Heredity
... GLE 0507.4.2 Recognize that some characteristics are inherited while others result frominteractions with the environment. 0507.4.1 Explain how genetic information is transmitted from parents to offspring 0507.4.2 Create a chart that compares hereditary and environmental traits. 0507.4.3 Distinguish ...
... GLE 0507.4.2 Recognize that some characteristics are inherited while others result frominteractions with the environment. 0507.4.1 Explain how genetic information is transmitted from parents to offspring 0507.4.2 Create a chart that compares hereditary and environmental traits. 0507.4.3 Distinguish ...
Plant Transformation
... is added along with your gene • nucleic acid sequences encoding easily assayed proteins • Reporter genes include -galactosidase (encoded by lacZ), -glucuronidase (encoded by uidA), chloramphenicol acetyltransferase, luciferase and green fluorescent protein (GFP) . ...
... is added along with your gene • nucleic acid sequences encoding easily assayed proteins • Reporter genes include -galactosidase (encoded by lacZ), -glucuronidase (encoded by uidA), chloramphenicol acetyltransferase, luciferase and green fluorescent protein (GFP) . ...
Gene Regulation
... create an mRNA molecule with a continuous coding sequence. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... create an mRNA molecule with a continuous coding sequence. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
According to NIDA`s Monitoring the Future Survey, we are seeing
... Why do some people become addicted, while others do not? Studies of identical twins indicate that as much as half of an individual’s risk of becoming addicted to nicotine, alcohol, or other drugs depends on his or her genes. Pinning down the biological basis for this risk is an important avenue of r ...
... Why do some people become addicted, while others do not? Studies of identical twins indicate that as much as half of an individual’s risk of becoming addicted to nicotine, alcohol, or other drugs depends on his or her genes. Pinning down the biological basis for this risk is an important avenue of r ...
genetics ppt - Schoolwires.net
... Molecular geneticists are trying to identify genes that put people at risk for disorders. With this kind of knowledge, parents can decide to abort pregnancies in which the fetus is suspected of having such disorders. ...
... Molecular geneticists are trying to identify genes that put people at risk for disorders. With this kind of knowledge, parents can decide to abort pregnancies in which the fetus is suspected of having such disorders. ...
Behavior Genetics: Predicting Individual Differences
... Molecular geneticists are trying to identify genes that put people at risk for disorders. With this kind of knowledge, parents can decide to abort pregnancies in which the fetus is suspected of having such disorders. ...
... Molecular geneticists are trying to identify genes that put people at risk for disorders. With this kind of knowledge, parents can decide to abort pregnancies in which the fetus is suspected of having such disorders. ...
Behavior Genetics: Predicting Individual Differences
... Molecular geneticists are trying to identify genes that put people at risk for disorders. With this kind of knowledge, parents can decide to abort pregnancies in which the fetus is suspected of having such disorders. ...
... Molecular geneticists are trying to identify genes that put people at risk for disorders. With this kind of knowledge, parents can decide to abort pregnancies in which the fetus is suspected of having such disorders. ...
Sex-linked genes, genes located on one of the sex chromosomes (X
... exhibit one of these X-linked traits, most of which are recessive mutations, she would have to have two copies of the allele (X'X'). ...
... exhibit one of these X-linked traits, most of which are recessive mutations, she would have to have two copies of the allele (X'X'). ...
Non Mendelian Genetics - Warren County Schools
... CR = red allele for coat color; CW= white allele for coat color ...
... CR = red allele for coat color; CW= white allele for coat color ...
Bio_11_Rev
... •It is a weakened version of the disease; incapable of causing serious harm. When a vaccine is injected, the immune system reads the pathogen and responds by making defensive proteins called antibodies. The immune system creates a defense system against this form of the disease. •In the future, if t ...
... •It is a weakened version of the disease; incapable of causing serious harm. When a vaccine is injected, the immune system reads the pathogen and responds by making defensive proteins called antibodies. The immune system creates a defense system against this form of the disease. •In the future, if t ...
Chapter 14
... • Certain genes control the normal growth, division, and specialization of cells in bodies. – Mutations in these genes can cause a normal somatic cell to “lose control” and begin growing and dividing abnormally. The group of cells that grows will become a tumor. – If the tumor cells begin to invade ...
... • Certain genes control the normal growth, division, and specialization of cells in bodies. – Mutations in these genes can cause a normal somatic cell to “lose control” and begin growing and dividing abnormally. The group of cells that grows will become a tumor. – If the tumor cells begin to invade ...
Analysis of Microarray Data Using R
... Su et al ( PNAS 2004) hybridized 150 samples from 61 tissues to Affymetrix U133A and ...
... Su et al ( PNAS 2004) hybridized 150 samples from 61 tissues to Affymetrix U133A and ...
Slides
... as genes and proteins, and interactions between them that collectively carry out some cellular function. A genetic regulatory network refers to the network of controls that turn on/off gene transcription. ...
... as genes and proteins, and interactions between them that collectively carry out some cellular function. A genetic regulatory network refers to the network of controls that turn on/off gene transcription. ...
11-3 - Kleins
... hybrids When Mendel did this experiment he came created 556 seeds from the two original hybrid F1 seeds His results were very similar to what we see in our phenotypic probability ratio of ...
... hybrids When Mendel did this experiment he came created 556 seeds from the two original hybrid F1 seeds His results were very similar to what we see in our phenotypic probability ratio of ...
COMPLEX PATTERNS OF INHERITANCE
... including those that will give rise to the hairproducing skin cells A female that is heterozygous will have one or the other X inactivated in different groups of cells resulting in patches of black and orange fur ...
... including those that will give rise to the hairproducing skin cells A female that is heterozygous will have one or the other X inactivated in different groups of cells resulting in patches of black and orange fur ...
File
... 1. DNA or RNA? 2. Write the complimentary DNA sequence 3. Write the mRNA sequence 4. Write the protein sequence. ...
... 1. DNA or RNA? 2. Write the complimentary DNA sequence 3. Write the mRNA sequence 4. Write the protein sequence. ...
Summary notes on Genetics and Gene expression
... Each amino acid is coded for by a sequence of 3 bases on the mRNA strand A few amino acids have only one codon The code is degenerate (some amino acids can be coded for by different codons) Stop codons mark the end of the polypeptide chain (& they don’t code for amino acids) There is no ov ...
... Each amino acid is coded for by a sequence of 3 bases on the mRNA strand A few amino acids have only one codon The code is degenerate (some amino acids can be coded for by different codons) Stop codons mark the end of the polypeptide chain (& they don’t code for amino acids) There is no ov ...
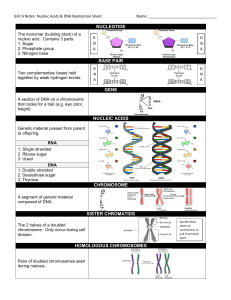
NUCLEOTIDE BASE PAIR GENE NUCLEIC ACIDS CHROMOSOME
... NUCLEOTIDE The monomer (building block) of a nucleic acid. Contains 3 parts: 1. Sugar 2. Phosphate group 3. Nitrogen base ...
... NUCLEOTIDE The monomer (building block) of a nucleic acid. Contains 3 parts: 1. Sugar 2. Phosphate group 3. Nitrogen base ...
PRACTICE TEST CHAPTER 13 1 ______ 1. Which of the following
... RNA is usually double-stranded and contains the base thymine. RNA is usually single-stranded and contains the base uracil. RNA is longer than DNA and uses five bases to encode information. RNA is made in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and stays there to carry out its functions. ...
... RNA is usually double-stranded and contains the base thymine. RNA is usually single-stranded and contains the base uracil. RNA is longer than DNA and uses five bases to encode information. RNA is made in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and stays there to carry out its functions. ...
Gene Manipulation-2 - Workforce Solutions
... • Products of interest can be produced, extracted, and purified for use ...
... • Products of interest can be produced, extracted, and purified for use ...
The Nature of Genes The Nature of Genes
... • Introns are spliced out of pre-mRNAs to produce the mature mRNA that is translated. • Alternative splicing recognizes different splice sites in different tissue types. • The mature mRNAs in each tissue possess different exons, resulting in different polypeptide products from the same gene. ...
... • Introns are spliced out of pre-mRNAs to produce the mature mRNA that is translated. • Alternative splicing recognizes different splice sites in different tissue types. • The mature mRNAs in each tissue possess different exons, resulting in different polypeptide products from the same gene. ...
Information flow within the cell
... i every cell ll synthesize type) This information must be stored safely but be accessible ibl for f d decoding di Every time a cell divides, an accurate and full copy must be made and correctly segregated to the d daughter ht cell ll ...
... i every cell ll synthesize type) This information must be stored safely but be accessible ibl for f d decoding di Every time a cell divides, an accurate and full copy must be made and correctly segregated to the d daughter ht cell ll ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.