An homologous pair of chromosomes…
... between pairs of alleles long before the details of meiosis were known. Where Mendel states that pairs of alleles of a gene separate independently during gamete production, we can now attribute this to random orientation of chromosomes during metaphase I. Mendel made this deduction when working with ...
... between pairs of alleles long before the details of meiosis were known. Where Mendel states that pairs of alleles of a gene separate independently during gamete production, we can now attribute this to random orientation of chromosomes during metaphase I. Mendel made this deduction when working with ...
Diamond Blackfan Anemia, Genetics, and You
... to the children of the affected person. In fewer than half of families, more than one family member is affected. For example, two or more siblings or both a parent and a child may have DBA. Signs of the disorder can be very minor, and some people have no signs at all. In a family with one of the kno ...
... to the children of the affected person. In fewer than half of families, more than one family member is affected. For example, two or more siblings or both a parent and a child may have DBA. Signs of the disorder can be very minor, and some people have no signs at all. In a family with one of the kno ...
AP Biology Unit 5 Packet-- Classical Genetics/Heredity
... Classical Genetics (Mendelian Genetics) Gregor Mendel: The Father of Genetics What is genetics? In its simplest form, genetics is the study of heredity. It explains how certain characteristics are passed on from parents to children. Much of what we know about genetics was discovered by the monk Greg ...
... Classical Genetics (Mendelian Genetics) Gregor Mendel: The Father of Genetics What is genetics? In its simplest form, genetics is the study of heredity. It explains how certain characteristics are passed on from parents to children. Much of what we know about genetics was discovered by the monk Greg ...
Lecture Notes in Population Genetics
... animal have a number of pairs of long linear molecules. In either case, the chromosome or chromosomes can be thought of as a string of letters from the alphabet T, C, A, G, where each letter corresponds to a specific nucleotide. From this point of view, a mouse is the same as a tomato to a geneticis ...
... animal have a number of pairs of long linear molecules. In either case, the chromosome or chromosomes can be thought of as a string of letters from the alphabet T, C, A, G, where each letter corresponds to a specific nucleotide. From this point of view, a mouse is the same as a tomato to a geneticis ...
Function of lanI in regulation of landomycin A biosynthesis in
... The 5⬘ terminal 916 bp fragment of lanI gene including its promoter and region encoding Wrst 196 amino acids and 3⬘ terminal region of lndI (317 bp fragment, including region coding for last 65 amino acid residues of LndI protein) were ampliWed with the LaF1/R1 and LnIF2/R2 primer sets, respectively ...
... The 5⬘ terminal 916 bp fragment of lanI gene including its promoter and region encoding Wrst 196 amino acids and 3⬘ terminal region of lndI (317 bp fragment, including region coding for last 65 amino acid residues of LndI protein) were ampliWed with the LaF1/R1 and LnIF2/R2 primer sets, respectively ...
S3 Text.
... Comparing the main results obtained from our expression variability analysis with those obtained with CV on the human embryo data set. In order to investigate the impact of the statistic used to study expression variability, we repeated our analyses using the CV to see whether we would obtain simila ...
... Comparing the main results obtained from our expression variability analysis with those obtained with CV on the human embryo data set. In order to investigate the impact of the statistic used to study expression variability, we repeated our analyses using the CV to see whether we would obtain simila ...
Biology 40S Genetics Booklet (StudentsCopy2)
... Gregor Mendel used pea plants to show how simple traits are passed from one generation to the next. He used purebred plants (where the offspring have all the same traits as their parents). He controlled pollination so that no other plants could introduce new genotypes. We can apply Mendel's laws to ...
... Gregor Mendel used pea plants to show how simple traits are passed from one generation to the next. He used purebred plants (where the offspring have all the same traits as their parents). He controlled pollination so that no other plants could introduce new genotypes. We can apply Mendel's laws to ...
Insertion of liver enriched transcription
... could be utilized in medicine for gene therapy. At present the usual method for selection of a tissue-specific promoter is to identify a gene, which is expressed at unusually high level in the target tissue, and then to use the promoter for this gene to drive expression of another therapeutic gene i ...
... could be utilized in medicine for gene therapy. At present the usual method for selection of a tissue-specific promoter is to identify a gene, which is expressed at unusually high level in the target tissue, and then to use the promoter for this gene to drive expression of another therapeutic gene i ...
PowerPoint 簡報
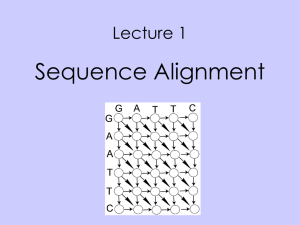
... Sequence alignment: why? • Early in the days of protein and gene sequence analysis, it was discovered that the sequences from related proteins or genes were similar, in the sense that one could align the sequences so that many corresponding residues match. • This discovery was very important: stron ...
... Sequence alignment: why? • Early in the days of protein and gene sequence analysis, it was discovered that the sequences from related proteins or genes were similar, in the sense that one could align the sequences so that many corresponding residues match. • This discovery was very important: stron ...
11.0 RECOMBINANT DNA/RNA
... appropriate agency (including but not limited to the NIH-OBA and CDC-Select Agent Program) has occurred within the required time frame. Environmental Health and Safety (EHS) EHS Biological and Chemical Safety Program (EHS-B&C) is responsible for auditing all research and clinical laboratories on cam ...
... appropriate agency (including but not limited to the NIH-OBA and CDC-Select Agent Program) has occurred within the required time frame. Environmental Health and Safety (EHS) EHS Biological and Chemical Safety Program (EHS-B&C) is responsible for auditing all research and clinical laboratories on cam ...
DNA Replication
... 2. A free 3'OH group is required for replication, but when the two chains separate no group of that nature exists. RNA primers are synthesized, and the free 3'OH of the primer is used to begin replication. 3. The replication fork moves in one direction, but DNA replication only goes in the 5' to 3' ...
... 2. A free 3'OH group is required for replication, but when the two chains separate no group of that nature exists. RNA primers are synthesized, and the free 3'OH of the primer is used to begin replication. 3. The replication fork moves in one direction, but DNA replication only goes in the 5' to 3' ...
Cells, Development, Chromosomes
... DNA wrapped 1 3/4 times around a core of 8 histone proteins (small and very conserved in evolution). A string of beads. – Modifications of the histones, such as adding acetyl or phosphate groups, affects how tightly condensed the chromatin is, which affects whether it can be transcribed or not. ...
... DNA wrapped 1 3/4 times around a core of 8 histone proteins (small and very conserved in evolution). A string of beads. – Modifications of the histones, such as adding acetyl or phosphate groups, affects how tightly condensed the chromatin is, which affects whether it can be transcribed or not. ...
Nucleotide sequence changes in the MSX1 and IRF6 genes in
... TBX22, PVRL1, etc.) [1], which have now been shown to contribute a major genetic effect on the etiology of syndromic OFC. Recent findings suggest that at least some of such genes (MSX1, IRF6, PVRL1, and TBX22 in the first place [14] can be used to demonstrate a significant overlap between syndromic ...
... TBX22, PVRL1, etc.) [1], which have now been shown to contribute a major genetic effect on the etiology of syndromic OFC. Recent findings suggest that at least some of such genes (MSX1, IRF6, PVRL1, and TBX22 in the first place [14] can be used to demonstrate a significant overlap between syndromic ...
Importance of Genetic Studies in Consanguineous Populations for
... Consanguineous offspring have elevated levels of homozygosity. Autozygous stretches within their genome are likely to harbour loss of function (LoF) mutations which will lead to complete inactivation or dysfunction of genes. Studying consanguineous offspring with clinical phenotypes has been very us ...
... Consanguineous offspring have elevated levels of homozygosity. Autozygous stretches within their genome are likely to harbour loss of function (LoF) mutations which will lead to complete inactivation or dysfunction of genes. Studying consanguineous offspring with clinical phenotypes has been very us ...
Characterization of the neurohypophysial hormone gene loci in
... Background: Vasopressin and oxytocin are mammalian neurohypophysial hormones with distinct functions. Vasopressin is involved mainly in osmoregulation and oxytocin is involved primarily in parturition and lactation. Jawed vertebrates contain at least one homolog each of vasopressin and oxytocin, whe ...
... Background: Vasopressin and oxytocin are mammalian neurohypophysial hormones with distinct functions. Vasopressin is involved mainly in osmoregulation and oxytocin is involved primarily in parturition and lactation. Jawed vertebrates contain at least one homolog each of vasopressin and oxytocin, whe ...
Lectures 7 & 8 The Genetic Basis of Evolution
... Darwin on Selection In 1859 Darwin rocked the foundations of modern science with the publication of his seminal work “On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection” “When on board H.M.S. “Beagle”, as a naturalist, I was much struck with certain facts in the distribution of the inhabitants ...
... Darwin on Selection In 1859 Darwin rocked the foundations of modern science with the publication of his seminal work “On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection” “When on board H.M.S. “Beagle”, as a naturalist, I was much struck with certain facts in the distribution of the inhabitants ...
2. - Dickinson ISD
... So, what were the results? Did they have a mixture of all the traits? NO, all the hybrids had the characteristics of ...
... So, what were the results? Did they have a mixture of all the traits? NO, all the hybrids had the characteristics of ...
PTC Genetics Lab Student Worksheet
... time was that traits were a result of parental “essences” mixing together, rather like blending yellow and red paint to get orange. Mendel believed heredity was the result of distinct units of inheritance, and every individual unit (gene) acts independently in one’s genome. Mendel thought that all t ...
... time was that traits were a result of parental “essences” mixing together, rather like blending yellow and red paint to get orange. Mendel believed heredity was the result of distinct units of inheritance, and every individual unit (gene) acts independently in one’s genome. Mendel thought that all t ...
ecify proteins via transcription and translation
... genes and enzymes came a few years later, when Beadle and Edward Tatum began working with a bread mold, Neurospora crassa. Using a treatment shown in the 1920s to cause genetic changes, they bombarded Neurospora with X-rays and then looked among the survivors for mutants that differed in their nutri ...
... genes and enzymes came a few years later, when Beadle and Edward Tatum began working with a bread mold, Neurospora crassa. Using a treatment shown in the 1920s to cause genetic changes, they bombarded Neurospora with X-rays and then looked among the survivors for mutants that differed in their nutri ...
S1 Supporting Information
... The amplified 5.1 kb fragment was BglII digested and ligated with the 3.4 kb pyrG fragment to give plasmid pMAT768. A 5.5 kb replacement fragment harboring the pyrG gene flanked by 1.1 kb and 1.0 kb of sequences adjacent to 136157 was released from plasmid pMAT768 by PvuII digestion, amplified with ...
... The amplified 5.1 kb fragment was BglII digested and ligated with the 3.4 kb pyrG fragment to give plasmid pMAT768. A 5.5 kb replacement fragment harboring the pyrG gene flanked by 1.1 kb and 1.0 kb of sequences adjacent to 136157 was released from plasmid pMAT768 by PvuII digestion, amplified with ...
Acquisition of 1,000 eubacterial genes physiologically transformed a
... lineage, 162 of which (15%) have been retained in all 10 haloarchaeans sampled. The Ms, Mc, and Mm lineages have—like the haloarchaea—independently acquired hundreds of eubacterial genes, but the crucial observation is that they have remained strict anaerobes, and they have furthermore remained obli ...
... lineage, 162 of which (15%) have been retained in all 10 haloarchaeans sampled. The Ms, Mc, and Mm lineages have—like the haloarchaea—independently acquired hundreds of eubacterial genes, but the crucial observation is that they have remained strict anaerobes, and they have furthermore remained obli ...
Document
... Study Guide B continued Refer to your cell sketch in the last box on the previous page. Also refer to Figure 2.3 if necessary. 1. In the first box below, show what your cell would look like at the end of meiosis I. Remember, the result will be two cells that have one duplicated chromosome from each ...
... Study Guide B continued Refer to your cell sketch in the last box on the previous page. Also refer to Figure 2.3 if necessary. 1. In the first box below, show what your cell would look like at the end of meiosis I. Remember, the result will be two cells that have one duplicated chromosome from each ...
Evidence for massive gene exchange between archaeal and
... zinc-finger-containing nucleic acidbinding protein; the remaining genes encode uncharacterized proteins, most of which are conserved in archaea and Aquifex only. ...
... zinc-finger-containing nucleic acidbinding protein; the remaining genes encode uncharacterized proteins, most of which are conserved in archaea and Aquifex only. ...
Leukaemia Section t(2 14)(p13-16 32)
... myeloid leukemias in mice and lymphoid malignancies in humans; the conserved N-terminus of BCL11A. deregulated expression of BCL11A may play a major role in the pathogenesis; gains and amplifications of the region of chromosome 2p13-16 have been reported in B-cell malignancies, REL, a NF-kappaB gene ...
... myeloid leukemias in mice and lymphoid malignancies in humans; the conserved N-terminus of BCL11A. deregulated expression of BCL11A may play a major role in the pathogenesis; gains and amplifications of the region of chromosome 2p13-16 have been reported in B-cell malignancies, REL, a NF-kappaB gene ...
Evidence for association between single nucleotide polymorphisms
... replaced by ‘‘C’’ in the Myb or c-Myb binding target sequence, it results in an increase in the efficiency of transcription. Although this hypothesis can be used to explain the higher expression of TCP1 in the hippocampal tissue of patients with schizophrenia, this needs to be confirmed further. The ...
... replaced by ‘‘C’’ in the Myb or c-Myb binding target sequence, it results in an increase in the efficiency of transcription. Although this hypothesis can be used to explain the higher expression of TCP1 in the hippocampal tissue of patients with schizophrenia, this needs to be confirmed further. The ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.