L3.2ReducingYourRisk - jj-sct
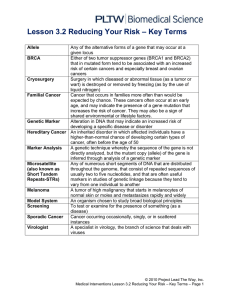
... age, and may indicate the presence of a gene mutation that increases the risk of cancer. They may also be a sign of shared environmental or lifestyle factors. Genetic Marker Alteration in DNA that may indicate an increased risk of developing a specific disease or disorder Hereditary Cancer An inheri ...
... age, and may indicate the presence of a gene mutation that increases the risk of cancer. They may also be a sign of shared environmental or lifestyle factors. Genetic Marker Alteration in DNA that may indicate an increased risk of developing a specific disease or disorder Hereditary Cancer An inheri ...
Homeotic genes - Teacherschoice
... Genes that affect embryo development by specifying the character of a body segment. The classic example is Antennapedia, a gene that, when mutated, causes a fruitfly to grow a leg in place of antenna. Homeotic genes are homeobox genes that are responsible for segment identity in metazoan organisms. ...
... Genes that affect embryo development by specifying the character of a body segment. The classic example is Antennapedia, a gene that, when mutated, causes a fruitfly to grow a leg in place of antenna. Homeotic genes are homeobox genes that are responsible for segment identity in metazoan organisms. ...
Homeotic genes
... Genes that affect embryo development by specifying the character of a body segment. The classic example is Antennapedia, a gene that, when mutated, causes a fruitfly to grow a leg in place of antenna. Homeotic genes are homeobox genes that are responsible for segment identity in metazoan organisms. ...
... Genes that affect embryo development by specifying the character of a body segment. The classic example is Antennapedia, a gene that, when mutated, causes a fruitfly to grow a leg in place of antenna. Homeotic genes are homeobox genes that are responsible for segment identity in metazoan organisms. ...
UNIT 4: DNA and Genetics
... _____11. Sexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically different from either parent but have some of the characteristics of both parents’ lineages. _____12. Organisms that are sexually reproducing are from the Animal, Plant, some members of the Fungal and some Protist Kingdoms. _____13 ...
... _____11. Sexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically different from either parent but have some of the characteristics of both parents’ lineages. _____12. Organisms that are sexually reproducing are from the Animal, Plant, some members of the Fungal and some Protist Kingdoms. _____13 ...
Genetics Online Scavenger Hunt
... 2. Click on Heredity and Traits. 3. Scroll down the next page and find the following topics: a. How Do Scientists Read Chromosomes? b. Making a Karyotype c. Using Karyotypes to Predict Genetic Disorders 4. As you go from one tutorial to the next answer the corresponding questions for each topic. ...
... 2. Click on Heredity and Traits. 3. Scroll down the next page and find the following topics: a. How Do Scientists Read Chromosomes? b. Making a Karyotype c. Using Karyotypes to Predict Genetic Disorders 4. As you go from one tutorial to the next answer the corresponding questions for each topic. ...
Exp 4 Lecture - Seattle Central College
... In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria often contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. • Plasmid DNA usually contains genes for more than one trait. Genetic engineering involves inserting genes coding for new traits into a plasmid. • In this experiment, the pGLO plasmi ...
... In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria often contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. • Plasmid DNA usually contains genes for more than one trait. Genetic engineering involves inserting genes coding for new traits into a plasmid. • In this experiment, the pGLO plasmi ...
Bacterial Gene Finding
... Demystification is the order of our day, all the cats are jumping out of all the bags and even beginning to mingle. We immediately suspect ego insecurity in people who may still try to hide behind the jargon of a specialty or pretend to some data base forever "beyond" the reach of a layman. Anybody ...
... Demystification is the order of our day, all the cats are jumping out of all the bags and even beginning to mingle. We immediately suspect ego insecurity in people who may still try to hide behind the jargon of a specialty or pretend to some data base forever "beyond" the reach of a layman. Anybody ...
Genetics Study Guide Answers What are different forms of a
... 9. What is used to organize possible offspring combinations? 10. A genotype with one recessive and one dominant gene 11. A genotype with two dominant or two recessive genes 12. What are chromosomes that carry the same sets of genes? 13. What carries the genes that determine sex? 14. How are sex cell ...
... 9. What is used to organize possible offspring combinations? 10. A genotype with one recessive and one dominant gene 11. A genotype with two dominant or two recessive genes 12. What are chromosomes that carry the same sets of genes? 13. What carries the genes that determine sex? 14. How are sex cell ...
Living Environment 1
... What would be a hypothesis for the following problem? What is the optimum pH for ...
... What would be a hypothesis for the following problem? What is the optimum pH for ...
DNA Technology
... 2. All RFLP’s from sample inserted into a well in a gel 3. An electrical charge is applied to the gel, which causes RFLP’s to migrate down gel according to length (how? chromatography), resulting in a distinct pattern of bands based on genetic code. 4. Gel’s have many wells so that different samples ...
... 2. All RFLP’s from sample inserted into a well in a gel 3. An electrical charge is applied to the gel, which causes RFLP’s to migrate down gel according to length (how? chromatography), resulting in a distinct pattern of bands based on genetic code. 4. Gel’s have many wells so that different samples ...
4 Applied Genetics
... A. a change in genes or chromosome’s appearance or number of that causes a new trait to be inherited B. Hugo de Vries 1. looked at primroses 2. saw mutations within the plants C. Occurs on all body cells (skin cells, sex cells etc.) 1. if on sex cells, will pass onto the offspring a. deformation b. ...
... A. a change in genes or chromosome’s appearance or number of that causes a new trait to be inherited B. Hugo de Vries 1. looked at primroses 2. saw mutations within the plants C. Occurs on all body cells (skin cells, sex cells etc.) 1. if on sex cells, will pass onto the offspring a. deformation b. ...
No Slide Title
... 3) Transduction – genes can be moved from one prokaryote species to another via viruses. ...
... 3) Transduction – genes can be moved from one prokaryote species to another via viruses. ...
pdffile - UCI Math - University of California, Irvine
... Within a living cell, genes are arranged in linear order among microscopic threadlike bodies called chromosomes, which typically contains several thousand genes. The position of a gene along a chromosome is called the locus of the gene. In most higher organisms, each cell contains two copies of eac ...
... Within a living cell, genes are arranged in linear order among microscopic threadlike bodies called chromosomes, which typically contains several thousand genes. The position of a gene along a chromosome is called the locus of the gene. In most higher organisms, each cell contains two copies of eac ...
Terms and Definitions 2017 File
... Features of organisms e.g eye colour, leaf shape Cell control centre containing chromosomes Both copies of alleles are the same e.g. BB or bb Thread -like structure in cell nucleus, made of DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Section of a chromosome that codes for a characteristic An alternative/different for ...
... Features of organisms e.g eye colour, leaf shape Cell control centre containing chromosomes Both copies of alleles are the same e.g. BB or bb Thread -like structure in cell nucleus, made of DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Section of a chromosome that codes for a characteristic An alternative/different for ...
ASPM
... • Clues to diseases: It demonstrate that the human and chimpanzee species have tolerated more deleterious mutations than other mammals. This confirms an important evolutionary prediction, and may account for greater innovation in primates than rodents, as well as a high incidence of genetic diseases ...
... • Clues to diseases: It demonstrate that the human and chimpanzee species have tolerated more deleterious mutations than other mammals. This confirms an important evolutionary prediction, and may account for greater innovation in primates than rodents, as well as a high incidence of genetic diseases ...
No Slide Title
... • Proteins: macromolecules composed of one or more chains of amino acids • Amino acids: class of 20 different organic compounds containing a basic amino group (NH2) and an acidic carboxyl group (-COOH) • The order of amino acids is determined by the base sequence of nucleotides in the gene coding fo ...
... • Proteins: macromolecules composed of one or more chains of amino acids • Amino acids: class of 20 different organic compounds containing a basic amino group (NH2) and an acidic carboxyl group (-COOH) • The order of amino acids is determined by the base sequence of nucleotides in the gene coding fo ...
Study Guide
... How are the functions of mRNA and tRNA different? Describe the process of transcription and translation. What is a codon? What is an anticodon? How are they related? Why is RNA necessary for expressing the code in DNA? How does an organism’s DNA code for its traits? Summarize the process ...
... How are the functions of mRNA and tRNA different? Describe the process of transcription and translation. What is a codon? What is an anticodon? How are they related? Why is RNA necessary for expressing the code in DNA? How does an organism’s DNA code for its traits? Summarize the process ...
Chromosomes
... • AUA specifies methionine not isoleucine • UGA encodes tryptophan not stop-codon • AGA and AGG are stop-codons (they specify arginine in the nuclear genetic code) ...
... • AUA specifies methionine not isoleucine • UGA encodes tryptophan not stop-codon • AGA and AGG are stop-codons (they specify arginine in the nuclear genetic code) ...
COS 597c: DNA arrays Topics in Computational Molecular Biolo
... Interpreting the meaning and significance of 20,000 such numbers is a very big challenge, which becomes even more overwhelming because such a measurement is usually performed several times. The task of analyzing this amount of data is made easier by software packages. These packages are usually sold ...
... Interpreting the meaning and significance of 20,000 such numbers is a very big challenge, which becomes even more overwhelming because such a measurement is usually performed several times. The task of analyzing this amount of data is made easier by software packages. These packages are usually sold ...
Micro Quiz #3R Stu F2011 - the Biology Scholars Program Wiki
... d. Circle one of the deoxyribose molecules. e. Indicate one of the phosphodiester bonds with an arrow. f. Would the strand shown be a leading strand during replication? ...
... d. Circle one of the deoxyribose molecules. e. Indicate one of the phosphodiester bonds with an arrow. f. Would the strand shown be a leading strand during replication? ...
IMPLICATIONS OF ANTHROPGENY FOR MEDICINE AND
... Homo erectus: An extinct hominin species with fossil evidence Population: A defined group of similar individuals among whom from 1.9 million (possibly earlier) to 70 thousand years ago and ...
... Homo erectus: An extinct hominin species with fossil evidence Population: A defined group of similar individuals among whom from 1.9 million (possibly earlier) to 70 thousand years ago and ...
Document
... A. In humans XX is female and XY is male 1. The SRY gene has been shown to trigger the development into a male fetus at about 2 months old. 2. SRY probably regulates other genes 3. Some XX male and XY females exist with mutated SRY genes ...
... A. In humans XX is female and XY is male 1. The SRY gene has been shown to trigger the development into a male fetus at about 2 months old. 2. SRY probably regulates other genes 3. Some XX male and XY females exist with mutated SRY genes ...
Part I: To Transcribe! In previous lessons, you`ve learned the
... stored in segments called genes. A gene is a specific sequence of nucleotides in a strand of DNA that codes for a specific sequence of amino acids. The amino acids form chains that make a certain protein depending on the order of the nitrogen bases. Just like 26 letters of the alphabet make words, 2 ...
... stored in segments called genes. A gene is a specific sequence of nucleotides in a strand of DNA that codes for a specific sequence of amino acids. The amino acids form chains that make a certain protein depending on the order of the nitrogen bases. Just like 26 letters of the alphabet make words, 2 ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.























