Mendel/Genetics Enduring Understandings • The work of Gregor
... • What are different patterns by which heritable information passed from one generation to the next? • How does this unit provide evidence of the relatedness of living things in the world? Targets Vocabulary—Heredity, genetics, pea plants, monohybrid cross, true-breeding/purebreeding, P generation, ...
... • What are different patterns by which heritable information passed from one generation to the next? • How does this unit provide evidence of the relatedness of living things in the world? Targets Vocabulary—Heredity, genetics, pea plants, monohybrid cross, true-breeding/purebreeding, P generation, ...
Traits: The Puppeteering of Genetics
... multiple unrelated phenotypic traits ◦ Pleio- = Many; -tropic = affecting ...
... multiple unrelated phenotypic traits ◦ Pleio- = Many; -tropic = affecting ...
6. What is quantitative genetic variation?
... in progeny (as was Mendel's approach), one can deduce ...
... in progeny (as was Mendel's approach), one can deduce ...
Inheritance - Glen Rose FFA
... a leg does that mean his children will be born with out a leg???? ...
... a leg does that mean his children will be born with out a leg???? ...
Chapter 17 Test Study Topics
... Test Date: Monday, April 4 Section 17-1: Genes and Variation Terms to define/identify/give an example: Allele frequency Gene pool Polygenic trait Single-gene trait Other topics to know: - The genetic definition of evolution - Now natural selection affects genotypes by acting on phenotypes - Sources ...
... Test Date: Monday, April 4 Section 17-1: Genes and Variation Terms to define/identify/give an example: Allele frequency Gene pool Polygenic trait Single-gene trait Other topics to know: - The genetic definition of evolution - Now natural selection affects genotypes by acting on phenotypes - Sources ...
Two trait Crosses
... Summary of Mendel’s Principles • Principle of Segregation – In most sexually reproducing organisms, each adult has two copies of each gene- one from each parent. These genes are segregated from each other when gametes are formed. • Principle of Independent Assortment – The alleles for different gen ...
... Summary of Mendel’s Principles • Principle of Segregation – In most sexually reproducing organisms, each adult has two copies of each gene- one from each parent. These genes are segregated from each other when gametes are formed. • Principle of Independent Assortment – The alleles for different gen ...
5. Complex Pedigrees
... vs. Mendelian traits, which are dichotomous characters +/R. A. Fischer demonstrated that characters controlled by many independent Mendelian factors would display quantitative variation. Variable character depending on many genes will show a normal distribution (Fig. 4.11) Example for I.Q. that was ...
... vs. Mendelian traits, which are dichotomous characters +/R. A. Fischer demonstrated that characters controlled by many independent Mendelian factors would display quantitative variation. Variable character depending on many genes will show a normal distribution (Fig. 4.11) Example for I.Q. that was ...
Chapter 14 (Part 1) Mendel and the Gene Theory
... the nervous system beginning at 35-45 years old) ...
... the nervous system beginning at 35-45 years old) ...
Gene and Gene Regulation
... Process of using genes from DNA to synthesize proteins to express/show traits/characteristics on an organism. ...
... Process of using genes from DNA to synthesize proteins to express/show traits/characteristics on an organism. ...
Genetics - World of Teaching
... Occurs when genes make a mistake mixing and produce new or different traits in the offspring. ...
... Occurs when genes make a mistake mixing and produce new or different traits in the offspring. ...
Enduring Understandings • The work of Gregor Mendel describes
... How is heritable information passed from one generation to the next? ...
... How is heritable information passed from one generation to the next? ...
this - ERA
... Molecular-genetic and genomic approaches can be implemented to dissect the basis of complex traits at the genetic and molecular level. Furthermore, these approaches can provide understanding of the key interactions between genotype and environment. In this project we have applied association mapping ...
... Molecular-genetic and genomic approaches can be implemented to dissect the basis of complex traits at the genetic and molecular level. Furthermore, these approaches can provide understanding of the key interactions between genotype and environment. In this project we have applied association mapping ...
HUMAN GENETICS ARCHITECTURE LEARNING OBJECTIVES
... • Just like X-linked inheritance, there will be a lack of male-to-male inheritance, which makes it distinguishable from autosomal traits. • One example of a X-linked trait is Coffin-Lowry syndrome, which is caused by a mutation in ribosomal protein gene. • This mutation results in skeletal, craniofa ...
... • Just like X-linked inheritance, there will be a lack of male-to-male inheritance, which makes it distinguishable from autosomal traits. • One example of a X-linked trait is Coffin-Lowry syndrome, which is caused by a mutation in ribosomal protein gene. • This mutation results in skeletal, craniofa ...
Genetic Basis of Continuous Traits
... • Using coins and a cup, we will generate distributions of “coinotypes” that will be analogous to genotypes in a population • The penny is one gene ...
... • Using coins and a cup, we will generate distributions of “coinotypes” that will be analogous to genotypes in a population • The penny is one gene ...
5 Agents of Evolutionary Change
... trait to become more common or rarer over time • Can produce evolutionary change • not caused by environmental or other kinds of stresses on individuals • Easier seen in small populations ...
... trait to become more common or rarer over time • Can produce evolutionary change • not caused by environmental or other kinds of stresses on individuals • Easier seen in small populations ...
Document
... produce more betta fish that are royal blue. If you were to cross two betta fish with the genotypes (B1 B2) and (B1 B2). What are the phenotypic percentages of the offspring? Show your work. ...
... produce more betta fish that are royal blue. If you were to cross two betta fish with the genotypes (B1 B2) and (B1 B2). What are the phenotypic percentages of the offspring? Show your work. ...
Non - Mendelian Genetics
... Non-Mendelian Genetics • Mendel’s pea experiments displayed _______ ___________ patterns ...
... Non-Mendelian Genetics • Mendel’s pea experiments displayed _______ ___________ patterns ...
Notes
... Name: ________________________________ Date: ____________ Period _____ # _____ Inheritance Patterns 1. Single Genes w/ Two Alleles Trait controlled by a single gene with one__________________________ and one ____________________ allele These traits have __________________________________________ ...
... Name: ________________________________ Date: ____________ Period _____ # _____ Inheritance Patterns 1. Single Genes w/ Two Alleles Trait controlled by a single gene with one__________________________ and one ____________________ allele These traits have __________________________________________ ...
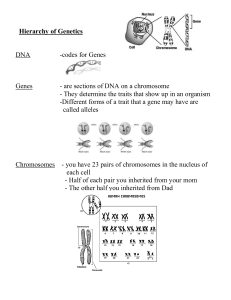
Hierarchy of Genetics
... - are sections of DNA on a chromosome - They determine the traits that show up in an organism -Different forms of a trait that a gene may have are called alleles ...
... - are sections of DNA on a chromosome - They determine the traits that show up in an organism -Different forms of a trait that a gene may have are called alleles ...
SR6e Chapter 3
... Single gene-pair inheritance ◦ Dominant gene = dominant trait ◦ Recessive genes Trait expressed if paired with a similar gene (Homozygous) Trait not expressed if paired with dissimilar gene (Heterozygous) ◦ Recessive traits: homozygous recessive ◦ Dominant traits: hetero or homozygous gene pair ...
... Single gene-pair inheritance ◦ Dominant gene = dominant trait ◦ Recessive genes Trait expressed if paired with a similar gene (Homozygous) Trait not expressed if paired with dissimilar gene (Heterozygous) ◦ Recessive traits: homozygous recessive ◦ Dominant traits: hetero or homozygous gene pair ...
IS IT GENETIC? How do genes, environment and chance interact to
... complex phenotype – one that can have a variety of different causes and modes of inheritance in different people multifactorial: a character that is determined by some unspecified combination of genetic and environmental factors polygenic: a character determined by the combined action of a number of ...
... complex phenotype – one that can have a variety of different causes and modes of inheritance in different people multifactorial: a character that is determined by some unspecified combination of genetic and environmental factors polygenic: a character determined by the combined action of a number of ...