Sequence of events in formation of eukaryotic mRNA
... splicing to occur? What would happen if there was a mutation in a splice site consensus sequence? •What is the significance of the lariat structure in splicing out introns? ...
... splicing to occur? What would happen if there was a mutation in a splice site consensus sequence? •What is the significance of the lariat structure in splicing out introns? ...
RNA processing - Faculty Web Pages
... splicing to occur? What would happen if there was a mutation in a splice site consensus sequence? •What is the significance of the lariat structure in splicing out introns? ...
... splicing to occur? What would happen if there was a mutation in a splice site consensus sequence? •What is the significance of the lariat structure in splicing out introns? ...
12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... The sugar in RNA is ribose instead of deoxyribose. RNA is generally single-stranded. RNA contains uracil in place of thymine. Types of RNA There are three main types of RNA: messenger RNA ribosomal RNA transfer RNA Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries copies of instructions for assembling amin ...
... The sugar in RNA is ribose instead of deoxyribose. RNA is generally single-stranded. RNA contains uracil in place of thymine. Types of RNA There are three main types of RNA: messenger RNA ribosomal RNA transfer RNA Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries copies of instructions for assembling amin ...
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter #4
... piece the cell is working on. How many ATPs formed will also depend on this. ...
... piece the cell is working on. How many ATPs formed will also depend on this. ...
CHNOPS Simulating Protein Synthesis
... Genes are the units that determine inherited characteristics, such as hair color and blood type. Genes are lengths of DNA molecules that determine the structure of polypeptides (the building blocks of proteins) that our cells make. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines the sequence of amino ...
... Genes are the units that determine inherited characteristics, such as hair color and blood type. Genes are lengths of DNA molecules that determine the structure of polypeptides (the building blocks of proteins) that our cells make. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines the sequence of amino ...
File - MRS. WILSON Science
... During transcription, a gene is transferred into RNA. Specific DNA sequences and a combination of accessory proteins help RNA polymerase recognize the start of a gene. RNA polymerase is a large enzyme that bonds nucleotides together to make RNA. RNA polymerase, in combination with the other proteins ...
... During transcription, a gene is transferred into RNA. Specific DNA sequences and a combination of accessory proteins help RNA polymerase recognize the start of a gene. RNA polymerase is a large enzyme that bonds nucleotides together to make RNA. RNA polymerase, in combination with the other proteins ...
Genetics problems - University of Toronto Mississauga
... autosomal (not sex-linked) recessive trait. What is the probability that their first child will be an albino? A. ...
... autosomal (not sex-linked) recessive trait. What is the probability that their first child will be an albino? A. ...
Chap2 DNA RNA and Protein
... Usually, but not always, the first AUG to be encountered is the initiation codon. However, the AUG triplet is not sufficient to determine whether it is the start codon, it is recognized efficiently as the initiation codon only when it is in the right context. An initiation codon may be recognized in ...
... Usually, but not always, the first AUG to be encountered is the initiation codon. However, the AUG triplet is not sufficient to determine whether it is the start codon, it is recognized efficiently as the initiation codon only when it is in the right context. An initiation codon may be recognized in ...
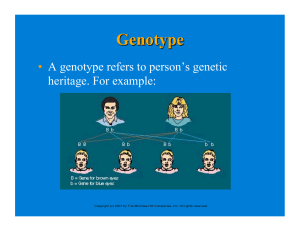
• A genotype refers to person`s genetic heritage. For example:
... traits are influenced by many pairs of genes in interaction with the environment. ...
... traits are influenced by many pairs of genes in interaction with the environment. ...
Genetics & Plant Breeding
... Sexual Propagation • Terms – DNA : Deoxyribonucleic Acid a polymeric molecule consisting of nucleotides (ribose, PO4, and adenine, cytosine, guanine, & thymine). Found in nucleus, chloroplasts, mitochondria. Makes RNA. ...
... Sexual Propagation • Terms – DNA : Deoxyribonucleic Acid a polymeric molecule consisting of nucleotides (ribose, PO4, and adenine, cytosine, guanine, & thymine). Found in nucleus, chloroplasts, mitochondria. Makes RNA. ...
Honors Biology
... information do they represent?, to what molecules do these terms refer to? redundancy of the DNA code: what advantage does having multiple codons for a single amino acid give when a mutation occurs? amino acid sequence in determining protein type: why is it important? transcription and mRNA pr ...
... information do they represent?, to what molecules do these terms refer to? redundancy of the DNA code: what advantage does having multiple codons for a single amino acid give when a mutation occurs? amino acid sequence in determining protein type: why is it important? transcription and mRNA pr ...
Chapter 8 Lecture Notes
... 7. RNA polymerase assembles the mRNA strand from free nucleotides through complimentary base pairing using the DNA template strand as a guide. 8. Transcription stops when the RNA polymerase reaches the terminator sequence, and the mRNA and the RNA polymerase are released from the DNA. 9. The process ...
... 7. RNA polymerase assembles the mRNA strand from free nucleotides through complimentary base pairing using the DNA template strand as a guide. 8. Transcription stops when the RNA polymerase reaches the terminator sequence, and the mRNA and the RNA polymerase are released from the DNA. 9. The process ...
Genetic Changes - Down the Rabbit Hole
... Significance of Mutations Most are neutral • Eye color • Birth marks • Some are harmful • Cystic Fibrosis • Down Syndrome • Some are beneficial • Sickle Cell Anemia to Malaria • Immunity to HIV ...
... Significance of Mutations Most are neutral • Eye color • Birth marks • Some are harmful • Cystic Fibrosis • Down Syndrome • Some are beneficial • Sickle Cell Anemia to Malaria • Immunity to HIV ...
Transgenic organisms - Ken Pitts` Biological Science Page
... 2) Human protein products such as insulin, growth hormone, and blood anti-clotting factors may soon be or have already been obtained from the milk of transgenic cows, sheep, or goats. Research is also underway to manufacture milk through transgenesis for treatment of debilitating diseases such as ph ...
... 2) Human protein products such as insulin, growth hormone, and blood anti-clotting factors may soon be or have already been obtained from the milk of transgenic cows, sheep, or goats. Research is also underway to manufacture milk through transgenesis for treatment of debilitating diseases such as ph ...
Recombinant DNA Technology
... • DNA library = collection of clones from one DNA donor – Categorized by: vector, source of DNA – Genomic library = all of the sequences from the genome of a single organism – cDNA library= complementary DNA, made using mRNA as a template ...
... • DNA library = collection of clones from one DNA donor – Categorized by: vector, source of DNA – Genomic library = all of the sequences from the genome of a single organism – cDNA library= complementary DNA, made using mRNA as a template ...
Subject:
... Bio.1.2.2 Analyze how cells grow and reproduce in terms of interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis. Bio.3.1.1 Explain the double-stranded, complementary nature of DNA as related to its function in the cell. Bio.3.1.2 Explain how DNA and RNA code for proteins and determine traits. Bio.3.1.3 Explain how m ...
... Bio.1.2.2 Analyze how cells grow and reproduce in terms of interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis. Bio.3.1.1 Explain the double-stranded, complementary nature of DNA as related to its function in the cell. Bio.3.1.2 Explain how DNA and RNA code for proteins and determine traits. Bio.3.1.3 Explain how m ...
slides
... Ura + cells. You inoculate a Ura + bacterium into media containing uracil and allow it to divide until there are 10 9 cells, which you then dilute and spread onto plates containing urabegone and uracil. You get 50 colonies in all. Which of the following statements are likely to be true? A. All of th ...
... Ura + cells. You inoculate a Ura + bacterium into media containing uracil and allow it to divide until there are 10 9 cells, which you then dilute and spread onto plates containing urabegone and uracil. You get 50 colonies in all. Which of the following statements are likely to be true? A. All of th ...
Chapter 13: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) DNA is the genetic material that is transmitted from one generation to the next and encodes the blueprints that direct the control of biochemical, anatomical, physiological, and behavioral traits of an organism. A strand of DNA is made up of nucleotide monomers, which co ...
... Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) DNA is the genetic material that is transmitted from one generation to the next and encodes the blueprints that direct the control of biochemical, anatomical, physiological, and behavioral traits of an organism. A strand of DNA is made up of nucleotide monomers, which co ...
How can my child have a condition passed from us if we are healthy?
... gene fault have a 1 in 4 chance of both passing on the gene that does not work to each child they have. ...
... gene fault have a 1 in 4 chance of both passing on the gene that does not work to each child they have. ...
3. polygenic traits
... Monogenic diseases form only a small portion of the total burden of human diseases (2%). A much larger component of our diseases burden is composed of congenital malformations and common adult diseases, such as cancer, heart disease, and diabetes. Although, they are not the result of single-gene mut ...
... Monogenic diseases form only a small portion of the total burden of human diseases (2%). A much larger component of our diseases burden is composed of congenital malformations and common adult diseases, such as cancer, heart disease, and diabetes. Although, they are not the result of single-gene mut ...
genetic engineering 2 - Hicksville Public Schools
... The combined DNA is called: Recombinant DNA 4)The recombinant DNA is inserted into the cell of another organism. ...
... The combined DNA is called: Recombinant DNA 4)The recombinant DNA is inserted into the cell of another organism. ...
Directed Reading B
... 14. What is the chance of a parent with one green allele and one blue allele giving a blue allele to an offspring? a. 100% chance b. 25% chance c. 50% chance d. 75% chance Read the description. Then, draw a line from the dot next to each ...
... 14. What is the chance of a parent with one green allele and one blue allele giving a blue allele to an offspring? a. 100% chance b. 25% chance c. 50% chance d. 75% chance Read the description. Then, draw a line from the dot next to each ...
Macro-Microarray
... of DNA that usually correspond to a known gene. These fragments serve as probes for the gene since complementary DNA (cDNA) will bind specifically to each fragment or “spot” on the array. Messenger RNA (mRNA) is extracted from cells and used as a template to create cDNA. This pool of cDNA is passed ...
... of DNA that usually correspond to a known gene. These fragments serve as probes for the gene since complementary DNA (cDNA) will bind specifically to each fragment or “spot” on the array. Messenger RNA (mRNA) is extracted from cells and used as a template to create cDNA. This pool of cDNA is passed ...
Final Exam Review
... called? (b) Give the complimentary tRNA sequence to the mRNA. What are the three letter “words” of tRNA called? (c) What is the amino acid sequence coded for by this DNA sequence? (d) A base is added as the result of exposure to acridine dye. At which position (2 or 4) would it have the most damagin ...
... called? (b) Give the complimentary tRNA sequence to the mRNA. What are the three letter “words” of tRNA called? (c) What is the amino acid sequence coded for by this DNA sequence? (d) A base is added as the result of exposure to acridine dye. At which position (2 or 4) would it have the most damagin ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.