Basic Principles of Human Genetics
... Eddy is a 4-year-old boy brought in by his parents because of recurrent cough. He has had two bouts of pneumonia, which were treated with antibiotics, over the past 2 months. Now he is sick again, having never stopped coughing since the last episode of pneumonia. He has also been noted by his parent ...
... Eddy is a 4-year-old boy brought in by his parents because of recurrent cough. He has had two bouts of pneumonia, which were treated with antibiotics, over the past 2 months. Now he is sick again, having never stopped coughing since the last episode of pneumonia. He has also been noted by his parent ...
Ch 7- The Cellular Basis of Inheritance
... inversion – It’s one of the main differences between humans and chimpanzees, our closest genetic relatives ...
... inversion – It’s one of the main differences between humans and chimpanzees, our closest genetic relatives ...
Dihybrid Crosses Gregor Mendel, the father of modern genetics
... for red fruit (R) is dominant to the gene for yellow fruit (r). If two tomato plants heterozygous (AaRr) for both traits are crossed, state what proportion of the offspring are expected to have: Red fruit: _______ Green stems and red fruit ______ Purple stems and red fruit ______ 14. If 640 seeds re ...
... for red fruit (R) is dominant to the gene for yellow fruit (r). If two tomato plants heterozygous (AaRr) for both traits are crossed, state what proportion of the offspring are expected to have: Red fruit: _______ Green stems and red fruit ______ Purple stems and red fruit ______ 14. If 640 seeds re ...
PDF
... markers were then used to sort the cells that comprise the CLV3 or WUS expression domains in a mutant plant that produces many floral meristems, thus providing access to a much larger number of cells of the required types than would otherwise be possible. The resulting gene expression profiling expe ...
... markers were then used to sort the cells that comprise the CLV3 or WUS expression domains in a mutant plant that produces many floral meristems, thus providing access to a much larger number of cells of the required types than would otherwise be possible. The resulting gene expression profiling expe ...
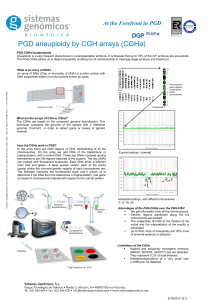
At the Forefront in PGD
... Fundamentals of combined chromosomal PGD Couples with one member carrying a balanced chromosomal rearrangement (translocation or inversion) have an increased risk of generating abnormal embryos as a result of segregation of the balanced abnormality. This causes, recurrent abortions and, in many case ...
... Fundamentals of combined chromosomal PGD Couples with one member carrying a balanced chromosomal rearrangement (translocation or inversion) have an increased risk of generating abnormal embryos as a result of segregation of the balanced abnormality. This causes, recurrent abortions and, in many case ...
University of Groningen A Branched Biosynthetic Pathway Is
... Other than for strictly personal use, it is not permitted to download or to forward/distribute the text or part of it without the consent of the author(s) and/or copyright holder(s), unless the work is under an open content license (like Creative Commons). Take-down policy If you believe that this d ...
... Other than for strictly personal use, it is not permitted to download or to forward/distribute the text or part of it without the consent of the author(s) and/or copyright holder(s), unless the work is under an open content license (like Creative Commons). Take-down policy If you believe that this d ...
Malattie XL, YL e Mitocondriali
... XIST RNA is only expressed in cells containing at least two Xs and is not normally expressed in male cells. Higher XIST expression can be seen in cells with more X chromosomes, as a counting mechanism dictates that only one X per cell can remain active. In such cells, XIST is expressed from all supe ...
... XIST RNA is only expressed in cells containing at least two Xs and is not normally expressed in male cells. Higher XIST expression can be seen in cells with more X chromosomes, as a counting mechanism dictates that only one X per cell can remain active. In such cells, XIST is expressed from all supe ...
Chapter 12 Human Genetics
... alike in length, shape, and gene sequence • Alleles are slightly different molecular forms of the same gene, which are suffled during meiosis ...
... alike in length, shape, and gene sequence • Alleles are slightly different molecular forms of the same gene, which are suffled during meiosis ...
Chapter 3 sample - Scion Publishing
... SECTION 3.2 | WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW – ESSENTIAL ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 59 ...
... SECTION 3.2 | WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW – ESSENTIAL ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 59 ...
dna & cell division
... Growth & Development –grow through cell division, rather than unlimited growth because if a cell gets too large, it cannot meet its own needs and maintain homeostasis. Renewal & Repair –used to replace cells that die from normal wear & tear; Ex: skin cells. ...
... Growth & Development –grow through cell division, rather than unlimited growth because if a cell gets too large, it cannot meet its own needs and maintain homeostasis. Renewal & Repair –used to replace cells that die from normal wear & tear; Ex: skin cells. ...
w latach 2016-2018 na Wydziale Biologii Uniwersytetu im. Adama
... The factors influencing frequency and chromosomal distribution of COs are poorly understood. This is due to low efficiency of traditional methods for CO measurements. We use modern techniques for CO assessment, which are based on fluorescent reporters. Those methods allow us to analyze thousands of ...
... The factors influencing frequency and chromosomal distribution of COs are poorly understood. This is due to low efficiency of traditional methods for CO measurements. We use modern techniques for CO assessment, which are based on fluorescent reporters. Those methods allow us to analyze thousands of ...
(green algae or cyanobacteria) section of the Fuel Cell Technologies Office Multi-Year Research, Development, and
... Tla strain with the highest efficiency identified ...
... Tla strain with the highest efficiency identified ...
Chapter 14
... By observing those three generations, Mendel laid the foundation for two important principles: 1. Law of Segregation 2. Law of Independent Assortment Let’s look at the tenets of the Law of Segregation in detail: a. There are multiple versions of the same gene (each version is a different allele; S ...
... By observing those three generations, Mendel laid the foundation for two important principles: 1. Law of Segregation 2. Law of Independent Assortment Let’s look at the tenets of the Law of Segregation in detail: a. There are multiple versions of the same gene (each version is a different allele; S ...
Genetics
... All of these animals don’t look alike, but you recognize them as dogs. What do they have in common? ...
... All of these animals don’t look alike, but you recognize them as dogs. What do they have in common? ...
Densovirus infection in silkworm Bombyx mori and genes
... Penstyldensovirus This particular genus is another newly introduced genus under the family of Densovirinae. The name stands for a siglum for Penaeus stylirostris, the host and also the founding member of this species. PstDV1, PmoPDV1, PmoPDV2 and PstDV2 are the viruses included this genus. Iteradens ...
... Penstyldensovirus This particular genus is another newly introduced genus under the family of Densovirinae. The name stands for a siglum for Penaeus stylirostris, the host and also the founding member of this species. PstDV1, PmoPDV1, PmoPDV2 and PstDV2 are the viruses included this genus. Iteradens ...
Practice Exam 3, Biology 211, Sections 1 and 4, Fall, 2007
... c. The number of DNA molecules per chromatid varies between one and two depending on the time in the cell cycle. d. The number of DNA molecules per chromatid is described by the term ploidy. Thus, diploid cells contain two, tetraploid four, etc. e. Each gene is a DNA molecule, and chromosomes contai ...
... c. The number of DNA molecules per chromatid varies between one and two depending on the time in the cell cycle. d. The number of DNA molecules per chromatid is described by the term ploidy. Thus, diploid cells contain two, tetraploid four, etc. e. Each gene is a DNA molecule, and chromosomes contai ...
Biosynthetic Pathway
... phosphorus and chelated mineral cations are largely unavailable in the diets of non-ruminants due to a lack of digestive enzymes to remove phosphate groups. Phytate phosphorus is excreted in manure, accumulates in soil, and eventually enters watersheds. As a result, phytate is considered both an ant ...
... phosphorus and chelated mineral cations are largely unavailable in the diets of non-ruminants due to a lack of digestive enzymes to remove phosphate groups. Phytate phosphorus is excreted in manure, accumulates in soil, and eventually enters watersheds. As a result, phytate is considered both an ant ...
Mendel`s Legacy
... Heterozygous Advantage • Until recently homozygous recessive individuals never lived to adulthood. Therefore the presence of the allele should have decreasing each generation. However in some African regions nearly half of an entire population would be heterozygous for the condition. • How could t ...
... Heterozygous Advantage • Until recently homozygous recessive individuals never lived to adulthood. Therefore the presence of the allele should have decreasing each generation. However in some African regions nearly half of an entire population would be heterozygous for the condition. • How could t ...
Exam3-1406_Fall2007ch9-10-11.doc
... C) There will be more genetic diversity among the offspring. D) The offspring will have a diploid chromosome number twice that of their parents. E) There will be fewer mutations. 55) Which of the following is a haploid? A) zygote B) gamete (sex cell) C) muscle cell D) embryo E) brain cell 56) Chromo ...
... C) There will be more genetic diversity among the offspring. D) The offspring will have a diploid chromosome number twice that of their parents. E) There will be fewer mutations. 55) Which of the following is a haploid? A) zygote B) gamete (sex cell) C) muscle cell D) embryo E) brain cell 56) Chromo ...
GENERAL GENETICS
... stage is set for the union of two genomes. If the parents differ genetically, new combinations of genes can occur in their offspring. Taking these three mechanisms together, it is safe to conclude that no two human beings have ever shared an identical genome unless they had an identical sibling; tha ...
... stage is set for the union of two genomes. If the parents differ genetically, new combinations of genes can occur in their offspring. Taking these three mechanisms together, it is safe to conclude that no two human beings have ever shared an identical genome unless they had an identical sibling; tha ...
Physical Mapping of Important Trait Loci in the Pig
... the genetic background of inherited diseases. An important goal is also to develop new and more specific pharmaceuticals with less side effects. The drug industry can utilize the genome information in order to find candidate drug targets. It will also be possible to create individual treatments, sin ...
... the genetic background of inherited diseases. An important goal is also to develop new and more specific pharmaceuticals with less side effects. The drug industry can utilize the genome information in order to find candidate drug targets. It will also be possible to create individual treatments, sin ...
Genetics Unit Review Guide
... 20) Explain the difference between sex influenced and sex linked inheritance and give an example of each. 21) Know what it means to be a carrier of a disorder, what types of disorders this works for (or doesn’t) and what gender of individuals can be carriers for particular traits. 22) Know how calcu ...
... 20) Explain the difference between sex influenced and sex linked inheritance and give an example of each. 21) Know what it means to be a carrier of a disorder, what types of disorders this works for (or doesn’t) and what gender of individuals can be carriers for particular traits. 22) Know how calcu ...
Site-specific recombinase technology

Nearly every human gene has a counterpart in the mouse (regardless of the fact that a minor set of orthologues had to follow species specific selection routes). This made the mouse the major model for elucidating the ways in which our genetic material encodes information. In the late 1980s gene targeting in murine embryonic stem (ES-)cells enabled the transmission of mutations into the mouse germ line and emerged as a novel option to study the genetic basis of regulatory networks as they exist in the genome. Still, classical gene targeting proved to be limited in several ways as gene functions became irreversibly destroyed by the marker gene that had to be introduced for selecting recombinant ES cells. These early steps led to animals in which the mutation was present in all cells of the body from the beginning leading to complex phenotypes and/or early lethality. There was a clear need for methods to restrict these mutations to specific points in development and specific cell types. This dream became reality when groups in the USA were able to introduce bacteriophage and yeast-derived site-specific recombination (SSR-) systems into mammalian cells as well as into the mouse