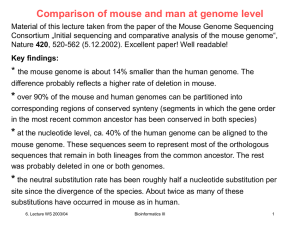
GENETICS accepted
... A necessary early step in crossing over is the SPO11-dependent formation of double-strand breaks (DSBs) (KEENEY et al. 1997). In S. cerevisiae, at least nine other proteins interact with SPO11 to regulate the recruitment and activation of SPO11 (KEENEY and NEALE 2006). These proteins that regulate t ...
... A necessary early step in crossing over is the SPO11-dependent formation of double-strand breaks (DSBs) (KEENEY et al. 1997). In S. cerevisiae, at least nine other proteins interact with SPO11 to regulate the recruitment and activation of SPO11 (KEENEY and NEALE 2006). These proteins that regulate t ...
Inclusive Fitness and the Sociobiology of the Genome Herbert Gintis
... (1964b) provided a plausible explanation of social cooperation. However, inclusive fitness theory renders equally plausible biochemical and social behaviors that are comparatively rarely observed. This is because, as is clear from (3) and (4), Hamilton’s Rule does not place any limitations on the si ...
... (1964b) provided a plausible explanation of social cooperation. However, inclusive fitness theory renders equally plausible biochemical and social behaviors that are comparatively rarely observed. This is because, as is clear from (3) and (4), Hamilton’s Rule does not place any limitations on the si ...
Identical mutations in RAG1 or RAG2 genes leading
... 2 mutations in RAG2 were found either as homozygous or compound heterozygous. The mutations were always found inherited from both parents. In OM3, OM5, and OM8, mutations were either nonsense (Y333X in OM8) or involved deletion of one (⌬T631 in OM3 and OM5) or 2 (⌬AA368 in OM8) nucleotides resulting ...
... 2 mutations in RAG2 were found either as homozygous or compound heterozygous. The mutations were always found inherited from both parents. In OM3, OM5, and OM8, mutations were either nonsense (Y333X in OM8) or involved deletion of one (⌬T631 in OM3 and OM5) or 2 (⌬AA368 in OM8) nucleotides resulting ...
THE EFFECT OF INBREEDING ON THE VARIATION DUE TO
... population of lines will not reiliain the sanie but will gradually decline as selection proceeds. The genetic variance will not depend on the inbreeding coefficient alone but also on the amount of selection and therefore on the nun1l)er of generations that the inbreeding and selection has proceeded. ...
... population of lines will not reiliain the sanie but will gradually decline as selection proceeds. The genetic variance will not depend on the inbreeding coefficient alone but also on the amount of selection and therefore on the nun1l)er of generations that the inbreeding and selection has proceeded. ...
Cancer Prone Disease Section Retinoblastoma Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Description: 180 kb genomic DNA containing 27 exons. Transcription: 4.7 kb mRNA with 2.7 kb open reading frame. Protein Description: 928 aa nuclear phosphoprotein. Localisation: Nucleus. Function: Involved in cell cycle regulation. Mutations Note: Mutations predisposing to retinoblastoma are one all ...
... Description: 180 kb genomic DNA containing 27 exons. Transcription: 4.7 kb mRNA with 2.7 kb open reading frame. Protein Description: 928 aa nuclear phosphoprotein. Localisation: Nucleus. Function: Involved in cell cycle regulation. Mutations Note: Mutations predisposing to retinoblastoma are one all ...
VECTOR SYSTEMS XXVII.indd
... Gram-positive bacteria are well known for their contributions to agricultural, medical and food biotechnology and for the production of recombinant proteins. Among them, Bacillus subtilis has been developed as an attractive host because of several reasons: It is non-pathogenic and is considered as ...
... Gram-positive bacteria are well known for their contributions to agricultural, medical and food biotechnology and for the production of recombinant proteins. Among them, Bacillus subtilis has been developed as an attractive host because of several reasons: It is non-pathogenic and is considered as ...
Diversity of DNA methyltransferases that recognize asymmetric
... palindromic DNA sequences and add a methyl group to the target base (either adenine or cytosine) on both strands. However, there are a number of MTases that recognize asymmetric target sequences and differ in their subunit organization. In a bacterial cell, after each round of replication, the subst ...
... palindromic DNA sequences and add a methyl group to the target base (either adenine or cytosine) on both strands. However, there are a number of MTases that recognize asymmetric target sequences and differ in their subunit organization. In a bacterial cell, after each round of replication, the subst ...
Archaeal phylogenomics provides evidence in support of a
... eukaryote-like histones [21,22] and cell division protein FtsZ [23], are found only in one particular branch of the Archaea known as the Euryarchaea. These observations suggested a root for eukaryotes either within or as sisters to the Euryarchaea—a hypothesis that was supported by SUPERTREE analyse ...
... eukaryote-like histones [21,22] and cell division protein FtsZ [23], are found only in one particular branch of the Archaea known as the Euryarchaea. These observations suggested a root for eukaryotes either within or as sisters to the Euryarchaea—a hypothesis that was supported by SUPERTREE analyse ...
Peer Review 1
... Assuming the result of this procedure is that tGLI1 is present in at least some of the tumours, I would proceed with the following experiment. The second experiment (the focus of this project) would be an “add something” experiment. Specifically, I would increase SUFU expression using a knocked-in g ...
... Assuming the result of this procedure is that tGLI1 is present in at least some of the tumours, I would proceed with the following experiment. The second experiment (the focus of this project) would be an “add something” experiment. Specifically, I would increase SUFU expression using a knocked-in g ...
Chapter 3 Clustering Microarray Data
... Two-way clustering may be used to identify a subset in one dimension that is useful for clustering the other dimension. This is the idea behind the interrelated two-way clustering method of Tang et al. (2001). In this method, the genes are clustered and each gene cluster is used to cluster the sampl ...
... Two-way clustering may be used to identify a subset in one dimension that is useful for clustering the other dimension. This is the idea behind the interrelated two-way clustering method of Tang et al. (2001). In this method, the genes are clustered and each gene cluster is used to cluster the sampl ...
Sequence comparison of aflR from different Aspergillus species
... Cys6 Zn2 DNA-binding domain and C-terminal transcription activation domain typical of GAL4-type fungal and yeast transcription factors. AflR binds to the partially palindromic consensus sequence 50 -TCGN5 CGR-30 found in promoters of most of the aflatoxin biosynthesis genes (Chang et al., 1995; Ehrlic ...
... Cys6 Zn2 DNA-binding domain and C-terminal transcription activation domain typical of GAL4-type fungal and yeast transcription factors. AflR binds to the partially palindromic consensus sequence 50 -TCGN5 CGR-30 found in promoters of most of the aflatoxin biosynthesis genes (Chang et al., 1995; Ehrlic ...
Novel cryptic chromosomal rearrangements in childhood acute
... as 22% of T-ALL patients. HOX11L2, an orphan homeobox gene located close to the chromosome 5 breakpoints was found to be transcriptionally activated as a result of this translocation.6 The t(7;11) also involves distal chromosome arm ends and cannot be detected upon banding analysis only, and thus ca ...
... as 22% of T-ALL patients. HOX11L2, an orphan homeobox gene located close to the chromosome 5 breakpoints was found to be transcriptionally activated as a result of this translocation.6 The t(7;11) also involves distal chromosome arm ends and cannot be detected upon banding analysis only, and thus ca ...
Chapter 44 Self Test (EOC)
... millions of years, typically, for many of the traits examined to evolve? Answer—Development is a highly conserved and constrained process; small perturbations can have drastic consequences, and most of these are negative. Given the thousands or hundreds of thousands of variables that can change in e ...
... millions of years, typically, for many of the traits examined to evolve? Answer—Development is a highly conserved and constrained process; small perturbations can have drastic consequences, and most of these are negative. Given the thousands or hundreds of thousands of variables that can change in e ...
Phage
... multiply inside bacteria by making use of some or all of the host biosynthetic machinery • Significance – Models for animal cell viruses – Gene transfer in bacteria – Medical applications • Identification of bacteria - phage typing • Treatment and prophylaxsis??? ...
... multiply inside bacteria by making use of some or all of the host biosynthetic machinery • Significance – Models for animal cell viruses – Gene transfer in bacteria – Medical applications • Identification of bacteria - phage typing • Treatment and prophylaxsis??? ...
The Maize Genome Poster
... in which scientific and technological progress translates basic discoveries into practical applications. To this end, the genome sequences of maize and other crops are significantly enhancing established breeding efforts. Soon it will be possible to reconstruct and fully understand the genetic basis ...
... in which scientific and technological progress translates basic discoveries into practical applications. To this end, the genome sequences of maize and other crops are significantly enhancing established breeding efforts. Soon it will be possible to reconstruct and fully understand the genetic basis ...
– findings from cross-species Anxiety genetics genome-wide approaches
... and better anxiolytics are needed, and their development requires understanding of the molecular mechanisms that regulate anxiety. Genetics offer an ideal route to the molecular background of anxiety as any identified genes can directly be linked to their function within the cell and the neural circ ...
... and better anxiolytics are needed, and their development requires understanding of the molecular mechanisms that regulate anxiety. Genetics offer an ideal route to the molecular background of anxiety as any identified genes can directly be linked to their function within the cell and the neural circ ...
The E-Class PPR Protein MEF3 of Arabidopsis
... proteins in the mapped genomic window into Ler protoplasts shows differential effects. Sequence analysis of the atp4 cDNA shows that gene At1g06140 strongly increases the level of RNA editing at the target site atp4-89 in the transfected protoplasts. Gene At1g06580 also alters the editing level in c ...
... proteins in the mapped genomic window into Ler protoplasts shows differential effects. Sequence analysis of the atp4 cDNA shows that gene At1g06140 strongly increases the level of RNA editing at the target site atp4-89 in the transfected protoplasts. Gene At1g06580 also alters the editing level in c ...
Quantitative RT-PCR Platform to Measure Transcript Levels of C and
... reads/ESTs prior to their assembly into transcripts (Mitchell et al. 2007). Another approach is to search ...
... reads/ESTs prior to their assembly into transcripts (Mitchell et al. 2007). Another approach is to search ...
Comparison of conserved structural and regulatory domains within
... band (665 bp), in agreement with sequence data available from GenBank (accession numbers D64000 and D90916 for the two identical rrn operons of this strain). In contrast, three bands (485, 650 and 710 bp) were consistently observed in each of 10 individual PCR amplifications for the filamentous Nost ...
... band (665 bp), in agreement with sequence data available from GenBank (accession numbers D64000 and D90916 for the two identical rrn operons of this strain). In contrast, three bands (485, 650 and 710 bp) were consistently observed in each of 10 individual PCR amplifications for the filamentous Nost ...
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... spliced mRNA into the genome; they are often recognized by the loss of some or all introns relative to other copies of the gene. Unprocessed pseudogenes arise e.g. from duplication of genomic regions. They sometimes contain all exons, but often have suffered deletions and rearrangements. Over time, ...
... spliced mRNA into the genome; they are often recognized by the loss of some or all introns relative to other copies of the gene. Unprocessed pseudogenes arise e.g. from duplication of genomic regions. They sometimes contain all exons, but often have suffered deletions and rearrangements. Over time, ...
MicroRNA Analysis
... assigning official names for novel miRNA genes prior to publication of their discovery ...
... assigning official names for novel miRNA genes prior to publication of their discovery ...
1 Defining the epigenetic mechanism of asymmetric cell division of
... Structure of the S. japonicus var. japonicus mating-type genes Overall, mating-type genes have been conserved across the fission yeast group, but only partial mat2-P and mat3-M sequences for S. japonicus were available from the Broad Institute database (RHIND ET AL. 2011). Thus far, the mat1 locus s ...
... Structure of the S. japonicus var. japonicus mating-type genes Overall, mating-type genes have been conserved across the fission yeast group, but only partial mat2-P and mat3-M sequences for S. japonicus were available from the Broad Institute database (RHIND ET AL. 2011). Thus far, the mat1 locus s ...
Molecular Analysis of the Coprinus cinereus Mating Type A Factor
... 1949). In C. cinereus, some of this polymorphism can be explained by the observations of A factor is made up of at DAY(1 960, 1963b) that the least two closely linked subunits, termed (Y and B. T h e functions of(Y and B appear redundantbecause genetic analysis has shown that an allelic difference a ...
... 1949). In C. cinereus, some of this polymorphism can be explained by the observations of A factor is made up of at DAY(1 960, 1963b) that the least two closely linked subunits, termed (Y and B. T h e functions of(Y and B appear redundantbecause genetic analysis has shown that an allelic difference a ...
Read the Nobel Lecture
... First we needed an assay – a way to detect if telomere elongation was happening. The first assay we tried explored whether a piece of DNA that included a telomere would incorporate DNA precursors more readily than a piece of DNA containing non-telomeric sequences. The idea was that if there was an ...
... First we needed an assay – a way to detect if telomere elongation was happening. The first assay we tried explored whether a piece of DNA that included a telomere would incorporate DNA precursors more readily than a piece of DNA containing non-telomeric sequences. The idea was that if there was an ...
Structural and Functional Studies of Insertion Element IS200
... The nucleotide sequence of the insertion element 15200 has been determined partially, including the junctions between the element and the host chromosome at the insertion site, At most, two bases (A-A) are found repeated at the junctions and could be duplications of host sequences generated by the i ...
... The nucleotide sequence of the insertion element 15200 has been determined partially, including the junctions between the element and the host chromosome at the insertion site, At most, two bases (A-A) are found repeated at the junctions and could be duplications of host sequences generated by the i ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.