AP Exam 5 Study Guide
... Step 1- DNA is unwound with an enzyme called helicase. This causes a replication fork to form. The replication fork is stabilized with single-stranded binding proteins. There are multiple replication forks in a DNA molecule at one time. Step 2- New nucleotides are brought in to match up to the templ ...
... Step 1- DNA is unwound with an enzyme called helicase. This causes a replication fork to form. The replication fork is stabilized with single-stranded binding proteins. There are multiple replication forks in a DNA molecule at one time. Step 2- New nucleotides are brought in to match up to the templ ...
PDF - AntiMatters
... “blank slate.” The tabula rasa concept was also central to the psychoanalysis of Freud, who held that one is largely determined by one’s upbringing, and in the 20th century it became popular in the social sciences. Yet nothing could be further from the truth. Already at birth, every (human) brain is ...
... “blank slate.” The tabula rasa concept was also central to the psychoanalysis of Freud, who held that one is largely determined by one’s upbringing, and in the 20th century it became popular in the social sciences. Yet nothing could be further from the truth. Already at birth, every (human) brain is ...
Chromosomes Eukaryote
... •(Mostly) numbered from biggest to smallest. •Help organize, protect, and regulate the expression of DNA. •Are only this compact during cell division. •Do not come in 23 colors. ...
... •(Mostly) numbered from biggest to smallest. •Help organize, protect, and regulate the expression of DNA. •Are only this compact during cell division. •Do not come in 23 colors. ...
Genome
... • ...just as bad, the project didn't even amount to hypothesisdriven science at all. Rather, critics charged, it was no more than a big fishing expedition, a mindless factory project that no scientists in their right minds would join. Science 291 (5507), 1182 ...
... • ...just as bad, the project didn't even amount to hypothesisdriven science at all. Rather, critics charged, it was no more than a big fishing expedition, a mindless factory project that no scientists in their right minds would join. Science 291 (5507), 1182 ...
Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... the condition (example: cystic fibrosis) • Huntington’s disease is an autosomal dominant disorder meaning that is a single Huntingtons allele is inherited, the individual will have the disease. ...
... the condition (example: cystic fibrosis) • Huntington’s disease is an autosomal dominant disorder meaning that is a single Huntingtons allele is inherited, the individual will have the disease. ...
Lecture 1
... • ...just as bad, the project didn't even amount to hypothesisdriven science at all. Rather, critics charged, it was no more than a big fishing expedition, a mindless factory project that no scientists in their right minds would join. Science 291 (5507), 1182 ...
... • ...just as bad, the project didn't even amount to hypothesisdriven science at all. Rather, critics charged, it was no more than a big fishing expedition, a mindless factory project that no scientists in their right minds would join. Science 291 (5507), 1182 ...
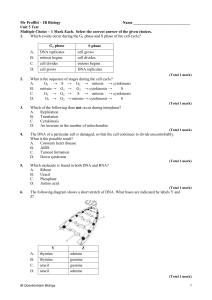
Mr Proffitt – IB Biology Name Unit 3 Test Multiple Choice – 1 Mark
... A sequence of nucleotides on rRNA that corresponds to an amino acid B. A sequence of nucleotides on mRNA that corresponds to an amino acid C. A sequence of nucleotides on tRNA that corresponds to an amino acid D. A sequence of nucleotides on DNA that corresponds to an amino acid (Total 1 mark) ...
... A sequence of nucleotides on rRNA that corresponds to an amino acid B. A sequence of nucleotides on mRNA that corresponds to an amino acid C. A sequence of nucleotides on tRNA that corresponds to an amino acid D. A sequence of nucleotides on DNA that corresponds to an amino acid (Total 1 mark) ...
Standard Grade Biology – Investigating Cells
... What do you notice about how the bases pair up? ______________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Each section of DNA is called a ______________. Each gene contains the instructions for building a different ______________. Ex ...
... What do you notice about how the bases pair up? ______________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Each section of DNA is called a ______________. Each gene contains the instructions for building a different ______________. Ex ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... are determined by RNA templates by employing a universal code called the genetic code. For survival of a species it is essential that the genetic information is utilised in an accurate manner and therefore nature has evolved distinct machineries for the faithful copying of all these templates into t ...
... are determined by RNA templates by employing a universal code called the genetic code. For survival of a species it is essential that the genetic information is utilised in an accurate manner and therefore nature has evolved distinct machineries for the faithful copying of all these templates into t ...
Heredity
... Mendel realized that each parent must have 2 “sets of instructions” for each trait ◦ When parents reproduced they each gave their offspring one set of each of their instructions (the child will then end up with 2 “sets of instructions” for each trait ...
... Mendel realized that each parent must have 2 “sets of instructions” for each trait ◦ When parents reproduced they each gave their offspring one set of each of their instructions (the child will then end up with 2 “sets of instructions” for each trait ...
Slide 1
... Step 2: Anneal – The primers cannot bind to the DNA strands at such a high temperature, so the vial is cooled to 60°C. At this temperature, the primers bind (anneal) to the single-stranded DNA. Step 3: Extend – is to allow the DNA polymerase to extend the copy DNA strand by raising the temperature t ...
... Step 2: Anneal – The primers cannot bind to the DNA strands at such a high temperature, so the vial is cooled to 60°C. At this temperature, the primers bind (anneal) to the single-stranded DNA. Step 3: Extend – is to allow the DNA polymerase to extend the copy DNA strand by raising the temperature t ...
Genetics HARDCOPY - New Hartford Central Schools
... 4. A freckled faced man has 3 children with a woman who has no freckles. They have 2 daughters, 1 with freckles and 1 without freckles, and a son who does not have freckles. [Shade in freckles.] ...
... 4. A freckled faced man has 3 children with a woman who has no freckles. They have 2 daughters, 1 with freckles and 1 without freckles, and a son who does not have freckles. [Shade in freckles.] ...
BIO 208 TERMS AND OBJECTIVES s08 Objectives Unit 2 Ch 4, 11
... 26. To transform competent E. coli with a GFP-containing plasmid (lab) 27. To calculate transformation efficiency (colonies/ug DNA) from given data (lab) 28. To contrast constitutively expressed housekeeping genes and genes that are regulated 29. To describe an operon and the usefulness to prokaryot ...
... 26. To transform competent E. coli with a GFP-containing plasmid (lab) 27. To calculate transformation efficiency (colonies/ug DNA) from given data (lab) 28. To contrast constitutively expressed housekeeping genes and genes that are regulated 29. To describe an operon and the usefulness to prokaryot ...
Genes and DNA2012
... you eat. Animals and plants also have genomes, do not forget. So, when you eat vegetables or any kind of meat or fruit, you're also ingesting that organism's genome. So, your body metabolizes all these things, along with proteins, lipids, carbs, etc. So, the nucleic acids are metabolized and broken ...
... you eat. Animals and plants also have genomes, do not forget. So, when you eat vegetables or any kind of meat or fruit, you're also ingesting that organism's genome. So, your body metabolizes all these things, along with proteins, lipids, carbs, etc. So, the nucleic acids are metabolized and broken ...
TAKS Review - SchoolNotes
... A biologist collects DNA samples from 2 sisters. The younger sister has blond hair. The older sister has red hair. The sisters have different traits because their DNA contains different A. orders of nucleotides B. types of sugar molecules C. sized phosphate groups D. types of nitrogenous bases ...
... A biologist collects DNA samples from 2 sisters. The younger sister has blond hair. The older sister has red hair. The sisters have different traits because their DNA contains different A. orders of nucleotides B. types of sugar molecules C. sized phosphate groups D. types of nitrogenous bases ...
Hemochromatosis gene nomenclature
... The gene symbol HFE has been in existence for many years in the human genetics community as the designated symbol for the gene for hemochromatosis, not of course identified at that time. The late Dr. Phyllis McAlpine, former chair of the Human Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC), approved the symbol ...
... The gene symbol HFE has been in existence for many years in the human genetics community as the designated symbol for the gene for hemochromatosis, not of course identified at that time. The late Dr. Phyllis McAlpine, former chair of the Human Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC), approved the symbol ...
Genetics practice test
... resistance of rare African rice varieties with the productivity and faster maturity of common Asian varieties. Another variety, called Stress-Tolerant Rice, was produced by inserting a pair of bacterial genes into rice plants for the production of trehalose (a sugar). Trehalose helps plants maintain ...
... resistance of rare African rice varieties with the productivity and faster maturity of common Asian varieties. Another variety, called Stress-Tolerant Rice, was produced by inserting a pair of bacterial genes into rice plants for the production of trehalose (a sugar). Trehalose helps plants maintain ...
When gene marriages don`t work out: divorce by subfunctionalization
... complementary, degenerative mutations. Genetics 151, 1531–1545 2 Lynch, M. (2004) Gene duplication and evolution. In Evolution: From Molecules to Ecosystems (Moya, A. and Font, E., eds), pp. 33–47, Oxford ...
... complementary, degenerative mutations. Genetics 151, 1531–1545 2 Lynch, M. (2004) Gene duplication and evolution. In Evolution: From Molecules to Ecosystems (Moya, A. and Font, E., eds), pp. 33–47, Oxford ...
Figure 3 (Biorad Laboratories, Inc.)
... expression of the GFP gene. How does it do this? To understand the mechanism, you must first understand how an operon works. Operons are stretches of DNA in bacterial cells that simultaneously control the expression of a group of genes. The genes in the operon generally code for proteins required in ...
... expression of the GFP gene. How does it do this? To understand the mechanism, you must first understand how an operon works. Operons are stretches of DNA in bacterial cells that simultaneously control the expression of a group of genes. The genes in the operon generally code for proteins required in ...
GENETICS
... Incomplete dominance – A form of dominance occurring in heterozygotes in which the dominant allele is only partially expressed, and usually resulting in an offspring with an intermediate phenotype. Alleles blend to create a new phenotype in the heterozygote! Example: In snapdragons, flower color can ...
... Incomplete dominance – A form of dominance occurring in heterozygotes in which the dominant allele is only partially expressed, and usually resulting in an offspring with an intermediate phenotype. Alleles blend to create a new phenotype in the heterozygote! Example: In snapdragons, flower color can ...
Lecture 14 Cloning and Expression E. coli Expression System
... The T7 polymerase is a processive enzyme that will transcribe around a circular plasmid several time and may transcribe genes that are not efficiently transcribed by E. coli enzyme. ...
... The T7 polymerase is a processive enzyme that will transcribe around a circular plasmid several time and may transcribe genes that are not efficiently transcribed by E. coli enzyme. ...
DNA replication
... strand) that tells the RNA polymerase both where to start and on which strand to continue synthesis. E.g. TATA box. • Terminator. Regulatory DNA region signaling end of transcription, at 3' end . • Transcription factor. A protein needed to initiate the transcription of a gene, binds either to specif ...
... strand) that tells the RNA polymerase both where to start and on which strand to continue synthesis. E.g. TATA box. • Terminator. Regulatory DNA region signaling end of transcription, at 3' end . • Transcription factor. A protein needed to initiate the transcription of a gene, binds either to specif ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.