Document
... – Use a calculator to find the correlation and leastsquare regression line. – Recognize the regression setting for a line. – Recognize the type of inference needed in a particular regression setting. – Inspect data for non-linear relationship, influential observations, skewed data, or nonconstant va ...
... – Use a calculator to find the correlation and leastsquare regression line. – Recognize the regression setting for a line. – Recognize the type of inference needed in a particular regression setting. – Inspect data for non-linear relationship, influential observations, skewed data, or nonconstant va ...
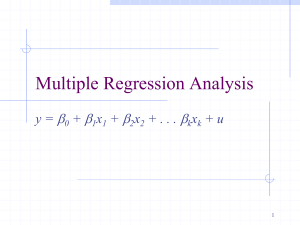
Multiple Regression
... Parallels with Simple Regression b0 is still the intercept b1 to bk all called slope parameters u is still the error term (or disturbance) Still need to make a zero conditional mean assumption, so now assume that E(u|x1,x2, …,xk) = 0 Still minimizing the sum of squared residuals, so have k+1 first ...
... Parallels with Simple Regression b0 is still the intercept b1 to bk all called slope parameters u is still the error term (or disturbance) Still need to make a zero conditional mean assumption, so now assume that E(u|x1,x2, …,xk) = 0 Still minimizing the sum of squared residuals, so have k+1 first ...
Session 7-9
... In statistics, you can analyze data based on a whole population, but more often you deal with sample data drawn from a given population. In this case, you need a decision rule that tells you if the values of the parameters of your sample-based linear regression model are likely to be close to the ‘t ...
... In statistics, you can analyze data based on a whole population, but more often you deal with sample data drawn from a given population. In this case, you need a decision rule that tells you if the values of the parameters of your sample-based linear regression model are likely to be close to the ‘t ...
Case statistics
... It is desirable to have measure of how well the regression model actually fits the data. More specifically, it is desirable to have an answer to the question ‘how well does the model containing the independent variables that was proposed actually explain the variation in the dependent variable?’ We ...
... It is desirable to have measure of how well the regression model actually fits the data. More specifically, it is desirable to have an answer to the question ‘how well does the model containing the independent variables that was proposed actually explain the variation in the dependent variable?’ We ...
0.1 Multiple Regression Models
... the sample variability in y can be explained through the linear model applied. For the example the output shows an R2 = 0.529. About 53% of the variation in the weight change can be explained through different values in acid-detergent fibre and digestion efficiency. R2 close to one indicates a very ...
... the sample variability in y can be explained through the linear model applied. For the example the output shows an R2 = 0.529. About 53% of the variation in the weight change can be explained through different values in acid-detergent fibre and digestion efficiency. R2 close to one indicates a very ...
Interaction (statistics)
In statistics, an interaction may arise when considering the relationship among three or more variables, and describes a situation in which the simultaneous influence of two variables on a third is not additive. Most commonly, interactions are considered in the context of regression analyses.The presence of interactions can have important implications for the interpretation of statistical models. If two variables of interest interact, the relationship between each of the interacting variables and a third ""dependent variable"" depends on the value of the other interacting variable. In practice, this makes it more difficult to predict the consequences of changing the value of a variable, particularly if the variables it interacts with are hard to measure or difficult to control.The notion of ""interaction"" is closely related to that of ""moderation"" that is common in social and health science research: the interaction between an explanatory variable and an environmental variable suggests that the effect of the explanatory variable has been moderated or modified by the environmental variable.