KTH | BB2430 Gene Technology and Molecular Biology, theory 5.5
... After passing the course, the student should be able to: describe the function of commonly used enzymes within the field of molecular biotechnology from a given problem, design a suitable PCR-setup/strategy; for example, how to clone a certain gene, and explain the function of all necessary componen ...
... After passing the course, the student should be able to: describe the function of commonly used enzymes within the field of molecular biotechnology from a given problem, design a suitable PCR-setup/strategy; for example, how to clone a certain gene, and explain the function of all necessary componen ...
Lecture 14 Cloning and Expression E. coli Expression System
... The T7 polymerase is a processive enzyme that will transcribe around a circular plasmid several time and may transcribe genes that are not efficiently transcribed by E. coli enzyme. ...
... The T7 polymerase is a processive enzyme that will transcribe around a circular plasmid several time and may transcribe genes that are not efficiently transcribed by E. coli enzyme. ...
Biotechnology - University of California, Los Angeles
... 4. Overhanging sequence of bases left after DNA is “cut” 5. Substance that can be used to identify cells with our gene of interest ...
... 4. Overhanging sequence of bases left after DNA is “cut” 5. Substance that can be used to identify cells with our gene of interest ...
DNA replication
... strand) that tells the RNA polymerase both where to start and on which strand to continue synthesis. E.g. TATA box. • Terminator. Regulatory DNA region signaling end of transcription, at 3' end . • Transcription factor. A protein needed to initiate the transcription of a gene, binds either to specif ...
... strand) that tells the RNA polymerase both where to start and on which strand to continue synthesis. E.g. TATA box. • Terminator. Regulatory DNA region signaling end of transcription, at 3' end . • Transcription factor. A protein needed to initiate the transcription of a gene, binds either to specif ...
Macromolecules - Essentials Education
... poypeptides usually make up a protein. They can also code for the production of an RNA molecule. ...
... poypeptides usually make up a protein. They can also code for the production of an RNA molecule. ...
File
... Why are your eyes a certain color? What makes your hair brown, blonde, red, or somewhere in between? Genes from your parents determine these traits. Genes usually occur in pairs, and you get one from each parent. Two children with the same parents may have different hair or eye color because they re ...
... Why are your eyes a certain color? What makes your hair brown, blonde, red, or somewhere in between? Genes from your parents determine these traits. Genes usually occur in pairs, and you get one from each parent. Two children with the same parents may have different hair or eye color because they re ...
Understanding selectivity in the CRISPR CAS9 system
... be reduced to a minimum because its occurrence can lead to modifications of genes rather than the one effectively targeted, with unpredictable consequences. Hence, an important question is to understand what are the intrinsic limits in terms of targeting selectivity that such system must have. For e ...
... be reduced to a minimum because its occurrence can lead to modifications of genes rather than the one effectively targeted, with unpredictable consequences. Hence, an important question is to understand what are the intrinsic limits in terms of targeting selectivity that such system must have. For e ...
INTRODUCTION TO BIOLOGY Course Description This class
... 1) To study the structure, function and organization of cells and cellular organelles. (Midterm I) 2) To explore cellular processes such as cellular respiration, reproduction and communication. (Midterms I and II) 3) To understand the principles governing the genetics of inheritance. (Midterm III) 4 ...
... 1) To study the structure, function and organization of cells and cellular organelles. (Midterm I) 2) To explore cellular processes such as cellular respiration, reproduction and communication. (Midterms I and II) 3) To understand the principles governing the genetics of inheritance. (Midterm III) 4 ...
Lecture 7 Manipulation of gene expression and secretion of foreign
... The cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter is frequently used as a strong promoter in plant systems, although the level of expression of a foreign protein under the control of this promoter is often lower than desired. To address this problem, it is necessary to test different promoter—gene construct ...
... The cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter is frequently used as a strong promoter in plant systems, although the level of expression of a foreign protein under the control of this promoter is often lower than desired. To address this problem, it is necessary to test different promoter—gene construct ...
Cell Division
... DNA coils to form Chromosomes A Gene is a section of DNA Genetic info is encoded in sequence of base triplets, called codons ...
... DNA coils to form Chromosomes A Gene is a section of DNA Genetic info is encoded in sequence of base triplets, called codons ...
Glucose - St. Bonaventure College and High School
... Genetics is the study of heredity and variations. ...
... Genetics is the study of heredity and variations. ...
8.4 Transcription
... 8.4 Transcription • Transcription makes three types of RNA. – Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the message that will be translated to form a protein. – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) forms part of ribosomes where proteins are made. – Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings amino acids from the cytoplasm to a ribosome (to ass ...
... 8.4 Transcription • Transcription makes three types of RNA. – Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the message that will be translated to form a protein. – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) forms part of ribosomes where proteins are made. – Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings amino acids from the cytoplasm to a ribosome (to ass ...
Mutations
... Genotypic variation leads to phenotypic variation. Genotypic variation is stored in a population’s gene pool. Made up of all alleles in a population Allele combinations form when organisms have offspring. ...
... Genotypic variation leads to phenotypic variation. Genotypic variation is stored in a population’s gene pool. Made up of all alleles in a population Allele combinations form when organisms have offspring. ...
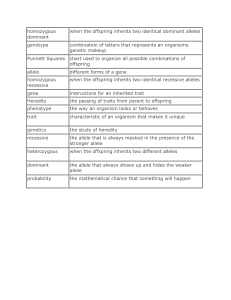
homozygous dominant when the offspring inherits two identical
... the allele that is always masked in the presence of the stronger allele ...
... the allele that is always masked in the presence of the stronger allele ...
Mentor: James A. MacKay Students: Amanda Williams, Holly Sofka
... Students: Amanda Williams, Holly Sofka Project Description: Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is believed to be an important molecule in the evolution of life and has functionally taken on many important biological roles. Given the many functions of RNA, molecular recognition of RNA represents an attractive go ...
... Students: Amanda Williams, Holly Sofka Project Description: Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is believed to be an important molecule in the evolution of life and has functionally taken on many important biological roles. Given the many functions of RNA, molecular recognition of RNA represents an attractive go ...
Gene Mapping Techniques - Nestlé Nutrition Institute
... hybridized with a sample of DNA prepared from interspecific cell hybrids segregating for a given set of chromosomes it is possible to identify, at least roughly, where the locus coding for this gene is located by matching the pattern of positive hybridizations with the pattern of chromosome presence ...
... hybridized with a sample of DNA prepared from interspecific cell hybrids segregating for a given set of chromosomes it is possible to identify, at least roughly, where the locus coding for this gene is located by matching the pattern of positive hybridizations with the pattern of chromosome presence ...
GENETICS – BIO 300
... element family many other families discovered in maize autonomous elements encode information necessary for the transposition of themselves and nonautonomous members of their family ...
... element family many other families discovered in maize autonomous elements encode information necessary for the transposition of themselves and nonautonomous members of their family ...
Spring Semester Exam Study Guide- Biology Every cell contains
... 35. Homologous genes are genes that descend from the same common ancestor gene in different species. A scientist sequences homologous genes in several different related species. To find out which two species are most closely related, how should the scientist analyze the data? a. Count the number of ...
... 35. Homologous genes are genes that descend from the same common ancestor gene in different species. A scientist sequences homologous genes in several different related species. To find out which two species are most closely related, how should the scientist analyze the data? a. Count the number of ...
Chapter 13 Presentation-Meiosis and Chromosomes
... organism to the next within a species. They are the vehicles of heredity. Minor differences in the sequences of base pairs on these chromosomes is what contributes to variation. ...
... organism to the next within a species. They are the vehicles of heredity. Minor differences in the sequences of base pairs on these chromosomes is what contributes to variation. ...
Slide 1
... Transcription – the genetic information from a strand of DNA is copied into a strand of mRNA 2. Translation – the mRNA, with the help of the ribosome, forms a chain of amino acids (eventually forming a protein) based on the information contained on the mRNA. ...
... Transcription – the genetic information from a strand of DNA is copied into a strand of mRNA 2. Translation – the mRNA, with the help of the ribosome, forms a chain of amino acids (eventually forming a protein) based on the information contained on the mRNA. ...
practice exam 3_answer key
... c. sister chromatids are attached to one another d. centrioles are located e. chromosomes are grouped during telophase 10. What is a sister chromatid? a. a chromosome found outside the nucleus b. a special region that holds two centromeres together c. another name for the chromosomes found in geneti ...
... c. sister chromatids are attached to one another d. centrioles are located e. chromosomes are grouped during telophase 10. What is a sister chromatid? a. a chromosome found outside the nucleus b. a special region that holds two centromeres together c. another name for the chromosomes found in geneti ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.