neutral theory, inbreeding - Cal State LA
... with recombination rate across Drosophila simulans genome in regions of low recombination, linked loci can’t escape the effects of selection on nearby genes if selection strongly favors “big C” allele of the C gene... ...
... with recombination rate across Drosophila simulans genome in regions of low recombination, linked loci can’t escape the effects of selection on nearby genes if selection strongly favors “big C” allele of the C gene... ...
ParameciumDB - Nucleic Acids Research
... RNA interference (RNAi) by feeding with bacteria that produce double-stranded RNA (9) have become routine laboratory procedures. Paramecium is a privileged model for investigation of nonMendelian heredity and the underlying epigenetic mechanisms. Sonneborn (10) was the first to document cytoplasmic ...
... RNA interference (RNAi) by feeding with bacteria that produce double-stranded RNA (9) have become routine laboratory procedures. Paramecium is a privileged model for investigation of nonMendelian heredity and the underlying epigenetic mechanisms. Sonneborn (10) was the first to document cytoplasmic ...
Deletions, Duplications and Inversions ppt
... The presence of chromosomes with duplications and deletions leads to non-viable gametes If two of the four chromatids are involved in the cross-over then 50% of the gametes will be non-viable ...
... The presence of chromosomes with duplications and deletions leads to non-viable gametes If two of the four chromatids are involved in the cross-over then 50% of the gametes will be non-viable ...
Possible risks of GMO-s
... • The promoter should be inducible rather than constitutive • Selection markers should be removed before cultivation • Prevent large-scale or commercial releases if scientific knowledge exist about possible risks • Post-release monitoring to detect environmental risks • Thorough risk-assesment, expe ...
... • The promoter should be inducible rather than constitutive • Selection markers should be removed before cultivation • Prevent large-scale or commercial releases if scientific knowledge exist about possible risks • Post-release monitoring to detect environmental risks • Thorough risk-assesment, expe ...
Sxl - Kodomo
... All numerator genes have other functions in development that clearly predate their roles in sex determination: segmentation (runt), neurogenesis (sc, da, dpn), signaling (upd) ...
... All numerator genes have other functions in development that clearly predate their roles in sex determination: segmentation (runt), neurogenesis (sc, da, dpn), signaling (upd) ...
PowerPoint-Präsentation
... geographic adaptability, barley is particularly noted for its tolerance to cold, drought, alkali, and salinity. The barley genome - with 5.3 billion letters of genetic code - is one of the largest in cereal crops measuring about twice the size of the human genome. Barley is a true diploid, thus, it ...
... geographic adaptability, barley is particularly noted for its tolerance to cold, drought, alkali, and salinity. The barley genome - with 5.3 billion letters of genetic code - is one of the largest in cereal crops measuring about twice the size of the human genome. Barley is a true diploid, thus, it ...
The diverse origins of the human gene pool
... at least a million years ago from the human lineage. In addition, gene flow from Denisovans to people in mainland Asia is likely to have occurred, and unpublished work shows that early modern humans mixed with Neanderthals when they arrived in Europe (Q. Fu, M. Hajdinjak and S.P., unpublished observ ...
... at least a million years ago from the human lineage. In addition, gene flow from Denisovans to people in mainland Asia is likely to have occurred, and unpublished work shows that early modern humans mixed with Neanderthals when they arrived in Europe (Q. Fu, M. Hajdinjak and S.P., unpublished observ ...
n - 1
... a population is polymorphic if it has more than one allele. Polymorphic loci are usually defined as having the most frequent allele at a frequency of less than 0.99 or less then 0.95. Monomorphic: Lacking genetic diversity. A locus in a population is monomorphic if it has only one allele present in ...
... a population is polymorphic if it has more than one allele. Polymorphic loci are usually defined as having the most frequent allele at a frequency of less than 0.99 or less then 0.95. Monomorphic: Lacking genetic diversity. A locus in a population is monomorphic if it has only one allele present in ...
Document
... 1. Genetics is the study of biological _________________ patterns and variation in organisms. 2. A man named Gregor ___________________ did early work that is the basis for much of our current understanding of genetics. 3. Mendel’s views on inheritance differed from the views of many scientists of h ...
... 1. Genetics is the study of biological _________________ patterns and variation in organisms. 2. A man named Gregor ___________________ did early work that is the basis for much of our current understanding of genetics. 3. Mendel’s views on inheritance differed from the views of many scientists of h ...
Briefing - Emerging Technology
... the random insertion of genes into plant genomes seen with traditional genetic engineering, the potential for unforeseen genomic interactions, genomic irregularities and unintended biochemical alterations still remains ...
... the random insertion of genes into plant genomes seen with traditional genetic engineering, the potential for unforeseen genomic interactions, genomic irregularities and unintended biochemical alterations still remains ...
Patient Informed Consent Form for Genetic Testing
... Gene product: The biochemical material, either RNA or protein, resulting from expression of a gene. The amount of gene product is used to measure how active a gene is; abnormal amounts can be correlated with disease causing alleles. Genome: All the genetic material in the chromosomes of a human. Mut ...
... Gene product: The biochemical material, either RNA or protein, resulting from expression of a gene. The amount of gene product is used to measure how active a gene is; abnormal amounts can be correlated with disease causing alleles. Genome: All the genetic material in the chromosomes of a human. Mut ...
Gene Section FOXC1 (forkhead box C1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... upstream of the FOXC1 forkhead domain. The team also identified a C-to-T transition within the forkhead domain, causing a ser131-to-leu (S131L) amino acid substitution. The Nishimura team found a C-to-G transversion within the forkhead domain. This change resulted in an ile126-to-met (I126M) amino a ...
... upstream of the FOXC1 forkhead domain. The team also identified a C-to-T transition within the forkhead domain, causing a ser131-to-leu (S131L) amino acid substitution. The Nishimura team found a C-to-G transversion within the forkhead domain. This change resulted in an ile126-to-met (I126M) amino a ...
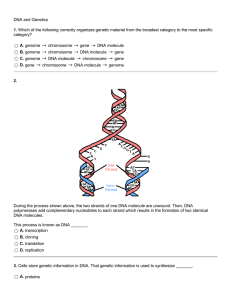
DNA and Genetics 1. Which of the following correctly organizes
... nitrogen bases between the old DNA molecules two strands. Proteins hold the two strands of the old DNA apart and prevent them from reuniting while DNA polymerases add nucleotides to the exposed nitrogen bases of the old DNA and check the new DNA molecule for errors. 24. -25. The Golgi apparatus is i ...
... nitrogen bases between the old DNA molecules two strands. Proteins hold the two strands of the old DNA apart and prevent them from reuniting while DNA polymerases add nucleotides to the exposed nitrogen bases of the old DNA and check the new DNA molecule for errors. 24. -25. The Golgi apparatus is i ...
GENETIC BASICS OF VARIATIONS IN BACTERIA
... number of consequences. In coding regions they may alter an amino acid in a polypeptide. The effect may be deleterious (inactivation or lower activity) or beneficial (enhanced or new activity). Changes in the targets for several antibiotics can result in functional proteins that are no longer sensit ...
... number of consequences. In coding regions they may alter an amino acid in a polypeptide. The effect may be deleterious (inactivation or lower activity) or beneficial (enhanced or new activity). Changes in the targets for several antibiotics can result in functional proteins that are no longer sensit ...
The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... Sturtevant used the testcross design to map the relative positions of three fruit fly genes: body color (b), wing size (vg), and eye color (cn). o Cinnabar (cn), one of many Drosophila genes affecting eye color, results in a bright red eye. o The recombination frequency between cn and b is 9%. o The ...
... Sturtevant used the testcross design to map the relative positions of three fruit fly genes: body color (b), wing size (vg), and eye color (cn). o Cinnabar (cn), one of many Drosophila genes affecting eye color, results in a bright red eye. o The recombination frequency between cn and b is 9%. o The ...
Lacroix_Insyght navigating amongst abundant - Migale
... neighbourhood conservation and phylogenetic profiles provide important clues to identify orthologous genes or infer gene functions (5,6). Conservation in the ordering of genes can help in assigning functions for a train of genes at once or providing clues for hypothetical proteins (7,8). Moreover, s ...
... neighbourhood conservation and phylogenetic profiles provide important clues to identify orthologous genes or infer gene functions (5,6). Conservation in the ordering of genes can help in assigning functions for a train of genes at once or providing clues for hypothetical proteins (7,8). Moreover, s ...
compEpiTools - Bioconductor
... Most informative GO terms to keep are defined here as those terms for which an enriched children term mapping to a very similar set of genes has not been also identified. If that happens, the children term is believed to contain most of the information, and typically better specifies the enrichmed G ...
... Most informative GO terms to keep are defined here as those terms for which an enriched children term mapping to a very similar set of genes has not been also identified. If that happens, the children term is believed to contain most of the information, and typically better specifies the enrichmed G ...
Document
... Definitions: Any two identical copies of an allele l are said to be identical by state (IBS). If these alleles are inherited from the same individual then they are also identical by descent (IBD). Clearly, IBD implies IBS but not vice versa. ...
... Definitions: Any two identical copies of an allele l are said to be identical by state (IBS). If these alleles are inherited from the same individual then they are also identical by descent (IBD). Clearly, IBD implies IBS but not vice versa. ...
Author comments - Springer Static Content Server
... 4) Adiponectin is an obvious candidate gene for the linkage peak on chromosome 3q. The authors should screen the gene for mutations to evaluate if the linkage is due to mutations identified in the gene; Guo X reported that mutations in the adiponectin gene were not responsible for the linkage observ ...
... 4) Adiponectin is an obvious candidate gene for the linkage peak on chromosome 3q. The authors should screen the gene for mutations to evaluate if the linkage is due to mutations identified in the gene; Guo X reported that mutations in the adiponectin gene were not responsible for the linkage observ ...
e. dominant relationships
... The heterozygote is intermediate between the phenotypes of the two homozygotes, and not exactly like either one of them. Snap dragons r=red, w=white Rr x ww rw = pink rw x rw = 1 red, 2 pink, 1 white Sometimes the phenotype of the heterozygote is not simply a blending o compromise between the two ...
... The heterozygote is intermediate between the phenotypes of the two homozygotes, and not exactly like either one of them. Snap dragons r=red, w=white Rr x ww rw = pink rw x rw = 1 red, 2 pink, 1 white Sometimes the phenotype of the heterozygote is not simply a blending o compromise between the two ...
File
... 4. A cloned yeast gene of unknown function was subjected to in vitro mutagenesis in which a serine codon was replaced by arginine at amino acid position 10 in the open reading frame. This gene was used to replace the resident wild-type gene. The resulting cell still showed a wild-type phenotype. Why ...
... 4. A cloned yeast gene of unknown function was subjected to in vitro mutagenesis in which a serine codon was replaced by arginine at amino acid position 10 in the open reading frame. This gene was used to replace the resident wild-type gene. The resulting cell still showed a wild-type phenotype. Why ...
UNIT SIX: MOLECULAR GENETICS AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
... d. Nucleotides form long chains, with the phosphate group of one nucleotide bonding to the deoxyribose sugar of the adjacent nucleotide. e. The amount of adenine always equals the amount of thymine, and the amount of cytosine is always equal to the amount of guanine: Chargoff’s rule (see page 329, F ...
... d. Nucleotides form long chains, with the phosphate group of one nucleotide bonding to the deoxyribose sugar of the adjacent nucleotide. e. The amount of adenine always equals the amount of thymine, and the amount of cytosine is always equal to the amount of guanine: Chargoff’s rule (see page 329, F ...
Biology 1060 Chapter 17 - College of Southern Maryland
... Describe the three stages of transcription Discuss the factors important in RNA polymerase binding and initiation of transcription Discuss how the cell increases the efficiency of transcription to mRNA Describe termination in prokaryotes and eukaryotes ...
... Describe the three stages of transcription Discuss the factors important in RNA polymerase binding and initiation of transcription Discuss how the cell increases the efficiency of transcription to mRNA Describe termination in prokaryotes and eukaryotes ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.