Chapter 1 - Bioinformatics Research Center
... markers is expressed as units of recombination. The genetic markers are most often physical attributes of the DNA (such as sequence tags, simple repeats, or restriction enzyme polymorphisms), but may include phenotypes associated with Mendelian loci. In diploid organisms, genetic maps are typically ...
... markers is expressed as units of recombination. The genetic markers are most often physical attributes of the DNA (such as sequence tags, simple repeats, or restriction enzyme polymorphisms), but may include phenotypes associated with Mendelian loci. In diploid organisms, genetic maps are typically ...
A Simple Mouthwash Method for Obtaining Genomic DNA in
... (finger stick, cheek scrapings or brushes, and saline rinse) or do not yield an adequate amount (urine, hair roots, and saliva) or quality (paraffin blocks) of DNA. Also, some of these methods require the samples to be stored in a preservative solution that is toxic, which makes it problematic for u ...
... (finger stick, cheek scrapings or brushes, and saline rinse) or do not yield an adequate amount (urine, hair roots, and saliva) or quality (paraffin blocks) of DNA. Also, some of these methods require the samples to be stored in a preservative solution that is toxic, which makes it problematic for u ...
Bio 115 Lab 7: Probability and Genetics
... chromosome of a homologous pair comes from the mother, and one comes from the father. In humans, there are 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes. We each received chromosome numbers 1 through 23 from our mother, and 1 through 23 from our father. The 2 chromosomes designated number 1 are a homologous pa ...
... chromosome of a homologous pair comes from the mother, and one comes from the father. In humans, there are 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes. We each received chromosome numbers 1 through 23 from our mother, and 1 through 23 from our father. The 2 chromosomes designated number 1 are a homologous pa ...
On epistasis: why it is unimportant in polygenic directional selection References
... Students of development and evo-devo, as well as some human geneticists, have paid particular interest to interactions. For those in these fields, epistasis is an interesting phenomenon on its own and studying it gives deeper insights into developmental and evolutionary processes. Ultimately one wan ...
... Students of development and evo-devo, as well as some human geneticists, have paid particular interest to interactions. For those in these fields, epistasis is an interesting phenomenon on its own and studying it gives deeper insights into developmental and evolutionary processes. Ultimately one wan ...
7. molecular genetics.
... Each time a somatic cell divides, two daughter cells are produced. Each of these cells receives an identical copy of the parent cell´s genetic information. ...
... Each time a somatic cell divides, two daughter cells are produced. Each of these cells receives an identical copy of the parent cell´s genetic information. ...
Translation Section 1 From Genes to Proteins Chapter 10
... • Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are able to regulate which genes are expressed and which are not, depending on the cell’s needs. • The piece of DNA that overlaps the promoter site and serves as the on-off switch is called an operator. ...
... • Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are able to regulate which genes are expressed and which are not, depending on the cell’s needs. • The piece of DNA that overlaps the promoter site and serves as the on-off switch is called an operator. ...
SERIES: ‘‘GENETICS OF ASTHMA AND COPD IN THE POSTGENOME ERA’’
... comparing the mathematical distribution of alleles in the population of interest and the population from which its founders are likely to have emigrated [1]. Genetic drift, however, is caused by the nature of sexual reproduction, in which each individual allele in a parent has a 50% chance of being ...
... comparing the mathematical distribution of alleles in the population of interest and the population from which its founders are likely to have emigrated [1]. Genetic drift, however, is caused by the nature of sexual reproduction, in which each individual allele in a parent has a 50% chance of being ...
We`re on the brink of a DNA revolution – where your genetic code
... what does it mean? “It means you’ve got a one in four chance of getting Alzheimer’s by your late 80s,” says Dr Jenkins in my consultation. “The average probability is one in eight.” Other conditions, such as the risk of high blood pressure, were also in the moderate (orange) zone of the spectrum – s ...
... what does it mean? “It means you’ve got a one in four chance of getting Alzheimer’s by your late 80s,” says Dr Jenkins in my consultation. “The average probability is one in eight.” Other conditions, such as the risk of high blood pressure, were also in the moderate (orange) zone of the spectrum – s ...
The Study of Genetics: A Historical Perspective Ross Edwards
... The Rise of Political Empowerment As genetics grew as a science, the general public became interested in its many prospects. Unfortunately, it is from this public interest that a number of negative perspectives emerged from the abuse of Mendel’s concepts. Prior to turn of the century, a natural hist ...
... The Rise of Political Empowerment As genetics grew as a science, the general public became interested in its many prospects. Unfortunately, it is from this public interest that a number of negative perspectives emerged from the abuse of Mendel’s concepts. Prior to turn of the century, a natural hist ...
REVIEW Pathways to understanding the extended phenotype of
... basis of manipulated behaviors would be to sequence the genomes of parasites that manipulate and do not manipulate their hosts and ask what is different between the two. This has not yet been done for any parasite known to affect behavior but it has intrinsic appeal due to the commonness of such an ...
... basis of manipulated behaviors would be to sequence the genomes of parasites that manipulate and do not manipulate their hosts and ask what is different between the two. This has not yet been done for any parasite known to affect behavior but it has intrinsic appeal due to the commonness of such an ...
Drugs and addiction: an introduction to epigenetics
... provide a possible mechanism by which the effects of external environmental factors at specific stages in development can produce long-term changes in behaviour. The role of epigenetic mechanisms in mediating phenotypic effects of environmental stimuli is supported by evidence that the environment c ...
... provide a possible mechanism by which the effects of external environmental factors at specific stages in development can produce long-term changes in behaviour. The role of epigenetic mechanisms in mediating phenotypic effects of environmental stimuli is supported by evidence that the environment c ...
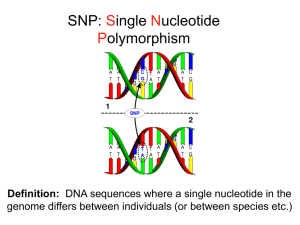
SNP presentation
... T allele- nonsense SNP. People with two T alleles have no functional alpha-actin-3 (TT are endurance athletes) A study of olympic weightlifters everyone of them has at least one copy of C Would you change your behavior if you knew your genotype? ...
... T allele- nonsense SNP. People with two T alleles have no functional alpha-actin-3 (TT are endurance athletes) A study of olympic weightlifters everyone of them has at least one copy of C Would you change your behavior if you knew your genotype? ...
toxicity in bread wheat - BMC Plant Biology
... variation for Al tolerance in rice has also been identified in QTL analysis [20]. The limited impact of single functional genes in plant stress tolerance has been associated with the polygenic nature of such traits. Thus, the identification and characterization of key regulatory genes that act as ma ...
... variation for Al tolerance in rice has also been identified in QTL analysis [20]. The limited impact of single functional genes in plant stress tolerance has been associated with the polygenic nature of such traits. Thus, the identification and characterization of key regulatory genes that act as ma ...
Dept Of Genetics And Plant Breeding
... (a) UP (b) MP (c) AP (d) Rajasthan 3.The oilseed showing highest productivity in India among them is (a) Groundnut (b) Castor (c) Sesame (d) Sunflower 4. Presently the country leading in the Milk production is (a) Australia (b) America (c) Canada (d) India 5. Saltation is a type of (a) Water erosion ...
... (a) UP (b) MP (c) AP (d) Rajasthan 3.The oilseed showing highest productivity in India among them is (a) Groundnut (b) Castor (c) Sesame (d) Sunflower 4. Presently the country leading in the Milk production is (a) Australia (b) America (c) Canada (d) India 5. Saltation is a type of (a) Water erosion ...
Blood types of the Cherokee Indians
... Indian ancestry is evident, especially in types 0 and A. Noteworthy is the presence of three individuals of type B among the full-blooded Indians. Gene frequencies are given separately for the full-blooded and for the combined mixed sample (from 1/32 up to full-blooded). ABO gene frequencies were co ...
... Indian ancestry is evident, especially in types 0 and A. Noteworthy is the presence of three individuals of type B among the full-blooded Indians. Gene frequencies are given separately for the full-blooded and for the combined mixed sample (from 1/32 up to full-blooded). ABO gene frequencies were co ...
Chapter 11 Meiosis and Genetics
... B the allele for short plants is dominant C the allele for tall plants is dominant D they were truebreeding like their parents 14 The principles of probability can be used to A determine the actual outcomes of genetic crosses B predict the traits of the parents used in genetic crosses C decide whic ...
... B the allele for short plants is dominant C the allele for tall plants is dominant D they were truebreeding like their parents 14 The principles of probability can be used to A determine the actual outcomes of genetic crosses B predict the traits of the parents used in genetic crosses C decide whic ...
Evolution of the fibrinogen γ′ chain: implications for the binding of
... [5,6], or in this case non-splicing. The result in humans is a c chain 20 residues longer than the more usual spliced form. The extension is markedly anionic, in part because of two sulfated tyrosines [7] that have been implicated in binding to thrombin. Interestingly, mouse fibrin does not bind thro ...
... [5,6], or in this case non-splicing. The result in humans is a c chain 20 residues longer than the more usual spliced form. The extension is markedly anionic, in part because of two sulfated tyrosines [7] that have been implicated in binding to thrombin. Interestingly, mouse fibrin does not bind thro ...
DNA Extraction - Utah Agriculture in the Classroom
... sources of DNA, such as grapes, also contain a lot of water. If the blended cell soup is too watery, there won't be enough DNA to see. To fix this, go back to the first step and add less water. The cell soup should be opaque, meaning that you can't see through it. ...
... sources of DNA, such as grapes, also contain a lot of water. If the blended cell soup is too watery, there won't be enough DNA to see. To fix this, go back to the first step and add less water. The cell soup should be opaque, meaning that you can't see through it. ...
Identification of an Arabidopsis thaliana gene for
... the CLS gene was searched in the full-length cDNA library [23]. The cDNA clone RAFL08-16-C14 (R11367) was found to correspond to the CLS gene and to contain an open-reading frame (ORF) of 1023 bp encoding a polypeptide of 341 amino acids (molecular mass, 38 042 Da). As shown in Fig. 2, the deduced a ...
... the CLS gene was searched in the full-length cDNA library [23]. The cDNA clone RAFL08-16-C14 (R11367) was found to correspond to the CLS gene and to contain an open-reading frame (ORF) of 1023 bp encoding a polypeptide of 341 amino acids (molecular mass, 38 042 Da). As shown in Fig. 2, the deduced a ...
Cancer Prone Disease Section Oculocutaneous Albinism Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... TYR mutations are responsible for OCA1. A few OCA2 mutations have been associated with autosomal recessive ocular albinism (AROA). OCA1 is an endoplasmic reticulum retention (ER) disorder and all the missense mutations that have been functionally characterized have yielded ER -retained proteins. ...
... TYR mutations are responsible for OCA1. A few OCA2 mutations have been associated with autosomal recessive ocular albinism (AROA). OCA1 is an endoplasmic reticulum retention (ER) disorder and all the missense mutations that have been functionally characterized have yielded ER -retained proteins. ...
Founder mutations - Dr. Gajendra Tulsian
... this seeming benefit can actually become unhealthy, potentially causing multipleorgan damage and even death. Someone with this condition, called hereditary hemochromatosis, often has it because each of his parents passed on to him the same mutation in a specific gene, an error that originated long a ...
... this seeming benefit can actually become unhealthy, potentially causing multipleorgan damage and even death. Someone with this condition, called hereditary hemochromatosis, often has it because each of his parents passed on to him the same mutation in a specific gene, an error that originated long a ...
Review Set for 2.4 *Heredity
... for an acquired trait? • A. genotype • B. phenotype • C. environment • D. chromosomes ...
... for an acquired trait? • A. genotype • B. phenotype • C. environment • D. chromosomes ...
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY of THE RISK ASSESSMENT AND RISK
... All four types of GM cotton also contain the antibiotic resistance gene nptII from Escherichia coli (a bacterium) as a selectable marker, which confers resistance to neomycin antibiotics such as kanamycin. The marker gene was used in the laboratory during the development of the GMOs for identificati ...
... All four types of GM cotton also contain the antibiotic resistance gene nptII from Escherichia coli (a bacterium) as a selectable marker, which confers resistance to neomycin antibiotics such as kanamycin. The marker gene was used in the laboratory during the development of the GMOs for identificati ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.