GENE THERAPY: REALITIES AND PROSPECTS
... Though this technology is less than two decades, it has already been applied to treat patients. There is still room for development in the future. ...
... Though this technology is less than two decades, it has already been applied to treat patients. There is still room for development in the future. ...
File
... of DNA, is only the length of one gene, has Uracil instead of Thymine. tRNA – single strands twisted into a clover shape, has an anticodon to match to the mRNA’s codon, carries amino acids. Protein – LARGE molecules (in comparison), made of amino acids formed into polypeptide chains. ...
... of DNA, is only the length of one gene, has Uracil instead of Thymine. tRNA – single strands twisted into a clover shape, has an anticodon to match to the mRNA’s codon, carries amino acids. Protein – LARGE molecules (in comparison), made of amino acids formed into polypeptide chains. ...
Colonial Influence
... runner will be determined with the help of his or her chromosomes. 3. What is a chromosome? Chromosomes come in pairs, and there are hundreds, sometimes thousands, of genes in one chromosome. The chromosomes and genes are made of DNA, which is short for deoxyribonucleic acid, and can be found in a c ...
... runner will be determined with the help of his or her chromosomes. 3. What is a chromosome? Chromosomes come in pairs, and there are hundreds, sometimes thousands, of genes in one chromosome. The chromosomes and genes are made of DNA, which is short for deoxyribonucleic acid, and can be found in a c ...
Biology Lecture 2 – Genes
... o Operator: binds repressor protein to prevent RNA polymerase from binding, or binds activator protein to facilitate RNA polymerase binding o Promoter: binds RNA polymerase in the absence of repressor o Multiple genes will appear on single transcript o Lac operon: repressor protein allosterically de ...
... o Operator: binds repressor protein to prevent RNA polymerase from binding, or binds activator protein to facilitate RNA polymerase binding o Promoter: binds RNA polymerase in the absence of repressor o Multiple genes will appear on single transcript o Lac operon: repressor protein allosterically de ...
Unit 4
... Know from AP Cliffs Book 11. Explain how viruses may cause disease symptoms, and describe some medical weapons used to fight viral infections. Damage or kill cells. In response to a viral infection, lysosomes may release hydrolytic enzymes. Be toxic themselves or cause infected cells to produce tox ...
... Know from AP Cliffs Book 11. Explain how viruses may cause disease symptoms, and describe some medical weapons used to fight viral infections. Damage or kill cells. In response to a viral infection, lysosomes may release hydrolytic enzymes. Be toxic themselves or cause infected cells to produce tox ...
Heredity Notes The passing of traits from parents to
... • When the sperm and egg meet in human reproduction the results are up to chancewith 23 pairs of chromosomes matching up, there are over 1,000,000 different combinations possible. You will never be identical to a brother or sister born at a different time. ...
... • When the sperm and egg meet in human reproduction the results are up to chancewith 23 pairs of chromosomes matching up, there are over 1,000,000 different combinations possible. You will never be identical to a brother or sister born at a different time. ...
8th Grade Science Second Semester 4th Grading Period
... LS4.A: Evidence of Common Ancestry and Diversity The collection of fossils and their placement in chronological order (e.g., through the location of the sedimentary layers in which they are found or through radioactive dating) is known as the fossil record. It documents the existence, diversity, ...
... LS4.A: Evidence of Common Ancestry and Diversity The collection of fossils and their placement in chronological order (e.g., through the location of the sedimentary layers in which they are found or through radioactive dating) is known as the fossil record. It documents the existence, diversity, ...
Biology – Wilson Name: Meiosis: DNA – NOVA: Life`s Greatest
... 16. Do the baby’s and mother’s blood ever mix? 17. Why is birth more dangerous for humans than for other animals? ...
... 16. Do the baby’s and mother’s blood ever mix? 17. Why is birth more dangerous for humans than for other animals? ...
Evolution of genes and genomes
... Most genes are evolving neutrally Some genes show adaptive evolution Polymorphisms in an allele are transient; a new allele that has arisen by mutation will either be fixed or lost by genetic drift Most change in DNA sequences will be in regions that do not affect fitness ...
... Most genes are evolving neutrally Some genes show adaptive evolution Polymorphisms in an allele are transient; a new allele that has arisen by mutation will either be fixed or lost by genetic drift Most change in DNA sequences will be in regions that do not affect fitness ...
Bioinformatics Tools
... “The field of science in which biology, computer science, and information technology merge to form a single discipline” ...
... “The field of science in which biology, computer science, and information technology merge to form a single discipline” ...
BIO 245: Principles of Genetics Course description BIO 245
... - Goal #1: To learn and apply concepts of modern transmission and molecular genetics. o Objective 1A: To identify and describe the process and purposes of the cell cycle, meiosis, and mitosis, as well as predict the outcomes of these processes. o Objective 1B: To solve transmission genetics problems ...
... - Goal #1: To learn and apply concepts of modern transmission and molecular genetics. o Objective 1A: To identify and describe the process and purposes of the cell cycle, meiosis, and mitosis, as well as predict the outcomes of these processes. o Objective 1B: To solve transmission genetics problems ...
Mouse Hox gene expression
... Modify forms & specializations of a subset of repeating units In most cases, this does not involve the evolution of new genes Most developmental changes due to: Changes in patterns of expression of Hox & other genes that control pattern formation. • This is caused by changes in their regulatory ...
... Modify forms & specializations of a subset of repeating units In most cases, this does not involve the evolution of new genes Most developmental changes due to: Changes in patterns of expression of Hox & other genes that control pattern formation. • This is caused by changes in their regulatory ...
No Slide Title
... Genetics Primer Gene: basic unit of heredity Protein: product of a gene Genotype: genetic makeup of an individual (sum of all the genes) Phenotype: observed traits of an individual, due to expression of its genes and interaction with the environment ...
... Genetics Primer Gene: basic unit of heredity Protein: product of a gene Genotype: genetic makeup of an individual (sum of all the genes) Phenotype: observed traits of an individual, due to expression of its genes and interaction with the environment ...
Bio07_TR__U04_CH12.QXD
... 16. A(An) ________________________ is made up of three parts: a deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. 17. The principle of _________________________ states that hydrogen bonds can form only between certain bases in DNA. ...
... 16. A(An) ________________________ is made up of three parts: a deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. 17. The principle of _________________________ states that hydrogen bonds can form only between certain bases in DNA. ...
Polygenic and Multifactoral Traits
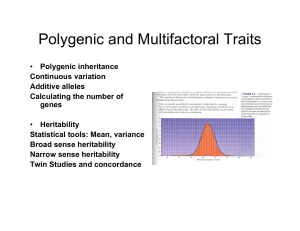
... Additive alleles Contribute a constant amount Non-additive add nothing All alleles add equally ...
... Additive alleles Contribute a constant amount Non-additive add nothing All alleles add equally ...
Science Notebook DNA, RNA, and Protein
... one amino acid nucleic acid made of ribose, phosphate, and one of four nitrogenous bases—adenine, cytosine, guanine, or uracil intervening DNA sequences that are transcribed and then removed from the final mRNA process by which mRNA directs the synthesis of a protein long strands of RNA that are com ...
... one amino acid nucleic acid made of ribose, phosphate, and one of four nitrogenous bases—adenine, cytosine, guanine, or uracil intervening DNA sequences that are transcribed and then removed from the final mRNA process by which mRNA directs the synthesis of a protein long strands of RNA that are com ...
Introduction to Genetics Terms
... 17. Incomplete Dominance: This is when one allele is not completely dominant over the other allele. For example, red and white flowers producing pink offspring. 18. Codominant Alleles: This is when both alleles contribute to the phenotype. For example, chickens that have black and white alleles have ...
... 17. Incomplete Dominance: This is when one allele is not completely dominant over the other allele. For example, red and white flowers producing pink offspring. 18. Codominant Alleles: This is when both alleles contribute to the phenotype. For example, chickens that have black and white alleles have ...
DNA and Gene Expression
... you want to know your genetic predispositions? • What if you were predisposed to an incurable disorder? • Complex interactions. Cognitive dissonance. • Probabilities and risk factors. Are people inherently good at these? • Support systems? ...
... you want to know your genetic predispositions? • What if you were predisposed to an incurable disorder? • Complex interactions. Cognitive dissonance. • Probabilities and risk factors. Are people inherently good at these? • Support systems? ...
Study Guide Genetics Final 2014
... 5. Where are proteins synthesized (in the process of translation) and how is this done? Explain each step. ...
... 5. Where are proteins synthesized (in the process of translation) and how is this done? Explain each step. ...
Notes - Humble ISD
... all genes on that chromosome! 2. These errors generally occur during meiosis or mitosis. 3. May result in a number disorder (extra chromosome or deleted chromosome) insertion, deletion, or translocation of a piece of chromosome and the corresponding genetic information. B. Gene Mutation Gene mutatio ...
... all genes on that chromosome! 2. These errors generally occur during meiosis or mitosis. 3. May result in a number disorder (extra chromosome or deleted chromosome) insertion, deletion, or translocation of a piece of chromosome and the corresponding genetic information. B. Gene Mutation Gene mutatio ...
HG06_geneexpression
... DNA is the gene,c material within the nucleus. The process of replica/on creates new copies of DNA. The process of transcrip/on creates an RNA using DNA informa,on. The process of transla ...
... DNA is the gene,c material within the nucleus. The process of replica/on creates new copies of DNA. The process of transcrip/on creates an RNA using DNA informa,on. The process of transla ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.