Answered copy of exam 3
... a short period of time. For simplicity, use arrows to indicate primers 1 and 2 that are just 7 bases long: 5’ ACCGTCAACTGCAATGCGCGCTAGAATCGTTGCATGATGG 3’ 3’TGGCAGTTGACGTTACGCGCGATCTTAGCAACGTACTACC 5’ Name of process? Polymerase Chain Reactio Enzyme used? ...
... a short period of time. For simplicity, use arrows to indicate primers 1 and 2 that are just 7 bases long: 5’ ACCGTCAACTGCAATGCGCGCTAGAATCGTTGCATGATGG 3’ 3’TGGCAGTTGACGTTACGCGCGATCTTAGCAACGTACTACC 5’ Name of process? Polymerase Chain Reactio Enzyme used? ...
Slide 1
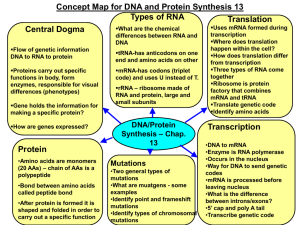
... functions in body, form enzymes, responsible for visual differences (phenotypes) Gene holds the information for making a specific protein? How are genes expressed? ...
... functions in body, form enzymes, responsible for visual differences (phenotypes) Gene holds the information for making a specific protein? How are genes expressed? ...
Mapping disease genes (lectures 8,10)
... SNP: presence of two different nucleotides at the same loci in genomic DNA from different individuals DNA fingerprinting: Detection of genotype at a number of unlinked highly polymorphic loci using one probe Genetic testing: Testing for a pathogenic mutation in a certain gene in an individual that i ...
... SNP: presence of two different nucleotides at the same loci in genomic DNA from different individuals DNA fingerprinting: Detection of genotype at a number of unlinked highly polymorphic loci using one probe Genetic testing: Testing for a pathogenic mutation in a certain gene in an individual that i ...
Chromosome Structure 1 - Dr. Kordula
... C. Histone Modification and Gene Expression The Nterminal tails of the histones tend to be accessible on the surface of the nucleosome. It is now known that Lys residues in these tails are often reversibly acetylated. The acetylated versions are less positively charged, resulting in less affin ...
... C. Histone Modification and Gene Expression The Nterminal tails of the histones tend to be accessible on the surface of the nucleosome. It is now known that Lys residues in these tails are often reversibly acetylated. The acetylated versions are less positively charged, resulting in less affin ...
DNA Review
... We can think about the DNA sequence of a gene as a sentence made up entirely of three-letter words. In the sequence, each three-letter word is a codon, specifying a single amino acid in a protein. Have a look at this sentence: ...
... We can think about the DNA sequence of a gene as a sentence made up entirely of three-letter words. In the sequence, each three-letter word is a codon, specifying a single amino acid in a protein. Have a look at this sentence: ...
Antibody Diversity 02/16/06
... recombination created vast number of genes for antibody formation • This introduced a new concept: targeted mutation or recombination of DNA: is it possible?? • Paradox: how could stability be maintained in C region and diversity exist in V region? ...
... recombination created vast number of genes for antibody formation • This introduced a new concept: targeted mutation or recombination of DNA: is it possible?? • Paradox: how could stability be maintained in C region and diversity exist in V region? ...
Gene Expression - Pleasantville High School
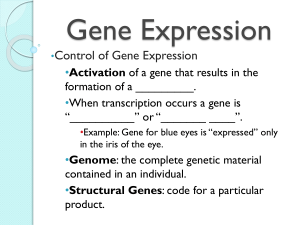
... •Example: Gene for blue eyes is “expressed” only in the iris of the eye. ...
... •Example: Gene for blue eyes is “expressed” only in the iris of the eye. ...
Revision sheet Biology Grade 12 A Genes in Action In the space
... _____ 3. The mutation that has no effect on a gene’s function is called a. missense. b. silent. c. frameshift. d. enhancer. _____ 4. The mutation in which a chromosome carries repetitive sets of alleles for a gene is called a(n) a. duplication. b. deletion. c. translocation. d. inversion. _____ 5. A ...
... _____ 3. The mutation that has no effect on a gene’s function is called a. missense. b. silent. c. frameshift. d. enhancer. _____ 4. The mutation in which a chromosome carries repetitive sets of alleles for a gene is called a(n) a. duplication. b. deletion. c. translocation. d. inversion. _____ 5. A ...
Study of the evolution of animal parasite bacteria and plant symbionts
... The alpha-proteobacteria include various microorganisms of biological and medical interest. Some of them are agents of human diseases such as typhus or cat-scratch disease, others are plants symbionts that enter plant roots and live inside it in a cooperative manner, each partner drawing benefit fro ...
... The alpha-proteobacteria include various microorganisms of biological and medical interest. Some of them are agents of human diseases such as typhus or cat-scratch disease, others are plants symbionts that enter plant roots and live inside it in a cooperative manner, each partner drawing benefit fro ...
OCR Biology B - Centre of the Cell
... 3.1.2 The developing individual: meiosis, growth and development 5.1.1 Patterns of inheritance 5.1.2 Population genetics and epigenetics 2.1.4 Nucleic acids (a) the structure of a nucleotide as the monomer from which nucleic acids are made (c) (i) the structure of the DNA molecule, including a revie ...
... 3.1.2 The developing individual: meiosis, growth and development 5.1.1 Patterns of inheritance 5.1.2 Population genetics and epigenetics 2.1.4 Nucleic acids (a) the structure of a nucleotide as the monomer from which nucleic acids are made (c) (i) the structure of the DNA molecule, including a revie ...
Chapter One
... structure, which is determined by it’s sequence • Therefore…DNA encodes protein function ...
... structure, which is determined by it’s sequence • Therefore…DNA encodes protein function ...
Genetics Vocabulary
... genes) which is half of amount that a normal body cell for that type of individual. 33. ___________________________ ...
... genes) which is half of amount that a normal body cell for that type of individual. 33. ___________________________ ...
Genetics Vocabulary Crossword Puzzle Across
... 1. joining of egg and sperm 2. the division of sex cells (results in 4 different haploid cells) 3. this type of reproduction involves 2 parents 4. a variety of different genes and traits 5. location on a chromosome that codes for a certain trait 7. _____ chromosomes are chromosome pairs, one from ea ...
... 1. joining of egg and sperm 2. the division of sex cells (results in 4 different haploid cells) 3. this type of reproduction involves 2 parents 4. a variety of different genes and traits 5. location on a chromosome that codes for a certain trait 7. _____ chromosomes are chromosome pairs, one from ea ...
Hematologic Malignancies - Jacquie Hirsch For ALL Foundation
... DNA is the genetic code inherited from your parents DNA is arranged in structures called chromosomes (X-like). ...
... DNA is the genetic code inherited from your parents DNA is arranged in structures called chromosomes (X-like). ...
Gene Hunting
... Added Statistical complexity • Two types of disease • Monogenic -- mutation in one gene leads to disease follows Mendelian inheritance • Polygenic -- mutations in several genes lead to disease follows complex inheritance patterns ...
... Added Statistical complexity • Two types of disease • Monogenic -- mutation in one gene leads to disease follows Mendelian inheritance • Polygenic -- mutations in several genes lead to disease follows complex inheritance patterns ...
Honors Biology
... 2. Relate the structure of the DNA molecule to the structure of chromatin and chromosomes. 3. Know the types and roles of RNAs. 4. Compare and contrast RNA with DNA (consider both the structure of each and the purpose of each in the cell). 5. Describe the process of protein synthesis (both transcrip ...
... 2. Relate the structure of the DNA molecule to the structure of chromatin and chromosomes. 3. Know the types and roles of RNAs. 4. Compare and contrast RNA with DNA (consider both the structure of each and the purpose of each in the cell). 5. Describe the process of protein synthesis (both transcrip ...
Genes, Chromosomes and DNA
... nucleus) contains the same _________. Each cell has 46 molecules of doublestranded DNA. Each molecule of DNA is made up of 50 to 250 million bases housed in a _________. The _________ in each chromosome contains many _________. A gene codes for a particular protein, which in turn affects the charact ...
... nucleus) contains the same _________. Each cell has 46 molecules of doublestranded DNA. Each molecule of DNA is made up of 50 to 250 million bases housed in a _________. The _________ in each chromosome contains many _________. A gene codes for a particular protein, which in turn affects the charact ...
Chapter 9 Biotechnology
... Yeast gene library DNA – fragment – restriction enzyme – fragments are inserted into plasmids – introduced into a bacterial cell • Each bacterial cell having the recombinant cell is a clone • Large # clones – a clone for each gene that exists in the yeast cell ...
... Yeast gene library DNA – fragment – restriction enzyme – fragments are inserted into plasmids – introduced into a bacterial cell • Each bacterial cell having the recombinant cell is a clone • Large # clones – a clone for each gene that exists in the yeast cell ...
Lecture 6
... • Statistical analysis of the rates of homologous recombination of several different genes could determine their order on a certain chromosome, and information from many such experiments could be combined to create a genetic map specifying the rough location of known genes relative to each other. • ...
... • Statistical analysis of the rates of homologous recombination of several different genes could determine their order on a certain chromosome, and information from many such experiments could be combined to create a genetic map specifying the rough location of known genes relative to each other. • ...
Genetics in the New Millennium: From Plants to People
... Genes carry the information to build proteins each 3 bases in DNA code for one sub-unit of a protein proteins have many and varied functions structural carriers enzymes ...
... Genes carry the information to build proteins each 3 bases in DNA code for one sub-unit of a protein proteins have many and varied functions structural carriers enzymes ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.