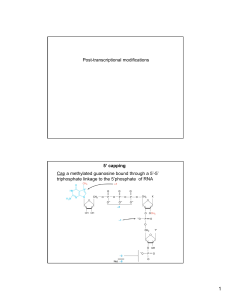
Post-transcriptional modifications Cap a
... Several current models hold that silencing signals are “aberrant” RNAs (aRNA), that differ in some way from normal mRNAs. The most likely candidates are small antisense RNAs (asRNA) and double-stranded RNAs (dsRNA). Most current models assume that silencing signals interact with target RNAs in a seq ...
... Several current models hold that silencing signals are “aberrant” RNAs (aRNA), that differ in some way from normal mRNAs. The most likely candidates are small antisense RNAs (asRNA) and double-stranded RNAs (dsRNA). Most current models assume that silencing signals interact with target RNAs in a seq ...
Unit 3 - kehsscience.org
... Your genome has about 25,000 genes, so there are many genes on each chromosome. Each chromosome you got from your mother “matches” up with a chromosome that you got from your father…..so it is the “combination of instructions” that you received in those 23 pairs of chromosomes that makes you unique. ...
... Your genome has about 25,000 genes, so there are many genes on each chromosome. Each chromosome you got from your mother “matches” up with a chromosome that you got from your father…..so it is the “combination of instructions” that you received in those 23 pairs of chromosomes that makes you unique. ...
Microbiology
... purine nucleotides. The cluster is a single transcription unit and is organized into three groups of overlapping genes followed by the last gene : ptlrEKB-ptlrC(or-QLFparMNH( J)-ptlrD (Ebbole & Zalkin, 1987). Mutants resistant to 8-azaguanine (pbuG mutants) appear to be defective in hypoxanthine and ...
... purine nucleotides. The cluster is a single transcription unit and is organized into three groups of overlapping genes followed by the last gene : ptlrEKB-ptlrC(or-QLFparMNH( J)-ptlrD (Ebbole & Zalkin, 1987). Mutants resistant to 8-azaguanine (pbuG mutants) appear to be defective in hypoxanthine and ...
Biol120 Mock Final Examination (v2.0)
... Questions and answers for this mock exam will be posted after today’s event http://www.usask.ca/ulc/sss, ...
... Questions and answers for this mock exam will be posted after today’s event http://www.usask.ca/ulc/sss, ...
24. DNA testing
... Loss of function mutations Loss of function mutations Fairly large gene: 250 kb genomic DNA Giant gene: 2400 kb genomic DNA 27 exons, 6.5 kb mRNA 79 exons, 14 kb mRNA Almost all mutations are single nt changes, 65% of mutations are deletions of 1 or although most common is a 3 nt deletion more exons ...
... Loss of function mutations Loss of function mutations Fairly large gene: 250 kb genomic DNA Giant gene: 2400 kb genomic DNA 27 exons, 6.5 kb mRNA 79 exons, 14 kb mRNA Almost all mutations are single nt changes, 65% of mutations are deletions of 1 or although most common is a 3 nt deletion more exons ...
Transcription and Translation
... are made in the cytoplasm. mRNA serves as a “messenger” and carries the protein building instructions to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
... are made in the cytoplasm. mRNA serves as a “messenger” and carries the protein building instructions to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
Advanced Mendelian Genetics
... Independent Assortment • The alleles for seed shape segregated independently of those for seed color. This principle is known as independent assortment. • Genes that segregate independently do not influence each other’s inheritance . ...
... Independent Assortment • The alleles for seed shape segregated independently of those for seed color. This principle is known as independent assortment. • Genes that segregate independently do not influence each other’s inheritance . ...
Inheritence of Genes - New Century Academy
... -Chromosomes alternate between fertilization (2n or Diploid) and Meiosis (1n or Haploid) -Somatic Cells are all cells except sex cells -Sex Chromosomes determine male and female gender -All other chromosomes are called Autosomes ...
... -Chromosomes alternate between fertilization (2n or Diploid) and Meiosis (1n or Haploid) -Somatic Cells are all cells except sex cells -Sex Chromosomes determine male and female gender -All other chromosomes are called Autosomes ...
Presentation
... patterns and variation. • Gregor Mendel showed that traits are inherited as discrete units. • Many in Mendel’s day thought traits were blended. ...
... patterns and variation. • Gregor Mendel showed that traits are inherited as discrete units. • Many in Mendel’s day thought traits were blended. ...
PATENT PROTECTION FOR GENE SEQUENCES WHAT IS
... to synchronize patent law among member states of the EU. Inventors can file patent applications in one state cognizable in all member states at the European Patent Office (EPO). The EPO is authorized to examine a patent application, reject it, or issue it. The patentee receives a bundle of national ...
... to synchronize patent law among member states of the EU. Inventors can file patent applications in one state cognizable in all member states at the European Patent Office (EPO). The EPO is authorized to examine a patent application, reject it, or issue it. The patentee receives a bundle of national ...
Ch. 11 - Introduction to Genetics
... Eye color in fruit flies involves the interactions of three ...
... Eye color in fruit flies involves the interactions of three ...
Mendel and Heredity (Chapter 8)
... A. Heredity: the passing of traits from parents to offspring (Characteristic=Trait) before DNA and chromosomes were discovered, heredity was a great mystery ...
... A. Heredity: the passing of traits from parents to offspring (Characteristic=Trait) before DNA and chromosomes were discovered, heredity was a great mystery ...
Chapter 20 Terms to Know
... Cut DNA with different restriction enzymes Each person has different #s of DNA fragments ...
... Cut DNA with different restriction enzymes Each person has different #s of DNA fragments ...
protein synthesis slides - week 1
... Protein Synthesis Booklet – pg. 1 1. Look at the cover page of your booklet. 2. Attempt to identify things you recognize from ...
... Protein Synthesis Booklet – pg. 1 1. Look at the cover page of your booklet. 2. Attempt to identify things you recognize from ...
Biology B Final Review ANSWERS
... A. They pass on to their offspring new characteristics they acquired during their lifetimes. B. They are better adapted to exist in their environment than others. C. They do not pass on to their offspring new characteristics they have acquired during their lifetimes. D. They tend to produce fewer of ...
... A. They pass on to their offspring new characteristics they acquired during their lifetimes. B. They are better adapted to exist in their environment than others. C. They do not pass on to their offspring new characteristics they have acquired during their lifetimes. D. They tend to produce fewer of ...
C. Would you expect cells treated with methotrexate to produce
... you have an extra copy of the chromosome containing a gene for a transcriptional activator, you will make even more of that activator relative to other transcriptional regulators, disrupting the regulation of many different gene (+1 for an explanation) ...
... you have an extra copy of the chromosome containing a gene for a transcriptional activator, you will make even more of that activator relative to other transcriptional regulators, disrupting the regulation of many different gene (+1 for an explanation) ...
Cloning a Paper Plasmid
... These are needed to transcribe the gene properly when it is read. In addition, the HindIII & EcoR1 restriction enzyme cutting sites (sequences of bases) are marked in bold on the Jellyfish Glo gene DNA. The two restriction enzymes and their respective restriction sites are listed below. These enzyme ...
... These are needed to transcribe the gene properly when it is read. In addition, the HindIII & EcoR1 restriction enzyme cutting sites (sequences of bases) are marked in bold on the Jellyfish Glo gene DNA. The two restriction enzymes and their respective restriction sites are listed below. These enzyme ...
4 Sex linkage - WordPress.com
... Early in a female’s embryonic development, one of the X chromosomes is inactivated. This supercoils to form a Barr Body. This occurs randomly in each cell, so all the cells that descend from that cell will have either their maternal or paternal X chromosome switched off. Tortoiseshell cats will have ...
... Early in a female’s embryonic development, one of the X chromosomes is inactivated. This supercoils to form a Barr Body. This occurs randomly in each cell, so all the cells that descend from that cell will have either their maternal or paternal X chromosome switched off. Tortoiseshell cats will have ...
7.014 Solution Set 4
... strand is bacterial, and which is human. Briefly justify your choices. Human DNA for the same protein is likely to be significantly longer than a bacterial gene encoding homologous bacterial protein because the human gene is likely to have introns. Those are represented by the large loops in the hum ...
... strand is bacterial, and which is human. Briefly justify your choices. Human DNA for the same protein is likely to be significantly longer than a bacterial gene encoding homologous bacterial protein because the human gene is likely to have introns. Those are represented by the large loops in the hum ...
Name __________________________________ Period _________ Ms Foglia • AP Biology Date ______________________
... These are needed to transcribe the gene properly when it is read. In addition, the HindIII & EcoR1 restriction enzyme cutting sites (sequences of bases) are marked in bold on the Jellyfish Glo gene DNA. The two restriction enzymes and their respective restriction sites are listed below. These enzyme ...
... These are needed to transcribe the gene properly when it is read. In addition, the HindIII & EcoR1 restriction enzyme cutting sites (sequences of bases) are marked in bold on the Jellyfish Glo gene DNA. The two restriction enzymes and their respective restriction sites are listed below. These enzyme ...
Slide 1
... Show pathway maps and find Enzyme ID (EC) using KEGG Identify functional domains and Gene Ontology Annotation of the protein sequence using Uniprot, Prosite, Pfam Find orthologs and perform multiple sequence alignment 2.2 Find ortholog protein sequences in Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus, Saccharomy ...
... Show pathway maps and find Enzyme ID (EC) using KEGG Identify functional domains and Gene Ontology Annotation of the protein sequence using Uniprot, Prosite, Pfam Find orthologs and perform multiple sequence alignment 2.2 Find ortholog protein sequences in Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus, Saccharomy ...
Chromosomes
... protein or RNA molecule • As a eukaryotic cell prepares to divide the DNA and proteins associated with the DNA coil into a structure called a chromosome. • Before DNA coils, the DNA is copied. • The two exact copies of DNA that make up the chromosome are called chromatids. ...
... protein or RNA molecule • As a eukaryotic cell prepares to divide the DNA and proteins associated with the DNA coil into a structure called a chromosome. • Before DNA coils, the DNA is copied. • The two exact copies of DNA that make up the chromosome are called chromatids. ...
Genomics of Autoimmune Diseases
... life threatening but still have many negative symptoms that can affect the quality of life for those that suffer from them. (Genes and Mutations Associated with Autoimmune Diseases) Each autoimmune disease has not only multiple genes associated with it, but also multiple SNP’s associated with each g ...
... life threatening but still have many negative symptoms that can affect the quality of life for those that suffer from them. (Genes and Mutations Associated with Autoimmune Diseases) Each autoimmune disease has not only multiple genes associated with it, but also multiple SNP’s associated with each g ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.























