
Genetics Vocabulary Answers The offspring of organisms often grow
... The offspring of organisms often grow up to look like one or both of their parents. This is because offspring inherit information from their parents that directs their development. ...
... The offspring of organisms often grow up to look like one or both of their parents. This is because offspring inherit information from their parents that directs their development. ...
Overview of Human Linkage Analysis Terry Speed
... Complex traits Definition vague, but usually thought of as having multiple, possibly interacting loci, with unknown penetrances; and phenocopies. The terms polygenic and oligogenic are also used, but these do have more specific meanings. There is some evidence that using a range of made-up models c ...
... Complex traits Definition vague, but usually thought of as having multiple, possibly interacting loci, with unknown penetrances; and phenocopies. The terms polygenic and oligogenic are also used, but these do have more specific meanings. There is some evidence that using a range of made-up models c ...
The 2 alleles on chromosome 13q14 must be inactivated
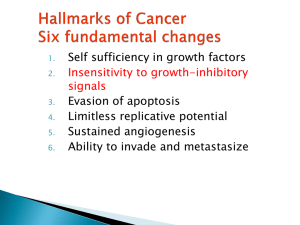
... Antigrowth signals can prevent cell proliferation by 2 mechanism: 1-Cause the dividing cell go to Go phase 2-The cell enter post-mitotic differentiated pool & lose replicative potential The molecular level of antigrowth signals exert their effects on G1-S checkpoint of the cell cycle, controlled by ...
... Antigrowth signals can prevent cell proliferation by 2 mechanism: 1-Cause the dividing cell go to Go phase 2-The cell enter post-mitotic differentiated pool & lose replicative potential The molecular level of antigrowth signals exert their effects on G1-S checkpoint of the cell cycle, controlled by ...
Document
... back into the organism. Recombinant microorganisms have been used to synthesize human gene products (e.g., insulin), as biological control agents (e.g., Ice– bacteria), and in bioremediation (e.g., oil-eating bacteria). C2. A. radiobacter synthesizes an antibiotic that kills A. tumefaciens. The gene ...
... back into the organism. Recombinant microorganisms have been used to synthesize human gene products (e.g., insulin), as biological control agents (e.g., Ice– bacteria), and in bioremediation (e.g., oil-eating bacteria). C2. A. radiobacter synthesizes an antibiotic that kills A. tumefaciens. The gene ...
Genetic Engineering
... • The goals of the Human Genome Project were to determine the nucleotide sequence of the entire human genome and map the location of every gene on each chromosome. • This information will advance the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of human genetic disorders. • The Human Genome Project included ...
... • The goals of the Human Genome Project were to determine the nucleotide sequence of the entire human genome and map the location of every gene on each chromosome. • This information will advance the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of human genetic disorders. • The Human Genome Project included ...
Document
... •Still looking good, in areas other than research •Used by pharmaceutical companies, medical diagnostics, etc. •In the future, just like silicon chips, likely to get cheaper, faster and more powerful ...
... •Still looking good, in areas other than research •Used by pharmaceutical companies, medical diagnostics, etc. •In the future, just like silicon chips, likely to get cheaper, faster and more powerful ...
mapping
... (1) Example, one phage might be A+ and B-, while the second phage will be Aand B+ 2. Analyze recombination frequency a) Recombinational frequency is proportional to distance between gene B. Linkage and multifactor crosses 1. Definitions a) Linkage (1) Two genes very close to each other so recombinat ...
... (1) Example, one phage might be A+ and B-, while the second phage will be Aand B+ 2. Analyze recombination frequency a) Recombinational frequency is proportional to distance between gene B. Linkage and multifactor crosses 1. Definitions a) Linkage (1) Two genes very close to each other so recombinat ...
5` 3`
... And when analyzing DNA data obtained in the lab, initiation codon might be located outside the sequenced region Alberts Fig. 6-50 ...
... And when analyzing DNA data obtained in the lab, initiation codon might be located outside the sequenced region Alberts Fig. 6-50 ...
Mating of haploid strains
... They do not affect other haploid specific genes or aspecific genes. α1 is a positive regulator of α-specific genes • Mutations in α2 allow the expression of a-specific genes, even in a MATα cell. α2 is a negative regulator of a-specific genes • Consequently, in a MATα cell the α genes are expresse ...
... They do not affect other haploid specific genes or aspecific genes. α1 is a positive regulator of α-specific genes • Mutations in α2 allow the expression of a-specific genes, even in a MATα cell. α2 is a negative regulator of a-specific genes • Consequently, in a MATα cell the α genes are expresse ...
gene
... • Are the sperm and egg cells • They contain half the genetic information of a normal body cell • When joined together the fertilised egg will have a complete set of genetic information (a complete genome) • This is why we might look a bit like our parents! ...
... • Are the sperm and egg cells • They contain half the genetic information of a normal body cell • When joined together the fertilised egg will have a complete set of genetic information (a complete genome) • This is why we might look a bit like our parents! ...
Identification of func
... SNPs in these genes with drug response as well as complex diseases in which environment/xenobiotics play a role. Objectives ...
... SNPs in these genes with drug response as well as complex diseases in which environment/xenobiotics play a role. Objectives ...
Notes # 9 Answer Key
... 4. Do some research, how can a transgenic organism be used? -To create complex proteins. It can help substitute parts of the body. It could increase the production speed of plants. Could be used for experimentation in labs. 5. It is estimated that every human carries between 5 and 8 harmful genes. W ...
... 4. Do some research, how can a transgenic organism be used? -To create complex proteins. It can help substitute parts of the body. It could increase the production speed of plants. Could be used for experimentation in labs. 5. It is estimated that every human carries between 5 and 8 harmful genes. W ...
A gene expression analysis system for medical diagnosis
... SVM methods for classification into multiple classes – One vs one – One vs all – Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) – Weston & Watkins – Cramer & Singer (Weston & Watkins, 1999; Platt, 2000; Yeang et al, 2001; Cramer & Singer, 2001; Hsu & Lin, 2002) ...
... SVM methods for classification into multiple classes – One vs one – One vs all – Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) – Weston & Watkins – Cramer & Singer (Weston & Watkins, 1999; Platt, 2000; Yeang et al, 2001; Cramer & Singer, 2001; Hsu & Lin, 2002) ...
Heredity Lab: The Passing of Traits from Grandparents to
... Each cup should have a total of six objects, three of each of the same color. The objects represent genes of each grandparent…those portions of the chromosome which determine the characteristics (traits) that the grandparents will pas on to their children and grandchildren. Color the diagram to show ...
... Each cup should have a total of six objects, three of each of the same color. The objects represent genes of each grandparent…those portions of the chromosome which determine the characteristics (traits) that the grandparents will pas on to their children and grandchildren. Color the diagram to show ...
Small DNA Tumor Viruses
... – by integra;ons that delete regions of viral genome required for replica;on but leave early genes intact. ...
... – by integra;ons that delete regions of viral genome required for replica;on but leave early genes intact. ...
(eg, cleft lip, polydactyly).
... that encode homeodomains. Since they are highly conserved, and can be detected by low-stringency hybridization across species. ...
... that encode homeodomains. Since they are highly conserved, and can be detected by low-stringency hybridization across species. ...
sin entered the world through one man [Adam], and in this way
... • Some faulty genes that increase the risk of cancer can be passed on from parent to child. These are called inherited cancer genes. This occurs when there is a mistake or a fault in the genes in an egg or sperm cell. Then the gene fault can be passed on to children. Genes that increase the risk of ...
... • Some faulty genes that increase the risk of cancer can be passed on from parent to child. These are called inherited cancer genes. This occurs when there is a mistake or a fault in the genes in an egg or sperm cell. Then the gene fault can be passed on to children. Genes that increase the risk of ...
gene expression
... • Discovering more about RNA’S that do not make protein • MicroRNAs (miRNA) – small, single stranded RNA generated from a hairpin on precursor RNA; associates with proteins that can degrade or prevent translation of mRNA with complementary sequence • Small interfering RNAs (siRNA) – like miRNA, but ...
... • Discovering more about RNA’S that do not make protein • MicroRNAs (miRNA) – small, single stranded RNA generated from a hairpin on precursor RNA; associates with proteins that can degrade or prevent translation of mRNA with complementary sequence • Small interfering RNAs (siRNA) – like miRNA, but ...
Document
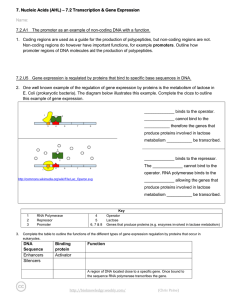
... Technologies II: Array based • cDNA arrays, long oligo arrays: immobilize a piece of DNA per gene. These are (usually) 2color arrays, i.e. two samples are labeled with different dyes and hybridized • Short oligo arrays (Affymetrix): immobilize several short oligonucleotides per gene. These are 1-co ...
... Technologies II: Array based • cDNA arrays, long oligo arrays: immobilize a piece of DNA per gene. These are (usually) 2color arrays, i.e. two samples are labeled with different dyes and hybridized • Short oligo arrays (Affymetrix): immobilize several short oligonucleotides per gene. These are 1-co ...
Genes and Cell Division
... nuclei create a bulge or bud, when the bud is completely grown it breaks off – Yeast reproduce this way ...
... nuclei create a bulge or bud, when the bud is completely grown it breaks off – Yeast reproduce this way ...
the evolution of populations
... Used to assess whether a population is evolving at a specific locus by determining what the population would be like if it were NOT evolving at that locus ...
... Used to assess whether a population is evolving at a specific locus by determining what the population would be like if it were NOT evolving at that locus ...
Gene expression profiling

In the field of molecular biology, gene expression profiling is the measurement of the activity (the expression) of thousands of genes at once, to create a global picture of cellular function. These profiles can, for example, distinguish between cells that are actively dividing, or show how the cells react to a particular treatment. Many experiments of this sort measure an entire genome simultaneously, that is, every gene present in a particular cell.DNA microarray technology measures the relative activity of previously identified target genes. Sequence based techniques, like serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE, SuperSAGE) are also used for gene expression profiling. SuperSAGE is especially accurate and can measure any active gene, not just a predefined set. The advent of next-generation sequencing has made sequence based expression analysis an increasingly popular, ""digital"" alternative to microarrays called RNA-Seq. However, microarrays are far more common, accounting for 17,000 PubMed articles by 2006.

















![sin entered the world through one man [Adam], and in this way](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001106899_1-d73e10265c84af259271c68920f7440e-300x300.png)



