Exploration 13 - Warner Pacific College
... If the table above is confusing to you, try substituting values for p and q. For example, instead of p sperm/ova with the A allele and q with the a allele, substitute 0.7 sperm/ova with A and 0.3 with a. Then, what percent of offspring with the genotype aa would you expect? The generation offspring ...
... If the table above is confusing to you, try substituting values for p and q. For example, instead of p sperm/ova with the A allele and q with the a allele, substitute 0.7 sperm/ova with A and 0.3 with a. Then, what percent of offspring with the genotype aa would you expect? The generation offspring ...
Ch 21 C ppt - Houston ISD
... specifies a 60-amino-acid homeodomain. • An identical or very similar sequence of nucleotides (often called Hox genes) are found in many other animals, including humans. • Related sequences are present in yeast and prokaryotes. • The homeobox DNA sequence must have evolved very early in the history ...
... specifies a 60-amino-acid homeodomain. • An identical or very similar sequence of nucleotides (often called Hox genes) are found in many other animals, including humans. • Related sequences are present in yeast and prokaryotes. • The homeobox DNA sequence must have evolved very early in the history ...
Genetics and genomics of infectious disease susceptibility
... mapping and identification may now be employed in studies of susceptibility to complex disease and most of these have been applied to at least one infectious disease. In general, two distinct approaches may be used. Either a genetic linkage study may be undertaken to search for co-segregation of a g ...
... mapping and identification may now be employed in studies of susceptibility to complex disease and most of these have been applied to at least one infectious disease. In general, two distinct approaches may be used. Either a genetic linkage study may be undertaken to search for co-segregation of a g ...
The scope of Population Genetics Forces acting on allele
... •Patterns of LD in the human genome •The HapMap project. ...
... •Patterns of LD in the human genome •The HapMap project. ...
Mapping of the Recessive White Locus and
... locus for tyrosinase in the fowl (Oetting et al., 1985). The tyrosinase gene in chickens has been cloned by Mochii et al. (1992). Tobita-Teramoto et al. (2000) reported that a 6-nucleotide deletion at a Cu-binding site of the tyrosinase gene leads to the albino chicken (ca). Some genes at the classi ...
... locus for tyrosinase in the fowl (Oetting et al., 1985). The tyrosinase gene in chickens has been cloned by Mochii et al. (1992). Tobita-Teramoto et al. (2000) reported that a 6-nucleotide deletion at a Cu-binding site of the tyrosinase gene leads to the albino chicken (ca). Some genes at the classi ...
Chapter 16: Gene Regulation in Bacteria
... Gene regulation can occur at a number of levels (Figure 16.1), but the most common is at the transcriptional level. The first section of this chapter examines the variety of means by which genes may be transcriptionally regulated in bacteria. In most cases, transcriptional regulation involves the ac ...
... Gene regulation can occur at a number of levels (Figure 16.1), but the most common is at the transcriptional level. The first section of this chapter examines the variety of means by which genes may be transcriptionally regulated in bacteria. In most cases, transcriptional regulation involves the ac ...
13_DetailLectOut_jkAR
... 1. During prophase I of meiosis, replicated homologous chromosomes line up and become physically connected along their lengths by a zipperlike protein complex, the synaptonemal complex, in a process called synapsis. Genetic rearrangement between nonsister chromatids called crossing over also occurs. ...
... 1. During prophase I of meiosis, replicated homologous chromosomes line up and become physically connected along their lengths by a zipperlike protein complex, the synaptonemal complex, in a process called synapsis. Genetic rearrangement between nonsister chromatids called crossing over also occurs. ...
High-Level Expression in Escherichia coli of Alkaline Phosphatase
... Tca APase activity was activated by Mg2+; however, it was inhibited by Ca2+, Co2+, Zn2+, and EDTA at 1 mM concentration (data not shown). This dependence of the catalytic activity on Mg2+ has already been observed in most of the APases investigated [2, 5, 10]. The above results thus indicate that pr ...
... Tca APase activity was activated by Mg2+; however, it was inhibited by Ca2+, Co2+, Zn2+, and EDTA at 1 mM concentration (data not shown). This dependence of the catalytic activity on Mg2+ has already been observed in most of the APases investigated [2, 5, 10]. The above results thus indicate that pr ...
Revision for biology test 2 File
... Q17. A salmon can regulate how much salt it can remove from its tissue. What type of adaptation is this? ...
... Q17. A salmon can regulate how much salt it can remove from its tissue. What type of adaptation is this? ...
CHAPTER 13 MEIOSIS AND SEXUAL LIFE CYCLES
... 1. During prophase I of meiosis, replicated homologous chromosomes line up and become physically connected along their lengths by a zipperlike protein complex, the synaptonemal complex, in a process called synapsis. Genetic rearrangement between nonsister chromatids called crossing over also occurs. ...
... 1. During prophase I of meiosis, replicated homologous chromosomes line up and become physically connected along their lengths by a zipperlike protein complex, the synaptonemal complex, in a process called synapsis. Genetic rearrangement between nonsister chromatids called crossing over also occurs. ...
Aggregation chimeras demonstrate that the primary
... the relative contribution of transgenic (ls/ls) and non-transgenic (wild-type) cells to various organs in the chimeric embryos (Table 1). Different organs from the same animal generally had similar transgenic compositions, although some organs within a given mouse varied as much as twofold in their ...
... the relative contribution of transgenic (ls/ls) and non-transgenic (wild-type) cells to various organs in the chimeric embryos (Table 1). Different organs from the same animal generally had similar transgenic compositions, although some organs within a given mouse varied as much as twofold in their ...
Epsilon Toxin Characterization
... Clostridium perfringens are gram positive, obligate anaerobes that produce multiple toxins and form endospores. These toxins can cause human disease such as food poisoning, gas gangrene and enterotoxemia. To date >15 different toxins have been identified in the genome of C. perfringens. Depending on ...
... Clostridium perfringens are gram positive, obligate anaerobes that produce multiple toxins and form endospores. These toxins can cause human disease such as food poisoning, gas gangrene and enterotoxemia. To date >15 different toxins have been identified in the genome of C. perfringens. Depending on ...
PowerPoint-presentatie
... rapidly associations were found between human diseases (syndromes) and specific chromosome abnormalities 1963 chromosome 5 short arm partial deletion in Cri du Chat syndrome 1963 D-chromosome deletion in patient with bilateral retinoblastoma ...
... rapidly associations were found between human diseases (syndromes) and specific chromosome abnormalities 1963 chromosome 5 short arm partial deletion in Cri du Chat syndrome 1963 D-chromosome deletion in patient with bilateral retinoblastoma ...
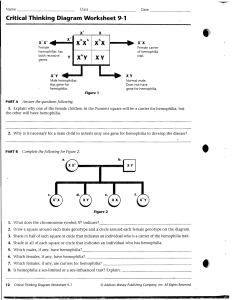
Critical Thinking Diagram Worksheet 9-1
... 1. Explain why one of the female children in the Punnett square will be a carrier for hemophilia, the other will have hemophilia. ...
... 1. Explain why one of the female children in the Punnett square will be a carrier for hemophilia, the other will have hemophilia. ...
A small organic compound enhances the religation reaction of
... Top1–DNA complex slowing down the religation of the cleaved DNA strand, thus inducing cell death [5]. Two water-soluble CPT derivatives, topotecan and irinotecan have been approved by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) for clinical use. The 3D structure of the topotecan–enzyme–DNA ternary comple ...
... Top1–DNA complex slowing down the religation of the cleaved DNA strand, thus inducing cell death [5]. Two water-soluble CPT derivatives, topotecan and irinotecan have been approved by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) for clinical use. The 3D structure of the topotecan–enzyme–DNA ternary comple ...
CHAPTER 13 MEIOSIS AND SEXUAL LIFE CYCLES
... 1. During prophase I of meiosis, replicated homologous chromosomes line up and become physically connected along their lengths by a zipperlike protein complex, the synaptonemal complex, in a process called synapsis. Genetic rearrangement between nonsister chromatids called crossing over also occurs. ...
... 1. During prophase I of meiosis, replicated homologous chromosomes line up and become physically connected along their lengths by a zipperlike protein complex, the synaptonemal complex, in a process called synapsis. Genetic rearrangement between nonsister chromatids called crossing over also occurs. ...
The Moss Physcomitrella patens, a Model System
... Wild-type strains are normally self-fertile. However, selfsterility is a pleiotropic effect of some mutations to auxotrophy. Strains carrying mutant alleles leading to a requirement for p-amino benzoic acid, nicotinic acid, or thiamine are all selfsterile when grown on medium containing the required ...
... Wild-type strains are normally self-fertile. However, selfsterility is a pleiotropic effect of some mutations to auxotrophy. Strains carrying mutant alleles leading to a requirement for p-amino benzoic acid, nicotinic acid, or thiamine are all selfsterile when grown on medium containing the required ...
Mendel and After - U3A Site Builder Home Page
... subunits, but which of them carries the hereditary information? ...
... subunits, but which of them carries the hereditary information? ...
Organoid assays
... wks) of each group showed signs of disease and abnormal crypt foci (ACF) were quantified numerically by methylene blue staining, (b) according to size (crypts per focus) and (c) by the percentage of ACFs that belong to defined size classes via counting the number of abnormal dysplastic crypts per AC ...
... wks) of each group showed signs of disease and abnormal crypt foci (ACF) were quantified numerically by methylene blue staining, (b) according to size (crypts per focus) and (c) by the percentage of ACFs that belong to defined size classes via counting the number of abnormal dysplastic crypts per AC ...
Davenport`s Dream: 21 st Century Reflections on Heredity and
... code was established by 1966, and gene expression was seen to be controlled by DNA-binding regulatory proteins between 1967 and 1969. Genetics, happily then, had no reasons to intersect politics, except in Russia, where the absurdity of its Lamarckian philosophy became painfully more clear to its in ...
... code was established by 1966, and gene expression was seen to be controlled by DNA-binding regulatory proteins between 1967 and 1969. Genetics, happily then, had no reasons to intersect politics, except in Russia, where the absurdity of its Lamarckian philosophy became painfully more clear to its in ...
Practice problems
... When DDT was first introduced, insects were very susceptible to it. The development of resistance to DDT by insects was the result of a. special creation. b. natural selection of forms that expressed genes for resistance. c. the high biotic potential of insects. d. a naturally occurring example of i ...
... When DDT was first introduced, insects were very susceptible to it. The development of resistance to DDT by insects was the result of a. special creation. b. natural selection of forms that expressed genes for resistance. c. the high biotic potential of insects. d. a naturally occurring example of i ...
AP Biology Exam Review Put Your Knowledge to the Test
... A test cross is when you are trying to figure out what the make up of the allele is, A_ (either A or a), and you cross it with a pure recessive allele ...
... A test cross is when you are trying to figure out what the make up of the allele is, A_ (either A or a), and you cross it with a pure recessive allele ...
Biology
... During DNA replication, the DNA molecule separates into two strands, then produces two new complementary strands following the rules of base pairing. Each strand of the double helix of DNA serves as a template for the new strand. ...
... During DNA replication, the DNA molecule separates into two strands, then produces two new complementary strands following the rules of base pairing. Each strand of the double helix of DNA serves as a template for the new strand. ...
VI. Gene flow can cause evolution by transferring alleles between
... For Darwin, the raw material for natural selection was variation in quantitative characters that vary along a continuum in a population. • We now know that continuous variation is usually determined by many segregating loci (polygenic inheritance). • As did Mendel, geneticists in the early 1900’s re ...
... For Darwin, the raw material for natural selection was variation in quantitative characters that vary along a continuum in a population. • We now know that continuous variation is usually determined by many segregating loci (polygenic inheritance). • As did Mendel, geneticists in the early 1900’s re ...
Site-specific recombinase technology

Nearly every human gene has a counterpart in the mouse (regardless of the fact that a minor set of orthologues had to follow species specific selection routes). This made the mouse the major model for elucidating the ways in which our genetic material encodes information. In the late 1980s gene targeting in murine embryonic stem (ES-)cells enabled the transmission of mutations into the mouse germ line and emerged as a novel option to study the genetic basis of regulatory networks as they exist in the genome. Still, classical gene targeting proved to be limited in several ways as gene functions became irreversibly destroyed by the marker gene that had to be introduced for selecting recombinant ES cells. These early steps led to animals in which the mutation was present in all cells of the body from the beginning leading to complex phenotypes and/or early lethality. There was a clear need for methods to restrict these mutations to specific points in development and specific cell types. This dream became reality when groups in the USA were able to introduce bacteriophage and yeast-derived site-specific recombination (SSR-) systems into mammalian cells as well as into the mouse