Chapter 10 .1 The Function of Digestion MACROMOLECULES AND
... - Proteins are assembled from small subunits are known as amino acids AMINO ACIDS – a building block of protein - Most protein molecules are made up of hundreds of amino aids joined together by peptide bonds into one of more chains PEPTIDE BONDS - a bond that holds together the amino acids in a prot ...
... - Proteins are assembled from small subunits are known as amino acids AMINO ACIDS – a building block of protein - Most protein molecules are made up of hundreds of amino aids joined together by peptide bonds into one of more chains PEPTIDE BONDS - a bond that holds together the amino acids in a prot ...
Ch 2d power point
... Most are globular proteins that act as biological catalysts Some enzymes are pure protein, some have a cofactor, usually a metal ion or an organic molecule derived from vitamins Enzymes are chemically specific ...
... Most are globular proteins that act as biological catalysts Some enzymes are pure protein, some have a cofactor, usually a metal ion or an organic molecule derived from vitamins Enzymes are chemically specific ...
2_4 Slides
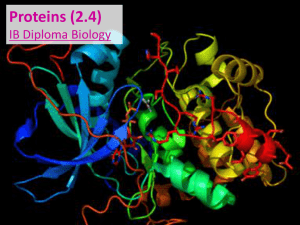
... 2.4.6 The amino acid sequence determines the three dimensional conformation of a protein. Polypeptides, or chains of amino acids, are the base (or primary) level of protein structure. But before they are functional, they must fold into specific structures based on the order / structure of their ami ...
... 2.4.6 The amino acid sequence determines the three dimensional conformation of a protein. Polypeptides, or chains of amino acids, are the base (or primary) level of protein structure. But before they are functional, they must fold into specific structures based on the order / structure of their ami ...
m/z
... able to • explain how structural information can be obtained by Tandem MS and MALDI-TOF/PSD • explain how mass spectrometry data can be used to identify known and unknown proteins ...
... able to • explain how structural information can be obtained by Tandem MS and MALDI-TOF/PSD • explain how mass spectrometry data can be used to identify known and unknown proteins ...
Amino acids and prot..
... • It is α-helical polypeptide chain, rich in cysteine and hydrophobic (non polar) amino acids so it is water insoluble. ...
... • It is α-helical polypeptide chain, rich in cysteine and hydrophobic (non polar) amino acids so it is water insoluble. ...
200-Level Biochemistry
... and the way in which nitrogen is metabolised. Finally, we look at signalling systems that integrate and control all of these different processes. The topics covered include aerobic and anaerobic energy metabolism; metabolism of fasting and fed states (particularly in humans); carbon fixation in phot ...
... and the way in which nitrogen is metabolised. Finally, we look at signalling systems that integrate and control all of these different processes. The topics covered include aerobic and anaerobic energy metabolism; metabolism of fasting and fed states (particularly in humans); carbon fixation in phot ...
Biochemistry
... • (b) Hydrogen bonds that form with nearby amino acids coil and fold the polypeptide into α-helices and β-pleated sheets; these constitute the polypeptide’s secondary structure. • (c) The polypeptide folds further to form its tertiary structure. These folds are stabilized by R-group interactions. • ...
... • (b) Hydrogen bonds that form with nearby amino acids coil and fold the polypeptide into α-helices and β-pleated sheets; these constitute the polypeptide’s secondary structure. • (c) The polypeptide folds further to form its tertiary structure. These folds are stabilized by R-group interactions. • ...
Assessment Questions Answer Key
... inserted into a bacterial cell. When the bacterial cell reproduces, it creates more cells that now have the recombinant plasmid and can produce the protein, insulin. ...
... inserted into a bacterial cell. When the bacterial cell reproduces, it creates more cells that now have the recombinant plasmid and can produce the protein, insulin. ...
Assessment Questions Answer Key
... inserted into a bacterial cell. When the bacterial cell reproduces, it creates more cells that now have the recombinant plasmid and can produce the protein, insulin. ...
... inserted into a bacterial cell. When the bacterial cell reproduces, it creates more cells that now have the recombinant plasmid and can produce the protein, insulin. ...
Cellular Energy Unit Vocabulary California Standard
... 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism’s cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: f. f. Students know usable energy is captured from sunlight by chloroplasts and is stored through the ...
... 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism’s cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: f. f. Students know usable energy is captured from sunlight by chloroplasts and is stored through the ...
TAKS biology review
... In the diagram above, what is the function of RNA? A. Carry the set of instructions that replicates another DNA molecule in the protein chain. B. Carry the set of instructions that places amino acids in the protein chain in the correct order. C. Carry the set of instructions that places phosphate mo ...
... In the diagram above, what is the function of RNA? A. Carry the set of instructions that replicates another DNA molecule in the protein chain. B. Carry the set of instructions that places amino acids in the protein chain in the correct order. C. Carry the set of instructions that places phosphate mo ...
Verification of Real Time Systems
... • Serve as catalytic enzymes for bio-chemical reactions. • Induce signal transductions. • Control transcriptions and translation of genes • Control degradation of proteins. ...
... • Serve as catalytic enzymes for bio-chemical reactions. • Induce signal transductions. • Control transcriptions and translation of genes • Control degradation of proteins. ...
Automatic Protein Structure Clustering Using
... During recent years, many efforts have been made to analyze the relation between structure and function. Most previous research work focused on classifying protein families based on homology [1][2][3]. A major assumption of previous works is that the protein families or functional categories are kno ...
... During recent years, many efforts have been made to analyze the relation between structure and function. Most previous research work focused on classifying protein families based on homology [1][2][3]. A major assumption of previous works is that the protein families or functional categories are kno ...
Word file (24 KB )
... targeting vector, containing a promoter-less lacZ and neomycin-resistance gene under control of the RNA polymerase II promoter (gift from R. Palmiter). A 7-kb Bam HI-Xho I fragment was used as a long arm. The targeting vector was electroporated into 129 SvEv-derived SM-1 ES cells and selected under ...
... targeting vector, containing a promoter-less lacZ and neomycin-resistance gene under control of the RNA polymerase II promoter (gift from R. Palmiter). A 7-kb Bam HI-Xho I fragment was used as a long arm. The targeting vector was electroporated into 129 SvEv-derived SM-1 ES cells and selected under ...
MOLECULES IN CELLS - SITH-ITB
... ! Describe the molecules in living organisms ! Explain basic structure and function of protein in cells ! Explain basic structure and function of carbohydrate in cells ! Explain basic structure and function of lipid in cells ! Explain basic structure and function of nucleic acid in cells ...
... ! Describe the molecules in living organisms ! Explain basic structure and function of protein in cells ! Explain basic structure and function of carbohydrate in cells ! Explain basic structure and function of lipid in cells ! Explain basic structure and function of nucleic acid in cells ...
I have put together a recommendation for teacher assignments
... D. molecules that transfer information out of the nucleus 2. Which path correctly describes the flow of information in cells? A. DNA→ RNA→ protein B. protein → RNA→ DNA C. protein → DNA→ RNA D. RNA→ DNA→ protein 3. The kinds of genes that an organism has is determined by the A. type of amino acids i ...
... D. molecules that transfer information out of the nucleus 2. Which path correctly describes the flow of information in cells? A. DNA→ RNA→ protein B. protein → RNA→ DNA C. protein → DNA→ RNA D. RNA→ DNA→ protein 3. The kinds of genes that an organism has is determined by the A. type of amino acids i ...
pptx - FenyoLab.org
... possible reactions not to dilute the cross-linked peptides. For identification of a cross-linked peptide pair, both peptides have to be sufficiently long and required to give informative fragmentation. ...
... possible reactions not to dilute the cross-linked peptides. For identification of a cross-linked peptide pair, both peptides have to be sufficiently long and required to give informative fragmentation. ...
Cellular imitations
... proteins are necessary to copy viral genomes in vitro. Considering the small size of the phi29 bacteriophage genome, it will be important to determine whether the system in its current form will be capable of copying genomes with greater than 20 encoded genes. Attempts to further simplify the constr ...
... proteins are necessary to copy viral genomes in vitro. Considering the small size of the phi29 bacteriophage genome, it will be important to determine whether the system in its current form will be capable of copying genomes with greater than 20 encoded genes. Attempts to further simplify the constr ...
Proteins and Nucleic Acids
... around each other in a spiral shape called a double helix. The double helix has the ability to wind and unwind so that the nucleic acid chain can duplicate itself. That duplication process happens every time a cell divides. The nucleotides in one strand of the double helix bond to nucleotides in the ...
... around each other in a spiral shape called a double helix. The double helix has the ability to wind and unwind so that the nucleic acid chain can duplicate itself. That duplication process happens every time a cell divides. The nucleotides in one strand of the double helix bond to nucleotides in the ...
Hit List vocabulary cards
... Deoxyribonucleic acid; doublestranded polynucleotide comprised of deoxyribose (sugar), phosphate, and 1 of 4 bases; genetic material in all ...
... Deoxyribonucleic acid; doublestranded polynucleotide comprised of deoxyribose (sugar), phosphate, and 1 of 4 bases; genetic material in all ...
slides
... Problem Statement and Motivation • The structure of proteins provide rich information about how cells work. With the success of structural genomics, soon we will have all human proteins mapped to structures. • However, we need to develop computational tools to extract information from these structur ...
... Problem Statement and Motivation • The structure of proteins provide rich information about how cells work. With the success of structural genomics, soon we will have all human proteins mapped to structures. • However, we need to develop computational tools to extract information from these structur ...
MHC II Function - Andrew Pierce -
... • “Real-time” PCR uses fluorescent probes to analyze the level of amplified cDNA at each PCR cycle, and is more quantitative than “end-point” PCR, where the final amplified sample is analyzed by gel electrophoresis. • For more information about real-time PCR, visit: http://www.appliedbiosystems.com/ ...
... • “Real-time” PCR uses fluorescent probes to analyze the level of amplified cDNA at each PCR cycle, and is more quantitative than “end-point” PCR, where the final amplified sample is analyzed by gel electrophoresis. • For more information about real-time PCR, visit: http://www.appliedbiosystems.com/ ...
Chemical Basis of Life
... Tertiary (3°) – folding of secondary structures on each other Quaternary (4°) – 2+ polypeptides interact to form a protein Denaturation destroys structure which alters or inhibits ...
... Tertiary (3°) – folding of secondary structures on each other Quaternary (4°) – 2+ polypeptides interact to form a protein Denaturation destroys structure which alters or inhibits ...
Biomolecules and Nanotechnology
... the effects in months instead of millennia. HIV reverse transcriptase, the enzyme that copies the virus’s genetic information, is particularly error-prone. Because of this, the population of viruses within an infected individual contains viruses with all possible single-site mutations—thousands of v ...
... the effects in months instead of millennia. HIV reverse transcriptase, the enzyme that copies the virus’s genetic information, is particularly error-prone. Because of this, the population of viruses within an infected individual contains viruses with all possible single-site mutations—thousands of v ...