Gene prediction
... to the same news in a foreign language, some similarities may become apparent ...
... to the same news in a foreign language, some similarities may become apparent ...
point of view that is personal rather than scientific
... the chronological order of the important discoveries in the structure of DNA is: Chargaff’s ratios of nucleotides Franklin makes an X-ray diffraction photo of DNA Watson and Crick identify the double helix ...
... the chronological order of the important discoveries in the structure of DNA is: Chargaff’s ratios of nucleotides Franklin makes an X-ray diffraction photo of DNA Watson and Crick identify the double helix ...
chapter 13 lecture slides
... • Mitochondria and chloroplasts contain genes • Traits controlled by these genes do not follow the chromosomal theory of inheritance • Genes from mitochondria and chloroplasts are often passed to the offspring by only one parent (mother) – Maternal inheritance ...
... • Mitochondria and chloroplasts contain genes • Traits controlled by these genes do not follow the chromosomal theory of inheritance • Genes from mitochondria and chloroplasts are often passed to the offspring by only one parent (mother) – Maternal inheritance ...
CH3L2
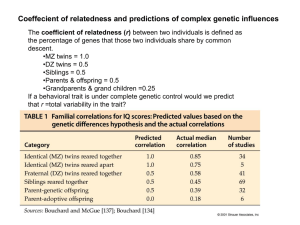
... Coeffecient of relatedness and predictions of complex genetic influences The coefficient of relatedness (r) between two individuals is defined as the percentage of genes that those two individuals share by common descent. •MZ twins = 1.0 •DZ twins = 0.5 •Siblings = 0.5 •Parents & offspring = 0.5 •Gr ...
... Coeffecient of relatedness and predictions of complex genetic influences The coefficient of relatedness (r) between two individuals is defined as the percentage of genes that those two individuals share by common descent. •MZ twins = 1.0 •DZ twins = 0.5 •Siblings = 0.5 •Parents & offspring = 0.5 •Gr ...
sample - Mouse Genome Informatics
... the same set of genes • Individual differences are due to allelic variation • “natural” background (eg. inbred line) • engineered variation (eg. knockout) ...
... the same set of genes • Individual differences are due to allelic variation • “natural” background (eg. inbred line) • engineered variation (eg. knockout) ...
Regulating Evolution - Nicolas Gompel`s lab
... The expression of a gene entails the transcription of the DNA sequence into a messenger RNA (mRNA) version and the translation of that mRNA into a protein sequence. The expression of most genes is regulated at the transcriptional level— cells do not waste energy making mRNAs and proteins they do no ...
... The expression of a gene entails the transcription of the DNA sequence into a messenger RNA (mRNA) version and the translation of that mRNA into a protein sequence. The expression of most genes is regulated at the transcriptional level— cells do not waste energy making mRNAs and proteins they do no ...
Mom and Dad are Fighting
... perhaps hundreds, of genes depend on whether you inherited them from your mother or your father. Dissimilarities arise because not all genes are actively expressed in our cells. Some of the genes get switched off, or silenced. Each time a cell divides and makes a new copy of its DNA, special enzymes ...
... perhaps hundreds, of genes depend on whether you inherited them from your mother or your father. Dissimilarities arise because not all genes are actively expressed in our cells. Some of the genes get switched off, or silenced. Each time a cell divides and makes a new copy of its DNA, special enzymes ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... from a strand of DNA is copied into a strand of mRNA 2. Translation – the mRNA, with the help of the ribosome, forms a chain of amino acids (eventually forming a protein) based on the information contained on the mRNA. ...
... from a strand of DNA is copied into a strand of mRNA 2. Translation – the mRNA, with the help of the ribosome, forms a chain of amino acids (eventually forming a protein) based on the information contained on the mRNA. ...
Modifier genes in Huntington`s desease - Ruhr
... phenotype, thirteen SNPs that define the major European mtDNA haplogroups were analysed. Genotype-dependent functional effects on intracellular ATP concentrations were assessed in peripheral leukocytes. In patients carrying the most common haplogroup H (48.3%), a significantly lower AO demonstrated ...
... phenotype, thirteen SNPs that define the major European mtDNA haplogroups were analysed. Genotype-dependent functional effects on intracellular ATP concentrations were assessed in peripheral leukocytes. In patients carrying the most common haplogroup H (48.3%), a significantly lower AO demonstrated ...
Plant Nuclear Genome Size Variation
... Most are likely paleopolyploids Aneuploid variation – gain or less of one or more chromosomes ...
... Most are likely paleopolyploids Aneuploid variation – gain or less of one or more chromosomes ...
Cells
... A mutation occurs when the sequence of bases in a gene is altered. Mutations may interfere with an organisms ability to produce vital protein and may lead to a new variety within the species, hence, evolution. ...
... A mutation occurs when the sequence of bases in a gene is altered. Mutations may interfere with an organisms ability to produce vital protein and may lead to a new variety within the species, hence, evolution. ...
The Human Genome Project
... body can make many kinds of proteins. (This process is called alternative splicing.) • If a gene is “expressed” that means it is turned on and it will make proteins. ...
... body can make many kinds of proteins. (This process is called alternative splicing.) • If a gene is “expressed” that means it is turned on and it will make proteins. ...
Define inheritance as the transmission of
... Describe how some alleles are on the X and Y sex chromosomes Understand how to use pedigree charts to make predictions about inheritance of a specific trait. Be able to make a pedigree chart showing a gene/allele being pass from one generation to the next. Calculate and predict the genotypic ...
... Describe how some alleles are on the X and Y sex chromosomes Understand how to use pedigree charts to make predictions about inheritance of a specific trait. Be able to make a pedigree chart showing a gene/allele being pass from one generation to the next. Calculate and predict the genotypic ...
Yr 10 Genetics File
... bodies (except our eggs or sperm – they have a half set of only 23 chromosomes.) ...
... bodies (except our eggs or sperm – they have a half set of only 23 chromosomes.) ...
DNA RNA structure
... DNA is in the nucleus. RNA is made in the nucleus but travels to the cytoplasm • RNA is made in the nucleoli but can travel out to the cytoplasm ...
... DNA is in the nucleus. RNA is made in the nucleus but travels to the cytoplasm • RNA is made in the nucleoli but can travel out to the cytoplasm ...
Chapter 4 – The Nucleus Controls the Functions of
... Science 9 – The Nucleus: Control Centre of the Cell 1. The nucleus is the control centre of the cell. What 3 sets of instructions does it determine for the cell? 2. What does DNA stand for? 3. The actual DNA structure is not really like a ladder, but like two coils wrapped around each other. This s ...
... Science 9 – The Nucleus: Control Centre of the Cell 1. The nucleus is the control centre of the cell. What 3 sets of instructions does it determine for the cell? 2. What does DNA stand for? 3. The actual DNA structure is not really like a ladder, but like two coils wrapped around each other. This s ...
Computational methods for the analysis of bacterial gene regulation
... operons (Fig. 1) and their occurrences offer one of the most important mechanisms of transcriptional regulation in bacterial cells. This mechanism of transcriptional coordination is present in all prokaryotes and it has been estimated that approximately 50% of all genes in bact ...
... operons (Fig. 1) and their occurrences offer one of the most important mechanisms of transcriptional regulation in bacterial cells. This mechanism of transcriptional coordination is present in all prokaryotes and it has been estimated that approximately 50% of all genes in bact ...
CHAPTER 1 – INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS I. SYLLABUS A
... a) Carl Correns, Hugo de Vries, and Erik von Tschermak rediscover Mendel’s work. b) Chromosome theory of inheritance (discussed in more detail later) E. The Dawn of Molecular Biology (1940’s-present) ...
... a) Carl Correns, Hugo de Vries, and Erik von Tschermak rediscover Mendel’s work. b) Chromosome theory of inheritance (discussed in more detail later) E. The Dawn of Molecular Biology (1940’s-present) ...
Linkage and Recombination
... You can think of recombination as a "cut and paste" of the two different forms of a gene within a single person. So far we've been thinking about each person as having either A, B or O type genes. But remember that every person actually has two different forms of a gene -- one from each parent. By t ...
... You can think of recombination as a "cut and paste" of the two different forms of a gene within a single person. So far we've been thinking about each person as having either A, B or O type genes. But remember that every person actually has two different forms of a gene -- one from each parent. By t ...
this poster
... in maize. Transcriptional profiling of ovaries from ago104 mutants showed an abundance of transcripts from transposons and repeats compared to the wild type plants suggesting a female gametophytic mechanism for transposon silencing in maize. We are further studying the role of AGO4-like proteins in ...
... in maize. Transcriptional profiling of ovaries from ago104 mutants showed an abundance of transcripts from transposons and repeats compared to the wild type plants suggesting a female gametophytic mechanism for transposon silencing in maize. We are further studying the role of AGO4-like proteins in ...
Lecture file (PowerPoint) - Department of Molecular & Cell Biology
... adults, to being relatively well even until old age. Increasing numbers of genetic loci have now been identified that can modulate sickle cell disease phenotype, from nucleotide motifs within the beta-globin gene cluster, to genes located on different chromosomes. With recent success of the human ge ...
... adults, to being relatively well even until old age. Increasing numbers of genetic loci have now been identified that can modulate sickle cell disease phenotype, from nucleotide motifs within the beta-globin gene cluster, to genes located on different chromosomes. With recent success of the human ge ...
Chapter 6 and 9 - Wando High School
... 12. Describe what happens during Interphase. Draw how a cell may appear during this phase. DNA is replicated Chromosomes are not yet visible Proteins and RNA are synthesized Cell is preparing for Meiosis 13. Is there an Interphase between Meiosis I and Meiosis II? No 14. Describe crossing over and w ...
... 12. Describe what happens during Interphase. Draw how a cell may appear during this phase. DNA is replicated Chromosomes are not yet visible Proteins and RNA are synthesized Cell is preparing for Meiosis 13. Is there an Interphase between Meiosis I and Meiosis II? No 14. Describe crossing over and w ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.