that monellin is composed of two separate polypeptide chains limits its usefulness as a sweetener because it is readily dissoci ...
What to Do When Clear Success Comes With an Unclear Risk?
... Daniel Salomon of the Scripps Institute in La Jolla, California, the FDA panel conf irmed what many had feared: A 3-year-old boy in the French trial has developed cancer that probably was caused by a modified retrovirus that was used to shuttle healthy genes into his cells. Yet panel members also re ...
... Daniel Salomon of the Scripps Institute in La Jolla, California, the FDA panel conf irmed what many had feared: A 3-year-old boy in the French trial has developed cancer that probably was caused by a modified retrovirus that was used to shuttle healthy genes into his cells. Yet panel members also re ...
BINF6201/8201 Dynamics of genes in populations 2
... selection without the knowledge of the genetic basis of evolution and the source of variation in populations. Ø Synthetic theory of evolution or neo-Darwinism: is the combination of Mendel’s genetics and Darwinism. It maintains that mutation provides the source of genetic variations, and natural se ...
... selection without the knowledge of the genetic basis of evolution and the source of variation in populations. Ø Synthetic theory of evolution or neo-Darwinism: is the combination of Mendel’s genetics and Darwinism. It maintains that mutation provides the source of genetic variations, and natural se ...
Do our genes determine what we should drink? The
... • Linked genetics and alcohol consumption in 105,000 light and heavy drinkers • β-Klotho (KLB) gene linked to social alcohol consumption • A allele is associated with reduced desire to consume alcohol (possessed by 40% of study population) ...
... • Linked genetics and alcohol consumption in 105,000 light and heavy drinkers • β-Klotho (KLB) gene linked to social alcohol consumption • A allele is associated with reduced desire to consume alcohol (possessed by 40% of study population) ...
Document
... between these two subclades is not much greater than between other clades. •B and D show the same extent of divergence but for historical reasons continue to be classified as clades, not subclades. •Clade B is the most common clade in North America and Europe. ...
... between these two subclades is not much greater than between other clades. •B and D show the same extent of divergence but for historical reasons continue to be classified as clades, not subclades. •Clade B is the most common clade in North America and Europe. ...
Newsletter - UC Cooperative Extension
... Chromosomes inherited from parents determine an animal's gene c make-up. Chromosomes come in pairs, one chromosome from each pair is inherited from an individual’s sire and the other chromosome is inherited from its dam. There are many genes in each chromosome. Genes are the basic unit of inherit ...
... Chromosomes inherited from parents determine an animal's gene c make-up. Chromosomes come in pairs, one chromosome from each pair is inherited from an individual’s sire and the other chromosome is inherited from its dam. There are many genes in each chromosome. Genes are the basic unit of inherit ...
Other Risk Factors File
... What are free radicals? When an atom in the molecule has an unpaired electron (desperate to find a partner) This desperation leads the atom to «steal» electrons from other molecules, damaging them. DNA (genes),enzymes, lipoproteins and platelets can be destroyed like this. ...
... What are free radicals? When an atom in the molecule has an unpaired electron (desperate to find a partner) This desperation leads the atom to «steal» electrons from other molecules, damaging them. DNA (genes),enzymes, lipoproteins and platelets can be destroyed like this. ...
Slide 1 - Annals of Internal Medicine
... shown) at 11q13 (chromosome 11, band q13) . B. The two copies of chromosome 11 from an endocrine tumor and its precursor cell, illustrating the first hit and the second normal copy of chromosome 11 before and after the second hit. The tumor could be from a case with MEN1 or from a case without MEN1 ...
... shown) at 11q13 (chromosome 11, band q13) . B. The two copies of chromosome 11 from an endocrine tumor and its precursor cell, illustrating the first hit and the second normal copy of chromosome 11 before and after the second hit. The tumor could be from a case with MEN1 or from a case without MEN1 ...
SupertaSter anatomy
... Supertasters, or individuals who are very sensitive to the bitter taste of the thioureas PTC and PROP, have a polymorphism in TAS2R38, a gene that codes for a receptor for these bitter tasting ...
... Supertasters, or individuals who are very sensitive to the bitter taste of the thioureas PTC and PROP, have a polymorphism in TAS2R38, a gene that codes for a receptor for these bitter tasting ...
Chromosome challenge activity pack
... The best way to gauge understanding of participants is to ask them questions like »» Has anyone here heard of DNA? »» Can anyone tell me what DNA is? Every living thing contains DNA. It is the unique set of instructions that tells a seed how to grown into a plant or a baby into adult. Everyone’s DNA ...
... The best way to gauge understanding of participants is to ask them questions like »» Has anyone here heard of DNA? »» Can anyone tell me what DNA is? Every living thing contains DNA. It is the unique set of instructions that tells a seed how to grown into a plant or a baby into adult. Everyone’s DNA ...
Rich Probabilistic Models for Genomic Data
... “Binding sites” attract a special class of proteins, known as “transcription factors”. What turns genes on (producing a protein) and off? Bound factors can initiate transcription (making RNA). When istranscription a gene turned on or off? Proteins inhibit canon? also be bound to their Where (inthat ...
... “Binding sites” attract a special class of proteins, known as “transcription factors”. What turns genes on (producing a protein) and off? Bound factors can initiate transcription (making RNA). When istranscription a gene turned on or off? Proteins inhibit canon? also be bound to their Where (inthat ...
Name: Chem 465 Biochemistry II - Test 3
... 12. In Chapter 24 you learned that much of the human genetic material consists of transposons. In Chapter 25 you learned that most transposons integrate using a recombination event. In Chapter 26 we learn that most eukariots transposons are retrotransposons. Put these three chapters together; what i ...
... 12. In Chapter 24 you learned that much of the human genetic material consists of transposons. In Chapter 25 you learned that most transposons integrate using a recombination event. In Chapter 26 we learn that most eukariots transposons are retrotransposons. Put these three chapters together; what i ...
What Can the Y Chromosome Tell Us about the Origin of Modern
... T by C), but they also include insertions or deletions of a few nucleotides and insertions of retroposon sequences. Microsatellites consist of small units (for example GATA) that are repeated in tandem. The number of copies varies between individuals: for example 11 on one Y chromosome and 12 on ano ...
... T by C), but they also include insertions or deletions of a few nucleotides and insertions of retroposon sequences. Microsatellites consist of small units (for example GATA) that are repeated in tandem. The number of copies varies between individuals: for example 11 on one Y chromosome and 12 on ano ...
Dosage sensitivity and the evolution of gene families in yeast
... chance; P , 1025 from randomization; see Methods). There is also a large excess of solo copy pairs (1,541 observed but only about 878 are expected by chance; P , 1025). After polyploidization the loss of duplicate copies of interacting genes one at a time leads to imbalance. The balance hypothesis t ...
... chance; P , 1025 from randomization; see Methods). There is also a large excess of solo copy pairs (1,541 observed but only about 878 are expected by chance; P , 1025). After polyploidization the loss of duplicate copies of interacting genes one at a time leads to imbalance. The balance hypothesis t ...
LECTURE OUTLINE (Chapter 11) I. An Introduction to Mendel and
... 2. Patterns of inheritance (single “faulty” allele of a gene causes damage, even with a “good” allele present): Figure 12.4b. C. Pedigrees (Section 12.3)—confronted with medical condition running in a family, geneticists like to create family tree diagrams or pedigrees, which can be used to determin ...
... 2. Patterns of inheritance (single “faulty” allele of a gene causes damage, even with a “good” allele present): Figure 12.4b. C. Pedigrees (Section 12.3)—confronted with medical condition running in a family, geneticists like to create family tree diagrams or pedigrees, which can be used to determin ...
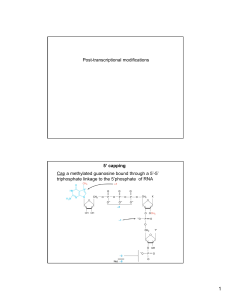
Post-transcriptional modifications Cap a
... In some cases, mobile, sequence-specific silencing signals can move from cell-to-cell or even over long distances in the plant. Several current models hold that silencing signals are “aberrant” RNAs (aRNA), that differ in some way from normal mRNAs. The most likely candidates are small antisense RNA ...
... In some cases, mobile, sequence-specific silencing signals can move from cell-to-cell or even over long distances in the plant. Several current models hold that silencing signals are “aberrant” RNAs (aRNA), that differ in some way from normal mRNAs. The most likely candidates are small antisense RNA ...
Genome Research - University of Oxford
... population: all individuals within a generation with the potential to contribute to the gene pool (including individuals who are reproductively successful as well as those who are not.) gene genealogies: lineages of transmission of copies of a gene from parents to offspring coalescence: where two tr ...
... population: all individuals within a generation with the potential to contribute to the gene pool (including individuals who are reproductively successful as well as those who are not.) gene genealogies: lineages of transmission of copies of a gene from parents to offspring coalescence: where two tr ...
Informed consent.
... disease-causing alterations of genetic disorders. Each gene and encoded protein has a specific function, although this function is not still known in many cases. Diseases or genetic disorders may be due to one or more genes that carry alterations: there is a missing or an additional fragment of gene ...
... disease-causing alterations of genetic disorders. Each gene and encoded protein has a specific function, although this function is not still known in many cases. Diseases or genetic disorders may be due to one or more genes that carry alterations: there is a missing or an additional fragment of gene ...
Site-specific recombinase technology

Nearly every human gene has a counterpart in the mouse (regardless of the fact that a minor set of orthologues had to follow species specific selection routes). This made the mouse the major model for elucidating the ways in which our genetic material encodes information. In the late 1980s gene targeting in murine embryonic stem (ES-)cells enabled the transmission of mutations into the mouse germ line and emerged as a novel option to study the genetic basis of regulatory networks as they exist in the genome. Still, classical gene targeting proved to be limited in several ways as gene functions became irreversibly destroyed by the marker gene that had to be introduced for selecting recombinant ES cells. These early steps led to animals in which the mutation was present in all cells of the body from the beginning leading to complex phenotypes and/or early lethality. There was a clear need for methods to restrict these mutations to specific points in development and specific cell types. This dream became reality when groups in the USA were able to introduce bacteriophage and yeast-derived site-specific recombination (SSR-) systems into mammalian cells as well as into the mouse