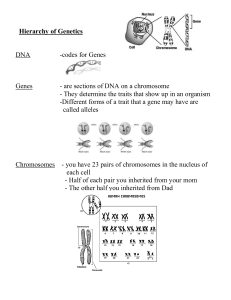
AP Biology Chapter 18, 19, 27 Study Guide Chapter 18: Regulation
... 3. What is differential gene expression? ...
... 3. What is differential gene expression? ...
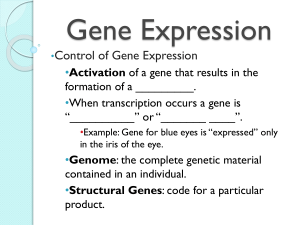
Gene Expression - Pleasantville High School
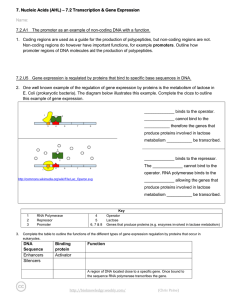
... RNA polymerase to promote transcription. Operator: Segment of DNA that can ________ _______________. Repressor Protein: ___________ a gene from being expressed (“turns off the gene”) Regulator Gene: _________ the expression of a specific gene by coding for a repressor. ...
... RNA polymerase to promote transcription. Operator: Segment of DNA that can ________ _______________. Repressor Protein: ___________ a gene from being expressed (“turns off the gene”) Regulator Gene: _________ the expression of a specific gene by coding for a repressor. ...
The Nutritional Genomics Laboratory at the HNRCA
... The Laboratory of Nutritional Genomics of the Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging is a pioneer in the study of gene-diet interactions in the area of cardiovascular diseases, utilizing both genetic epidemiology approaches as well as controlled dietary intervention studies. Our fo ...
... The Laboratory of Nutritional Genomics of the Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging is a pioneer in the study of gene-diet interactions in the area of cardiovascular diseases, utilizing both genetic epidemiology approaches as well as controlled dietary intervention studies. Our fo ...
Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains one of the most frequently
... defective mismatch repair (MMR) system, which is caused by mutations in one of MMR genes such as hMLH1 and hMSH2, epigenetic silencing of the hMLH1 gene, and oxidative inactivation of the MMR function. MSI has been detected in ~90% hereditary and ~15% of sporadic CRC, and CRC accounts for ~15% of al ...
... defective mismatch repair (MMR) system, which is caused by mutations in one of MMR genes such as hMLH1 and hMSH2, epigenetic silencing of the hMLH1 gene, and oxidative inactivation of the MMR function. MSI has been detected in ~90% hereditary and ~15% of sporadic CRC, and CRC accounts for ~15% of al ...
Epigenetics Glossary FINAL
... nucleotide bases, or "letters" of the genetic code. Imprinting: A genetic phenomenon by which certain genes are marked by biochemical modifications after conception so that only the gene copy inherited from one of the parents is expressed whereas the imprinted gene copy is silenced; for example, for ...
... nucleotide bases, or "letters" of the genetic code. Imprinting: A genetic phenomenon by which certain genes are marked by biochemical modifications after conception so that only the gene copy inherited from one of the parents is expressed whereas the imprinted gene copy is silenced; for example, for ...
Student Cancer Notes
... Cancer can be caused by a mutation in a gene whose products normally inhibit cell division. There are 3 ways this can happen through genetic change…. 1. Translocation → Cancer cells are frequently found to contain chromosomes that have broken and rejoined incorrectly → ______________________________ ...
... Cancer can be caused by a mutation in a gene whose products normally inhibit cell division. There are 3 ways this can happen through genetic change…. 1. Translocation → Cancer cells are frequently found to contain chromosomes that have broken and rejoined incorrectly → ______________________________ ...
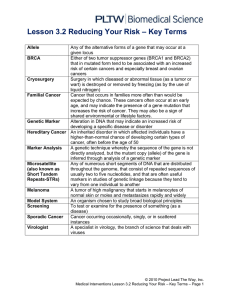
L3.2ReducingYourRisk - jj-sct
... Cancer that occurs in families more often than would be expected by chance. These cancers often occur at an early age, and may indicate the presence of a gene mutation that increases the risk of cancer. They may also be a sign of shared environmental or lifestyle factors. Genetic Marker Alteration i ...
... Cancer that occurs in families more often than would be expected by chance. These cancers often occur at an early age, and may indicate the presence of a gene mutation that increases the risk of cancer. They may also be a sign of shared environmental or lifestyle factors. Genetic Marker Alteration i ...
Slide 1
... DNA METHYLATION • When CpG dinucleotides are hypermethylated in a given locus, neighboring genes are usually silent • CpG hypomethylation correlates with gene expression me ...
... DNA METHYLATION • When CpG dinucleotides are hypermethylated in a given locus, neighboring genes are usually silent • CpG hypomethylation correlates with gene expression me ...
AP Biology - TeacherWeb
... 12. Explain how RNA processing is a mechanism of post-transcriptional regulation. ...
... 12. Explain how RNA processing is a mechanism of post-transcriptional regulation. ...
Nutrigenomics and nutrigenetics – are they the keys for healthy
... (1000 bases) to several megabases in size. CNVs contrast with SNPs, which affect only single nucleotide. ...
... (1000 bases) to several megabases in size. CNVs contrast with SNPs, which affect only single nucleotide. ...
Bill Nye - Genetics (worksheet)
... all living things derive from a _____________________________________. 15) Restriction enzymes are like “molecular scissors” that cut _______ molecules. ...
... all living things derive from a _____________________________________. 15) Restriction enzymes are like “molecular scissors” that cut _______ molecules. ...
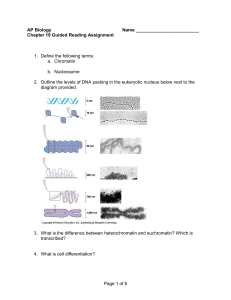
Chapter 19: Control of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
... 2.) What problem with the eukaryotic genome did the discovery of chromatin solve? 3.) What are histones? What are nucleosomes? 4.) What is the gene promoter? In order for RNA Polymerase to gain access to the promoter, what state must chromatin be in? 5.) What are the 3 ways (from lecture) that chrom ...
... 2.) What problem with the eukaryotic genome did the discovery of chromatin solve? 3.) What are histones? What are nucleosomes? 4.) What is the gene promoter? In order for RNA Polymerase to gain access to the promoter, what state must chromatin be in? 5.) What are the 3 ways (from lecture) that chrom ...
The DNA Connection
... The order of nitrogen bases along a gene forms a specific genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be produces ...
... The order of nitrogen bases along a gene forms a specific genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be produces ...
Thesis
... plants can be enhanced by different stress treatments. For the long-time transgenerational adaptation to environmental cues, the perceived information must be memorized in an epigenetic form that is propagated through mitotic and meiotic divisions, even when the initial signal is removed. However, ...
... plants can be enhanced by different stress treatments. For the long-time transgenerational adaptation to environmental cues, the perceived information must be memorized in an epigenetic form that is propagated through mitotic and meiotic divisions, even when the initial signal is removed. However, ...
Slide 1
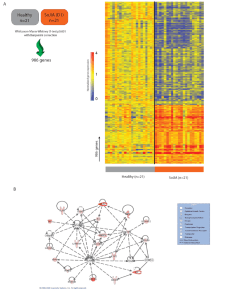
... Non parametric testing (Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney U-test; p<0.01 for class comparisons with Benjamini correction; p<0.05 for modular analyses with no multiple testing corrections) was used to rank genes based on their ability to discriminate among pre-specified groups of patients. 9,477 genes passing th ...
... Non parametric testing (Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney U-test; p<0.01 for class comparisons with Benjamini correction; p<0.05 for modular analyses with no multiple testing corrections) was used to rank genes based on their ability to discriminate among pre-specified groups of patients. 9,477 genes passing th ...
Epigenetics - BLI-Research-Synbio-2014-session-1
... of DNA wound around histones. • Amino acids on the terminal ends of the histones can bond with methyl, acetyl, or phosphate groups. ...
... of DNA wound around histones. • Amino acids on the terminal ends of the histones can bond with methyl, acetyl, or phosphate groups. ...
DNA Methylation
... DNA Methylation • DNA methylation, the addition of methyl groups to certain bases in DNA, is associated with reduced transcription in some species • DNA methylation can cause long-term inactivation of genes in cellular differentiation • In genomic imprinting, methylation regulates expression of eit ...
... DNA Methylation • DNA methylation, the addition of methyl groups to certain bases in DNA, is associated with reduced transcription in some species • DNA methylation can cause long-term inactivation of genes in cellular differentiation • In genomic imprinting, methylation regulates expression of eit ...
Epigenetics Theory www.AssignmentPoint.com In genetics
... The term "epigenetics", however, has been used to describe processes which have not been demonstrated to be heritable such as histone modification; there are therefore attempts to redefine it in broader terms that would avoid the constraints of requiring heritability. For example, Sir Adrian Bird de ...
... The term "epigenetics", however, has been used to describe processes which have not been demonstrated to be heritable such as histone modification; there are therefore attempts to redefine it in broader terms that would avoid the constraints of requiring heritability. For example, Sir Adrian Bird de ...
Study of Holocaust survivors finds trauma passed on to children
... However, research by Azim Surani at Cambridge University and colleagues, has recently shown that some epigenetic tags escape the cleaning process at fertilisation, slipping through the net. It’s not clear whether the gene changes found in the study would permanently affect the children’s health, nor ...
... However, research by Azim Surani at Cambridge University and colleagues, has recently shown that some epigenetic tags escape the cleaning process at fertilisation, slipping through the net. It’s not clear whether the gene changes found in the study would permanently affect the children’s health, nor ...
Epigenetics ppt
... Epigenetics: The study of the mechanisms by which genes bring about their phenotypic effects ...
... Epigenetics: The study of the mechanisms by which genes bring about their phenotypic effects ...