Name: Biology I: Chapter 14 Guided Reading Chapter 12.4 When
... Disorders that happen among sex-chromosomes can also occur. In females nondisjunction can lead to _____________________________. A female with this disorder usually inherits only _______ X chromosome. These women are ____________ which means that they are unable to _________________. Their sex organ ...
... Disorders that happen among sex-chromosomes can also occur. In females nondisjunction can lead to _____________________________. A female with this disorder usually inherits only _______ X chromosome. These women are ____________ which means that they are unable to _________________. Their sex organ ...
Section A: Eukaryotic Chromatin Structure
... amount of DNA relative to their condensed length. • Each human chromosome averages about 2 x 108 nucleotide pairs. • If extended, each DNA molecule would be about 6 cm long, thousands of times longer than the cell diameter. • This chromosome and 45 other human chromosomes fit into the nucleus. • Thi ...
... amount of DNA relative to their condensed length. • Each human chromosome averages about 2 x 108 nucleotide pairs. • If extended, each DNA molecule would be about 6 cm long, thousands of times longer than the cell diameter. • This chromosome and 45 other human chromosomes fit into the nucleus. • Thi ...
Model question Paper- Gene Technology MLAB 475
... Protein is responsible for preserving, copying and transmitting information within cells and from generation to generation. ...
... Protein is responsible for preserving, copying and transmitting information within cells and from generation to generation. ...
Searching for Genes
... All branches on the tree of life share common roots. One way to study those roots is to look to DNA sequences. So, when the Roberts lab began studying the evolution of cellulose synthesis, one place they looked was at the available DNA sequence information. Even now, as they expand their studies to ...
... All branches on the tree of life share common roots. One way to study those roots is to look to DNA sequences. So, when the Roberts lab began studying the evolution of cellulose synthesis, one place they looked was at the available DNA sequence information. Even now, as they expand their studies to ...
Nerve activates contraction
... amount of DNA relative to their condensed length. • Each human chromosome averages about 2 x 108 nucleotide pairs. • If extended, each DNA molecule would be about 6 cm long, thousands of times longer than the cell diameter. ...
... amount of DNA relative to their condensed length. • Each human chromosome averages about 2 x 108 nucleotide pairs. • If extended, each DNA molecule would be about 6 cm long, thousands of times longer than the cell diameter. ...
Lecture 2
... 5.4 Catabolite repression A diauxic growth curve results when two sugars are present –e.g. Glucose is used first followed by other sugars such as lactose or xylose. Glucose has been shown to block the expression of a number of operons controlling the catabolism of particular sugars such as lact ...
... 5.4 Catabolite repression A diauxic growth curve results when two sugars are present –e.g. Glucose is used first followed by other sugars such as lactose or xylose. Glucose has been shown to block the expression of a number of operons controlling the catabolism of particular sugars such as lact ...
Developmental Genetics of Higher Organisms
... references at the end of each chapter to about fifty, apart from a small number of so-called general references. Another interesting innovation in this series is a set of questions which the Editor has asked each author about the significance of their work and about the thoughts they may have for fu ...
... references at the end of each chapter to about fifty, apart from a small number of so-called general references. Another interesting innovation in this series is a set of questions which the Editor has asked each author about the significance of their work and about the thoughts they may have for fu ...
word - marric
... 6. Chromosomal mutations occurring in gametes of humans can affect the appearance of offspring because a. many traits are usually affected b. only one trait is usually affected c. these mutations usually speed up embryonic development d. these mutations usually result in sex-linked Traits ...
... 6. Chromosomal mutations occurring in gametes of humans can affect the appearance of offspring because a. many traits are usually affected b. only one trait is usually affected c. these mutations usually speed up embryonic development d. these mutations usually result in sex-linked Traits ...
GENETICS
... They can self pollinate They can be cross pollinated Many of the measurable traits were dominant or recessive Mendels First Experiment was a Monohybrid Cross. 1. Parental (P) generation. He began by crossing plants that “bred true” for one trait. Individuals true-breeding for a trait inherited ...
... They can self pollinate They can be cross pollinated Many of the measurable traits were dominant or recessive Mendels First Experiment was a Monohybrid Cross. 1. Parental (P) generation. He began by crossing plants that “bred true” for one trait. Individuals true-breeding for a trait inherited ...
Biology Keystone Review Packet Module 2 with Answers
... a. independent assortment – genes segregate independently and do not influence each other’s inheritance i. the principle of independent assortment states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes 12. some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive, a ...
... a. independent assortment – genes segregate independently and do not influence each other’s inheritance i. the principle of independent assortment states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes 12. some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive, a ...
Applications_of_Gene_Technology_Student_Notes
... The first stage of PCR is to heat the DNA to 95oC – this makes the 2 polynucleotide strands separate DNA nucleotides are added and the mixture is cooled to 40oC. The DNA polymerase attaches the new nucleotides to each strand (as in normal replication) The process can then be repeated _____________ – ...
... The first stage of PCR is to heat the DNA to 95oC – this makes the 2 polynucleotide strands separate DNA nucleotides are added and the mixture is cooled to 40oC. The DNA polymerase attaches the new nucleotides to each strand (as in normal replication) The process can then be repeated _____________ – ...
Next-Generation Sequencing Applications Complement
... high-risk cases of MDS, with 70% showing aberrant DNA methylation in ...
... high-risk cases of MDS, with 70% showing aberrant DNA methylation in ...
מצגת של PowerPoint
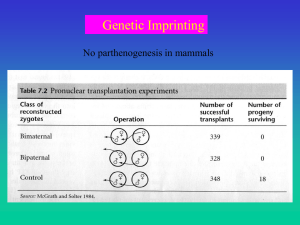
... copy only, and they play a key role in regulating complex biological processes, including offspring development and mother-offspring interactions. There are several competing theories attempting to explain the evolutionary origin of this monoallelic pattern of gene expression, but a prevailing view ...
... copy only, and they play a key role in regulating complex biological processes, including offspring development and mother-offspring interactions. There are several competing theories attempting to explain the evolutionary origin of this monoallelic pattern of gene expression, but a prevailing view ...
**Study all vocabulary terms!!** 1. Explain why people look like their
... Explain why people look like their parents. (Use ALL information we have discussed!) Explain why siblings do not look the same, even if they come from the same parents. Explain what DNA is. (Parts, what bonds with what, what is codes for) Describe how the structure of DNA was discovered. (who was in ...
... Explain why people look like their parents. (Use ALL information we have discussed!) Explain why siblings do not look the same, even if they come from the same parents. Explain what DNA is. (Parts, what bonds with what, what is codes for) Describe how the structure of DNA was discovered. (who was in ...
How does every cell get a copy of DNA?
... The mRNA has extra “junk” code in it called introns. These introns are cut out and the good code (called exons) are put ...
... The mRNA has extra “junk” code in it called introns. These introns are cut out and the good code (called exons) are put ...
Human Mitochondrial DNA
... • Scale-up – the process of increasing the size or volume of the production of a particular product ...
... • Scale-up – the process of increasing the size or volume of the production of a particular product ...
Essential knowledge 3.A.3:
... probabilities of the different ways. For example: Question: In a Mendelian cross between pea plants that are heterozygous for ...
... probabilities of the different ways. For example: Question: In a Mendelian cross between pea plants that are heterozygous for ...
Furry Family Genetics
... 11. A scientist crossed a pea plant with yellow wrinkled peas with a pea plant with green smooth peas. The resulting offspring were yellow smooth peas. What does this indicate? a. b. c. d. ...
... 11. A scientist crossed a pea plant with yellow wrinkled peas with a pea plant with green smooth peas. The resulting offspring were yellow smooth peas. What does this indicate? a. b. c. d. ...
Horizontal and Vertical Gene Transfer
... transferred genes among and between species. Most knowledge about horizontal gene transfer has been obtained from experience with prokaryocytes. Analysis of the genes of E.coli and Salmonella shows that 17% of the genomes were acquired by horizontal gene transfer during the past 100 million years. C ...
... transferred genes among and between species. Most knowledge about horizontal gene transfer has been obtained from experience with prokaryocytes. Analysis of the genes of E.coli and Salmonella shows that 17% of the genomes were acquired by horizontal gene transfer during the past 100 million years. C ...
Chapter 8 Microbial Genetics
... Diagram and describe how enzymes speed up biochemical reactions, and how they affect the energy required for a reaction to occur. Describe 3 different physical and chemical factors that can influence enzyme activity? ...
... Diagram and describe how enzymes speed up biochemical reactions, and how they affect the energy required for a reaction to occur. Describe 3 different physical and chemical factors that can influence enzyme activity? ...
Genetics 314 – Spring, 2005
... 3. You want to express the DNA sequence in bacteria. Your friend says you need to add additional sequences to get expression. What sequences do you need to add and what are they needed for to allow expression of the DNA sequence in bacteria? ...
... 3. You want to express the DNA sequence in bacteria. Your friend says you need to add additional sequences to get expression. What sequences do you need to add and what are they needed for to allow expression of the DNA sequence in bacteria? ...
Disease Inheritance
... syndrome where the development is apparently female, but without female secondary sexual characteristics. Two or more X chromosomes and one Y chromosome leads to Klinefelter syndrome, typified by males with very small genitalia and prostate gland and a tendency to a very ...
... syndrome where the development is apparently female, but without female secondary sexual characteristics. Two or more X chromosomes and one Y chromosome leads to Klinefelter syndrome, typified by males with very small genitalia and prostate gland and a tendency to a very ...
Human Chromosomes
... Key concepts: Why are sex-linked disorders more common in males than in females? What is nondisjunction, and what problems does it cause? I. Human Genes and Chromosomes ...
... Key concepts: Why are sex-linked disorders more common in males than in females? What is nondisjunction, and what problems does it cause? I. Human Genes and Chromosomes ...
6TH GRADE FAMILY LIFE
... Notice This curriculum will be taught on the dates determined by the Department of Academics. These dates will be determined annually. ...
... Notice This curriculum will be taught on the dates determined by the Department of Academics. These dates will be determined annually. ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.