File
... 1-4. Regression vs. Causation: Regression does not necessarily imply causation. A statistical relationship cannot logically imply causation. “A statistical relationship, however strong and however suggestive, can never establish causal connection: our ideas of causation must come from outside stati ...
... 1-4. Regression vs. Causation: Regression does not necessarily imply causation. A statistical relationship cannot logically imply causation. “A statistical relationship, however strong and however suggestive, can never establish causal connection: our ideas of causation must come from outside stati ...
Brief Summary of Quantitative Data Analysis
... Graphs like bar or pie graphs are used to display nominal or ordinal data Histograms and line graphs (frequency polygons) can display interval/ratio level data. Bivariate relationships can be displayed using contingency tables (nominal or ordinal) Relationships at the interval/ratio level are displa ...
... Graphs like bar or pie graphs are used to display nominal or ordinal data Histograms and line graphs (frequency polygons) can display interval/ratio level data. Bivariate relationships can be displayed using contingency tables (nominal or ordinal) Relationships at the interval/ratio level are displa ...
Correlation and Regression
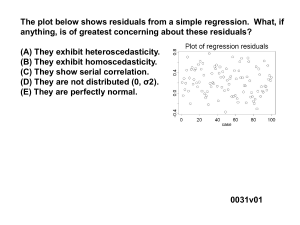
... The plot below shows residuals from a simple regression. What, if anything, is of greatest concerning about these residuals? (A) They exhibit heteroscedasticity. (B) They exhibit homoscedasticity. (C) They show serial correlation. (D) They are not distributed (0, σ2). (E) They are perfectly normal. ...
... The plot below shows residuals from a simple regression. What, if anything, is of greatest concerning about these residuals? (A) They exhibit heteroscedasticity. (B) They exhibit homoscedasticity. (C) They show serial correlation. (D) They are not distributed (0, σ2). (E) They are perfectly normal. ...
When to Use a Particular Statistical Test
... Leerkes and Crockenberg (1999) were studying the relationship between how a new mother was raised by her own mother 20+ years before (A=maternal care) and the new mother's level of selfefficacy as a mother (C=self-efficacy). The idea being that if your mother showed high levels of maternal care towa ...
... Leerkes and Crockenberg (1999) were studying the relationship between how a new mother was raised by her own mother 20+ years before (A=maternal care) and the new mother's level of selfefficacy as a mother (C=self-efficacy). The idea being that if your mother showed high levels of maternal care towa ...
Running a Moderated Regression
... something beginning with an “i” helps denote an interaction term). Place the variables that you want to create an interaction term from in the box that says “numeric expression.” You must multiply your variables together. For example, if you want to create an interaction between “ragree” and “recip” ...
... something beginning with an “i” helps denote an interaction term). Place the variables that you want to create an interaction term from in the box that says “numeric expression.” You must multiply your variables together. For example, if you want to create an interaction between “ragree” and “recip” ...
Models for Probability Distributions and Density Functions
... quantized version of real-valued X) • Other measures of the relationship between Y and X’s can also be used ...
... quantized version of real-valued X) • Other measures of the relationship between Y and X’s can also be used ...
Causality and confounding variables
... The ‘unstandardized coefficients’ give us the values of a and b in the regression equation. Thus the equation here is y = -8.219 + 0.457x The final column ‘Sig.’ gives values less than 0.01 thus we can say that the coefficients of the regression equation are significantly different from zero at the ...
... The ‘unstandardized coefficients’ give us the values of a and b in the regression equation. Thus the equation here is y = -8.219 + 0.457x The final column ‘Sig.’ gives values less than 0.01 thus we can say that the coefficients of the regression equation are significantly different from zero at the ...
Practice Exam
... Does a scatter plot suggest that the simple linear regression model will describe the relationship between the two variables? c. The summary statistics are Determine the equation of the least squares line. d. Predict the percentage of damaged squares when the age is 20 days by giving an interval of ...
... Does a scatter plot suggest that the simple linear regression model will describe the relationship between the two variables? c. The summary statistics are Determine the equation of the least squares line. d. Predict the percentage of damaged squares when the age is 20 days by giving an interval of ...
Interaction (statistics)
In statistics, an interaction may arise when considering the relationship among three or more variables, and describes a situation in which the simultaneous influence of two variables on a third is not additive. Most commonly, interactions are considered in the context of regression analyses.The presence of interactions can have important implications for the interpretation of statistical models. If two variables of interest interact, the relationship between each of the interacting variables and a third ""dependent variable"" depends on the value of the other interacting variable. In practice, this makes it more difficult to predict the consequences of changing the value of a variable, particularly if the variables it interacts with are hard to measure or difficult to control.The notion of ""interaction"" is closely related to that of ""moderation"" that is common in social and health science research: the interaction between an explanatory variable and an environmental variable suggests that the effect of the explanatory variable has been moderated or modified by the environmental variable.