Document
... Study Guide B continued Refer to your cell sketch in the last box on the previous page. Also refer to Figure 2.3 if necessary. 1. In the first box below, show what your cell would look like at the end of meiosis I. Remember, the result will be two cells that have one duplicated chromosome from each ...
... Study Guide B continued Refer to your cell sketch in the last box on the previous page. Also refer to Figure 2.3 if necessary. 1. In the first box below, show what your cell would look like at the end of meiosis I. Remember, the result will be two cells that have one duplicated chromosome from each ...
Gene Section CLTC (clathrin heavy polypeptide) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Disease ALCL are high grade non Hodgkin lymphomas; ALK+ ALCL are ALCL where ALK is involved in a fusion gene; ALK+ ALCL represent 50 to 60% of ALCL cases (they are CD30+, ALK+); belong to the "cytoplasmic ALK+" subset. Prognosis Althouth presenting as a high grade tumour, a 80% five yr survival is a ...
... Disease ALCL are high grade non Hodgkin lymphomas; ALK+ ALCL are ALCL where ALK is involved in a fusion gene; ALK+ ALCL represent 50 to 60% of ALCL cases (they are CD30+, ALK+); belong to the "cytoplasmic ALK+" subset. Prognosis Althouth presenting as a high grade tumour, a 80% five yr survival is a ...
Simulating cellular dynamics through a coupled transcription
... The dynamics of transcription and translation are accounted for by computing the temporal evolution of the populations of DNA, RNA, proteins and their various complexes within the cell. The model reads and transfers nucleotide and amino acid sequences through a polymerization kinetic model. The rapi ...
... The dynamics of transcription and translation are accounted for by computing the temporal evolution of the populations of DNA, RNA, proteins and their various complexes within the cell. The model reads and transfers nucleotide and amino acid sequences through a polymerization kinetic model. The rapi ...
Evidence for massive gene exchange between archaeal and
... zinc-finger-containing nucleic acidbinding protein; the remaining genes encode uncharacterized proteins, most of which are conserved in archaea and Aquifex only. ...
... zinc-finger-containing nucleic acidbinding protein; the remaining genes encode uncharacterized proteins, most of which are conserved in archaea and Aquifex only. ...
Evidence for association between single nucleotide polymorphisms
... replaced by ‘‘C’’ in the Myb or c-Myb binding target sequence, it results in an increase in the efficiency of transcription. Although this hypothesis can be used to explain the higher expression of TCP1 in the hippocampal tissue of patients with schizophrenia, this needs to be confirmed further. The ...
... replaced by ‘‘C’’ in the Myb or c-Myb binding target sequence, it results in an increase in the efficiency of transcription. Although this hypothesis can be used to explain the higher expression of TCP1 in the hippocampal tissue of patients with schizophrenia, this needs to be confirmed further. The ...
Geometrical ordering of DNA in bacteria
... domains to specific cellular positions has a strong influence on the spatial arrangement of the chromosome in the cell. In particular, we found that positioning of ori and ter to opposite cell poles in C. crescentus gives rise to the striking linear correlation found in reference 1. For E. coli we m ...
... domains to specific cellular positions has a strong influence on the spatial arrangement of the chromosome in the cell. In particular, we found that positioning of ori and ter to opposite cell poles in C. crescentus gives rise to the striking linear correlation found in reference 1. For E. coli we m ...
PATTERNS OF INHERITANCE
... inheritance of disorders within families: – Genetic counseling: Advice to be given to members of a family regarding the susceptibility of their developing the disease ...
... inheritance of disorders within families: – Genetic counseling: Advice to be given to members of a family regarding the susceptibility of their developing the disease ...
Selick, H.E., Barry, J., Cha, T. - Bruce Alberts
... the 44/62 complex. This interaction can result in a dramat ic increase in both the rate and processivity of DNA synthe sis by the polymerase molecule (l2-l5) The activity of the accessory proteins is most consistent with their format ion of a complex with the polymerase, which acts as a tt sliding c ...
... the 44/62 complex. This interaction can result in a dramat ic increase in both the rate and processivity of DNA synthe sis by the polymerase molecule (l2-l5) The activity of the accessory proteins is most consistent with their format ion of a complex with the polymerase, which acts as a tt sliding c ...
Use of Gene Replacement Transformation to Elucidate
... to exist in the qa genecluster. T h e DNA binding domain of the activator protein is located in the Nterminal183amino acids. Several mutations have been obtained in the qa-IF gene. T h e resulting mutants are recessive and noninducible which has lead to the hypothesis that they produce defective act ...
... to exist in the qa genecluster. T h e DNA binding domain of the activator protein is located in the Nterminal183amino acids. Several mutations have been obtained in the qa-IF gene. T h e resulting mutants are recessive and noninducible which has lead to the hypothesis that they produce defective act ...
Gene Regulation Notes
... Concept 18.2: Eukaryotic gene expression can be regulated at any stage • Points at which gene expression can be regulated: chromatin mod., transcription, RNA processing, transport to cytoplasm, translation, protein processing, transport to cell destination • In multicellular organisms gene expressi ...
... Concept 18.2: Eukaryotic gene expression can be regulated at any stage • Points at which gene expression can be regulated: chromatin mod., transcription, RNA processing, transport to cytoplasm, translation, protein processing, transport to cell destination • In multicellular organisms gene expressi ...
Modified Mendelian ratios
... Duplicate gene action • Spring growth is the result of duplicate gene action between two independent genes S and H • Spring growth: S_; H_ , S_; hh , ss; H_ • Winter growth: ss;hh • In duplicate gene action the dominant phenotype is evident when at least one dominant allele is present at each locus, ...
... Duplicate gene action • Spring growth is the result of duplicate gene action between two independent genes S and H • Spring growth: S_; H_ , S_; hh , ss; H_ • Winter growth: ss;hh • In duplicate gene action the dominant phenotype is evident when at least one dominant allele is present at each locus, ...
FAQs (frequently asked questions) Q.1 What are plasmids? Ans
... PstI, PvuI and Sca l lie within the β-lactamase gene. Cloning of a DNA fragment into any of these 11 sites results in the insertional inactivation of either one of the antibiotic resistance markers. ...
... PstI, PvuI and Sca l lie within the β-lactamase gene. Cloning of a DNA fragment into any of these 11 sites results in the insertional inactivation of either one of the antibiotic resistance markers. ...
IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE
... polymorphisms linked to coding region alleles using amplified DNA with a primer pair spanning a non-coding DNA region during the term of the '179 Patent in the provision of its HLA typing services. The provision of these testing services in this manner utilizes the invention as claimed in the '179 P ...
... polymorphisms linked to coding region alleles using amplified DNA with a primer pair spanning a non-coding DNA region during the term of the '179 Patent in the provision of its HLA typing services. The provision of these testing services in this manner utilizes the invention as claimed in the '179 P ...
Exploration 13 - Warner Pacific College
... If the table above is confusing to you, try substituting values for p and q. For example, instead of p sperm/ova with the A allele and q with the a allele, substitute 0.7 sperm/ova with A and 0.3 with a. Then, what percent of offspring with the genotype aa would you expect? The generation offspring ...
... If the table above is confusing to you, try substituting values for p and q. For example, instead of p sperm/ova with the A allele and q with the a allele, substitute 0.7 sperm/ova with A and 0.3 with a. Then, what percent of offspring with the genotype aa would you expect? The generation offspring ...
GENETICS TEST IV - Daytona State College
... • The TATA box is a core promoter element that binds the TATAbinding protein (TBP) of transcription factor TFIID and determines the start site of transcription ...
... • The TATA box is a core promoter element that binds the TATAbinding protein (TBP) of transcription factor TFIID and determines the start site of transcription ...
Similarity
... were known, they were able to determine stretches of amino acids that could serve to form an a-helix or a bsheet. These amino acids are called helix formers or sheet formers and can have different strengths for forming their structures. Once these nucleation sites are determined, adjacent amino acid ...
... were known, they were able to determine stretches of amino acids that could serve to form an a-helix or a bsheet. These amino acids are called helix formers or sheet formers and can have different strengths for forming their structures. Once these nucleation sites are determined, adjacent amino acid ...
Big Bird Little Bird
... highlighted in those notes: Dominant gene – a gene that produces the same phenotypic effect whether inherited with a homozygous or heterozygous allele. Recessive gene - a gene that is expressed only when the determining gene is present in the homozygous condition. ...
... highlighted in those notes: Dominant gene – a gene that produces the same phenotypic effect whether inherited with a homozygous or heterozygous allele. Recessive gene - a gene that is expressed only when the determining gene is present in the homozygous condition. ...
Name
... The genetic information (DNA) in our cells plays a major role in how our body works. Spelling mistakes often happen when this information is being transcribed. When these spelling mistakes occur on uncoded genes, there aren't any consequences. In a few rare cases, however, a spelling mistake – or mu ...
... The genetic information (DNA) in our cells plays a major role in how our body works. Spelling mistakes often happen when this information is being transcribed. When these spelling mistakes occur on uncoded genes, there aren't any consequences. In a few rare cases, however, a spelling mistake – or mu ...
Phylogenetic, amino acid content and indel analyses
... sequences encoding conserved amino acid sequences in the rpoB genes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (EMBL accession no. U12205), Mycobacterium leprae (Z14314), Mycobacterium smegmatis (U24494), Bacillus subtilis (L24376) and Staphylococcus aureus (X64172) and the rplL genes of Escherichia coli (V00339 ...
... sequences encoding conserved amino acid sequences in the rpoB genes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (EMBL accession no. U12205), Mycobacterium leprae (Z14314), Mycobacterium smegmatis (U24494), Bacillus subtilis (L24376) and Staphylococcus aureus (X64172) and the rplL genes of Escherichia coli (V00339 ...
Author`s personal copy
... Some bacteria are able to take up DNA from their general environment (transformation), including DNA that encodes resistance determinants. Resistance genes are rarely found in bacteriophages, but they can move DNA between cells (transduction), and their mechanisms for integration into host chromosom ...
... Some bacteria are able to take up DNA from their general environment (transformation), including DNA that encodes resistance determinants. Resistance genes are rarely found in bacteriophages, but they can move DNA between cells (transduction), and their mechanisms for integration into host chromosom ...
Chapter 11 PowerPoint
... • In his experiments, Mendel used pollen from the flowers of purebred tall plants to pollinate by hand the flowers of purebred short plants. • This process is called cross-pollination. ...
... • In his experiments, Mendel used pollen from the flowers of purebred tall plants to pollinate by hand the flowers of purebred short plants. • This process is called cross-pollination. ...
DNA Methylation, Imprinting and X
... • The imprinting mechanism acts in cis • Imprinted genes are clustered and are controlled by a single imprinting control region (ICR) • The ICR acquires an imprint in one gamete (often DNA methylation) • Imprinted gene clusters contain at least 1 long ncRNA ...
... • The imprinting mechanism acts in cis • Imprinted genes are clustered and are controlled by a single imprinting control region (ICR) • The ICR acquires an imprint in one gamete (often DNA methylation) • Imprinted gene clusters contain at least 1 long ncRNA ...
View Poster - Technology Networks
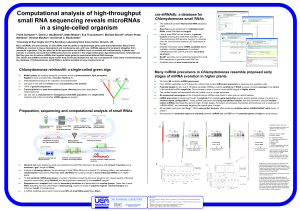
... We found 68 candidate miRNA precursors Four miRNA candidates out of 8 tested by northern blot showed differential expression in gametes and vegetative cells Potential targets for four out of 18 tested candidate miRNAs could be verified by 5’ RACE analysis, showing cleavage in the centre of the predi ...
... We found 68 candidate miRNA precursors Four miRNA candidates out of 8 tested by northern blot showed differential expression in gametes and vegetative cells Potential targets for four out of 18 tested candidate miRNAs could be verified by 5’ RACE analysis, showing cleavage in the centre of the predi ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.