02Spermatogenesistxt
... represents the fact that each gene locus can contain a maximum of 2 different gene alleles (e.g., one dominant and one recessive). “n” is the total number of homologous gene loci in the genome (a very big number). ...
... represents the fact that each gene locus can contain a maximum of 2 different gene alleles (e.g., one dominant and one recessive). “n” is the total number of homologous gene loci in the genome (a very big number). ...
Does Mendel`s work suggest that this is the only gene in the pea
... • The genotype of the F1 round, yellow plants can be symbolized as RrYy to indicate that the plant is heterozygous for the dominant and recessive alleles for two different traits. • Mendel’s principle of segregation predicts that 1/2 of the gametes produced by such a plant should carry the dominant ...
... • The genotype of the F1 round, yellow plants can be symbolized as RrYy to indicate that the plant is heterozygous for the dominant and recessive alleles for two different traits. • Mendel’s principle of segregation predicts that 1/2 of the gametes produced by such a plant should carry the dominant ...
Heredity 1. Technology Enhanced Questions are not available in
... 24. Guinea pig coat color is determined by a single gene. The allele for black coat color is dominant to brown. In a cross between two black-haired guinea pigs, 20 offspring are born. If both parents were heterozygous, probability would predict that approximately how many of the 20 offspring would h ...
... 24. Guinea pig coat color is determined by a single gene. The allele for black coat color is dominant to brown. In a cross between two black-haired guinea pigs, 20 offspring are born. If both parents were heterozygous, probability would predict that approximately how many of the 20 offspring would h ...
Does Mendel`s work suggest that this is the only gene in the pea
... • The genotype of the F1 round, yellow plants can be symbolized as RrYy to indicate that the plant is heterozygous for the dominant and recessive alleles for two different traits. • Mendel’s principle of segregation predicts that 1/2 of the gametes produced by such a plant should carry the dominant ...
... • The genotype of the F1 round, yellow plants can be symbolized as RrYy to indicate that the plant is heterozygous for the dominant and recessive alleles for two different traits. • Mendel’s principle of segregation predicts that 1/2 of the gametes produced by such a plant should carry the dominant ...
Organization and dynamics of plant interphase chromosomes
... with additional barley (Hordeum vulgare) or rye (Secale cereale) chromosomes or substitution of the equivalent rye or barley chromosome for the native wheat chromosome are available. Three-dimensional GISH imaging of intact tissues of hexaploid wheat carrying various different substitutions has demo ...
... with additional barley (Hordeum vulgare) or rye (Secale cereale) chromosomes or substitution of the equivalent rye or barley chromosome for the native wheat chromosome are available. Three-dimensional GISH imaging of intact tissues of hexaploid wheat carrying various different substitutions has demo ...
Chapter 13 Unintended Horizontal Transfer of Recombinant DNA
... requiring a more detailed understanding of the natural selection context of each GMO case. Common to all biosafety viewpoints is that they are founded on expert opinion, familiarity with the gene donor and inference, rather than conclusive empirical evidence. The latter is unachievable given the lim ...
... requiring a more detailed understanding of the natural selection context of each GMO case. Common to all biosafety viewpoints is that they are founded on expert opinion, familiarity with the gene donor and inference, rather than conclusive empirical evidence. The latter is unachievable given the lim ...
PowerPoint
... exerted on a given gene or DNA fragment • Need orthologous nucleotide sequence alignments • Observe nucleotide substitution patterns at given sites and correct numbers using, for example, the Pamilo-Bianchi-Li method (Li 1993; Pamilo and Bianchi 1993). • Correction is needed because of the following ...
... exerted on a given gene or DNA fragment • Need orthologous nucleotide sequence alignments • Observe nucleotide substitution patterns at given sites and correct numbers using, for example, the Pamilo-Bianchi-Li method (Li 1993; Pamilo and Bianchi 1993). • Correction is needed because of the following ...
OPTIMIZER: a web server for optimizing the codon usage of DNA
... a codon usage table in a variety of formats, including tables from the Codon Usage Database (9), or they can choose between 153 pre-computed codon usage tables for ribosomal protein genes or a group of highly expressed genes from prokaryotic genomes under translational selection. Users can also choo ...
... a codon usage table in a variety of formats, including tables from the Codon Usage Database (9), or they can choose between 153 pre-computed codon usage tables for ribosomal protein genes or a group of highly expressed genes from prokaryotic genomes under translational selection. Users can also choo ...
Module Document
... increased over the 60-year span of time. What this study suggests is that such a change can eliminate some species from the community—perhaps a barnacle species. So what? (California 1987; Foster 2009. Intertidal 2007) Barnacles are filter feeders that occur in large numbers in their communities. Th ...
... increased over the 60-year span of time. What this study suggests is that such a change can eliminate some species from the community—perhaps a barnacle species. So what? (California 1987; Foster 2009. Intertidal 2007) Barnacles are filter feeders that occur in large numbers in their communities. Th ...
network models for genetic testing
... genetic material in an individual makes it possible to identify the exact location of gene mutation, and predict the patient’s response to a specific drug leading to personalized medicine. Moreover, NGS technologies open the door to unexpected findings, which brings genetic testing to a higher level ...
... genetic material in an individual makes it possible to identify the exact location of gene mutation, and predict the patient’s response to a specific drug leading to personalized medicine. Moreover, NGS technologies open the door to unexpected findings, which brings genetic testing to a higher level ...
Chapter 8 Review Sheet
... 9.3 Define and distinguish between the following pairs of terms: genotype versus phenotype, dominant allele versus recessive allele, and heterozygous versus homozygous. Also define a monohybrid cross and a Punnett square. 9.3 Explain how Mendel's law of segregation describes the inheritance of a sin ...
... 9.3 Define and distinguish between the following pairs of terms: genotype versus phenotype, dominant allele versus recessive allele, and heterozygous versus homozygous. Also define a monohybrid cross and a Punnett square. 9.3 Explain how Mendel's law of segregation describes the inheritance of a sin ...
6 Meiosis and Mendel - Speedway High School
... Traits are characteristics* that are inherited, such as eye color, leaf shape, or tail length. Scientists recognized that traits are hereditary, or passed from one generation to the next, long before they understood how traits are passed on. Genetics is the study of biological inheritance patterns a ...
... Traits are characteristics* that are inherited, such as eye color, leaf shape, or tail length. Scientists recognized that traits are hereditary, or passed from one generation to the next, long before they understood how traits are passed on. Genetics is the study of biological inheritance patterns a ...
The cDNA-deduced Amino Acid Sequence for
... HE mammalian hair follicle is a derivative of the epidermis that develops within the dermal layer of the skin. In the follicle bulb, the epidermal cells surround a dermal papilla that is essential for the initial development of the follicle and the growth of the fiber (Oliver and Jahoda, 1989). The ...
... HE mammalian hair follicle is a derivative of the epidermis that develops within the dermal layer of the skin. In the follicle bulb, the epidermal cells surround a dermal papilla that is essential for the initial development of the follicle and the growth of the fiber (Oliver and Jahoda, 1989). The ...
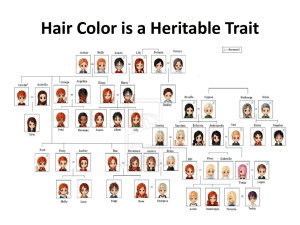
Hair Color is a Heritable Trait
... ‘Nature’ is not static • Genetic influences (heritability) can change over development • Individuals gain increased instrumental control over the environment (e.g., routine, occupation, spouse) • Over time, there is more opportunity for biases and dispositions (T&P) to influence; cumulative impact ...
... ‘Nature’ is not static • Genetic influences (heritability) can change over development • Individuals gain increased instrumental control over the environment (e.g., routine, occupation, spouse) • Over time, there is more opportunity for biases and dispositions (T&P) to influence; cumulative impact ...
Stretching DNA Fibers out of a Chromosome in Solution
... The chromosome is one of the small, rod-shaped, deeply staining bodies that become visible in the eucaryotic cell nucleus at mitosis. Most interphase chromosomes are too far extended and entangled for clearly observing their structures. In contrast, chromosomes from nearly all eucaryotic cells are r ...
... The chromosome is one of the small, rod-shaped, deeply staining bodies that become visible in the eucaryotic cell nucleus at mitosis. Most interphase chromosomes are too far extended and entangled for clearly observing their structures. In contrast, chromosomes from nearly all eucaryotic cells are r ...
Article Why There Are No Essential Genes on
... are differences between functions coded for by mobile genes and those in the “core” genome and that these differences can be seen between plasmids and chromosomes. In particular, it has been suggested that essential genes, such as those involved in the formation of structural proteins or in basic me ...
... are differences between functions coded for by mobile genes and those in the “core” genome and that these differences can be seen between plasmids and chromosomes. In particular, it has been suggested that essential genes, such as those involved in the formation of structural proteins or in basic me ...
Work sheet for assignment 13
... show the mRNA codons for each amino acid found in miacalcin. (Remember that some amino acids have more than one codon.) Position in the protein ...
... show the mRNA codons for each amino acid found in miacalcin. (Remember that some amino acids have more than one codon.) Position in the protein ...
Mutation Is Random
... The tendency is for students to revert back to the idea that there are differences in rate among genes because some genes are more important than others. Once students have a general idea, they should try to draw a graph that summarizes their perspective. For example, if their idea is that genes var ...
... The tendency is for students to revert back to the idea that there are differences in rate among genes because some genes are more important than others. Once students have a general idea, they should try to draw a graph that summarizes their perspective. For example, if their idea is that genes var ...
DNA sequence of the rat growth hormone gene: location of the 5
... All d i g e s t i o n s v/ere done with enzymes purchased fran e i t h e r Mew England Biolabs, rtethesda Pesearch Laboratories, o r Poehringer f'annheim. Digestions were usually done with a s u b s t a n t i a l excess of enzyme and approximately in accordance with t h e conditions provided by t h ...
... All d i g e s t i o n s v/ere done with enzymes purchased fran e i t h e r Mew England Biolabs, rtethesda Pesearch Laboratories, o r Poehringer f'annheim. Digestions were usually done with a s u b s t a n t i a l excess of enzyme and approximately in accordance with t h e conditions provided by t h ...
chromosome - OnMyCalendar
... • In a literal sense, children do not inherit particular physical traits from their parents…it is genes that are actually inherited. ...
... • In a literal sense, children do not inherit particular physical traits from their parents…it is genes that are actually inherited. ...
Mutations
... • Many cell divisions take place between zygote formation and meiosis in germ cells More chance to accumulate mutations ...
... • Many cell divisions take place between zygote formation and meiosis in germ cells More chance to accumulate mutations ...
WkntJs G*?t*ticsl - Greenslime Home Page
... only short plants. Although he could not explain his results at the time, Mendel realized that there must ...
... only short plants. Although he could not explain his results at the time, Mendel realized that there must ...
The Incompatible Desiderata of Gene Cluster Properties
... spatial patterns suggestive of common ancestry, and then design a search algorithm to find such patterns. The exact definition of the structures of interest is critical for sensitive detection of ancient homologies without inclusion of false positives. It is difficult to characterize what such regio ...
... spatial patterns suggestive of common ancestry, and then design a search algorithm to find such patterns. The exact definition of the structures of interest is critical for sensitive detection of ancient homologies without inclusion of false positives. It is difficult to characterize what such regio ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.