Thermodynamics
... • The variation of the enthalpy of a substance with temperature can sometimes be ignored under certain conditions or assumptions, such as when the temperature difference is small. • However, most substances in real life have enthalpies that change with the temperature. • When it is necessary to acco ...
... • The variation of the enthalpy of a substance with temperature can sometimes be ignored under certain conditions or assumptions, such as when the temperature difference is small. • However, most substances in real life have enthalpies that change with the temperature. • When it is necessary to acco ...
Analytical Chemistry
... substance migrates through the column. The weaker the interaction, the faster the substance migrates. ...
... substance migrates through the column. The weaker the interaction, the faster the substance migrates. ...
Resonance Superfluidity in a Quantum Degenerate Fermi Gas
... tion potentials. In a multichannel system, a bound state the derivation. Several papers have pointed out that the may cross the threshold as a function of magnetic field and presence of a scattering resonance in dilute alkali gases enter the continuum, resulting in a field-dependent Feshcan be used ...
... tion potentials. In a multichannel system, a bound state the derivation. Several papers have pointed out that the may cross the threshold as a function of magnetic field and presence of a scattering resonance in dilute alkali gases enter the continuum, resulting in a field-dependent Feshcan be used ...
10 Vapor Pressure - Blue Valley Schools
... ln(P). Note that the log function removes units. 4. For the liquid, go to Insert / Graph to create a plot of ln(P) vs. 1 / T(K). Not all of the data is to be used. Recall what was happening when you first connected the tube to the stopper. Determine the equation of the best-fit line for each. [If th ...
... ln(P). Note that the log function removes units. 4. For the liquid, go to Insert / Graph to create a plot of ln(P) vs. 1 / T(K). Not all of the data is to be used. Recall what was happening when you first connected the tube to the stopper. Determine the equation of the best-fit line for each. [If th ...
CNT Sensors for Detecting Gases with Low Adsorption Energy by Ionization
... to be roughly an order of magnitude larger than the ionization voltage. Starting from low pressure, the ...
... to be roughly an order of magnitude larger than the ionization voltage. Starting from low pressure, the ...
Final Review Answers
... How does each of the following affect the solubility of (a) a solid dissolved in a liquid, and (b) a gas dissolved in a liquid. a. an increase in temperature (a) more collisions between particles causing an increase in dissolving particles (b) decreases solubility, as T increases more dissolved gas ...
... How does each of the following affect the solubility of (a) a solid dissolved in a liquid, and (b) a gas dissolved in a liquid. a. an increase in temperature (a) more collisions between particles causing an increase in dissolving particles (b) decreases solubility, as T increases more dissolved gas ...
Stoichiometry
... 1. Identify whether the descriptions below describe an ideal gas or a real gas. a. The gas will not condense because the molecules do not attract each other. b. Collisions between molecules are perfectly elastic. c. Gas particles passing close to one another exert an attraction on each other. ...
... 1. Identify whether the descriptions below describe an ideal gas or a real gas. a. The gas will not condense because the molecules do not attract each other. b. Collisions between molecules are perfectly elastic. c. Gas particles passing close to one another exert an attraction on each other. ...
lect1f
... 1. System is the part of the world which we have a special interest in. E.g. a reaction vessel, an engine, an electric cell. There are two point of view for the description of a system: Phenomenological view: the system is a continuum, this is the method of thermodynamics. Particle view: the system ...
... 1. System is the part of the world which we have a special interest in. E.g. a reaction vessel, an engine, an electric cell. There are two point of view for the description of a system: Phenomenological view: the system is a continuum, this is the method of thermodynamics. Particle view: the system ...
Practice Test 2 Solutions Oct 2010 - University of KwaZulu
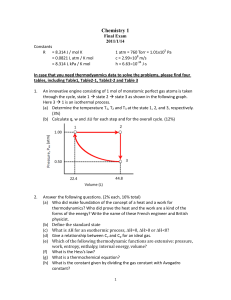
... The dissociation vapour pressure of NH4Cl at 427°C is 608 kPa but at 459°C it has risen to 1115 kPa. Calculate (a) the equilibrium constant, (b) the standard reaction Gibbs energy, (c) the standard enthalpy, (d) the standard entropy of dissociation, all at 427°C. Assume that the vapou ...
... The dissociation vapour pressure of NH4Cl at 427°C is 608 kPa but at 459°C it has risen to 1115 kPa. Calculate (a) the equilibrium constant, (b) the standard reaction Gibbs energy, (c) the standard enthalpy, (d) the standard entropy of dissociation, all at 427°C. Assume that the vapou ...
Lecture Slides - School of Chemical Sciences
... A collection of a very large number A of systems (of volume V, containing N molecules) in contact with a heat reservoir at temperature T. Each system has an energy that is one of the eigenvalues Ej of the Schrodinger equation. A state of the entire ensemble is specified by specifying the “occupation ...
... A collection of a very large number A of systems (of volume V, containing N molecules) in contact with a heat reservoir at temperature T. Each system has an energy that is one of the eigenvalues Ej of the Schrodinger equation. A state of the entire ensemble is specified by specifying the “occupation ...
isuintroduction
... destroyed, therefore two quarts of one gas plus one quart of another gas should produce three quarts of the product. This problem remained unsolved until the chemist, Amedeo Avogadro, postulated that hydrogen and oxygen did not exist as single atoms, but rather as pairs of hydrogen atoms and pairs o ...
... destroyed, therefore two quarts of one gas plus one quart of another gas should produce three quarts of the product. This problem remained unsolved until the chemist, Amedeo Avogadro, postulated that hydrogen and oxygen did not exist as single atoms, but rather as pairs of hydrogen atoms and pairs o ...
Period 4 - cloudfront.net
... 3. which is true about intramolecular forces and intermolecular forces A. intramolecular are in the same molecule while intermolecular forces are between neighboring molecules B. intermolecular forces have 3 types: ionic, covalent, metallic C. intramolecular forcers are weak D. intramolecular force ...
... 3. which is true about intramolecular forces and intermolecular forces A. intramolecular are in the same molecule while intermolecular forces are between neighboring molecules B. intermolecular forces have 3 types: ionic, covalent, metallic C. intramolecular forcers are weak D. intramolecular force ...
Chapter 13
... 24. For an ideal gas, volume and temperature described in kelvins are directly proportional if the number of gas particles and pressure are constant. This is a statement of Charles’ Law. 26. If the temperature and volume of an ideal gas are held constant, the number of gas particles in a container a ...
... 24. For an ideal gas, volume and temperature described in kelvins are directly proportional if the number of gas particles and pressure are constant. This is a statement of Charles’ Law. 26. If the temperature and volume of an ideal gas are held constant, the number of gas particles in a container a ...
5/14/01 - Oklahoma State University
... Problem Solving Resources: This is an interactive feature that can be used to help students develop problem-solving skills. Each tutorial consists of three prototype questions that are randomly sequenced. In the tutorial the student views the first question and is given three choices of how to inter ...
... Problem Solving Resources: This is an interactive feature that can be used to help students develop problem-solving skills. Each tutorial consists of three prototype questions that are randomly sequenced. In the tutorial the student views the first question and is given three choices of how to inter ...
Chapter 14: Gases
... Real Gases: - No gases are ideal. - Gas particles have volume (due to size and shape). - Subject to intermolecular forces * Most gases behave like “ideal” gases, except at high pressure and low temps ...
... Real Gases: - No gases are ideal. - Gas particles have volume (due to size and shape). - Subject to intermolecular forces * Most gases behave like “ideal” gases, except at high pressure and low temps ...
The Gas Laws
... • All real gases deviate to some degree from ideal gas behavior. However, most real gases behave nearly ideally when their particles are sufficiently far apart and have sufficiently high kinetic energy. Causes of non-ideal behavior: • The kinetic-molecular theory is more likely to hold true for ga ...
... • All real gases deviate to some degree from ideal gas behavior. However, most real gases behave nearly ideally when their particles are sufficiently far apart and have sufficiently high kinetic energy. Causes of non-ideal behavior: • The kinetic-molecular theory is more likely to hold true for ga ...
3, 4, 7, 8, 10, 11, 13, 16, 17, 21, 22 Problems
... Although this result was derived for the idealized Carnot cycle, it can be proven that the efficiency of all reversible engines are the same. (The explanation is given in the text, but you are not responsible for it) The efficiency of a real (i.e. irreversible) engine is lower than for reversible en ...
... Although this result was derived for the idealized Carnot cycle, it can be proven that the efficiency of all reversible engines are the same. (The explanation is given in the text, but you are not responsible for it) The efficiency of a real (i.e. irreversible) engine is lower than for reversible en ...
T h - Website Staff UI
... absolutely but only the differences, U or H The choice of standard state is purely a matter of convenience Analogy – differences in altitudes between 100 points and their elevation with respect ...
... absolutely but only the differences, U or H The choice of standard state is purely a matter of convenience Analogy – differences in altitudes between 100 points and their elevation with respect ...
Gas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma). A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or compound molecules made from a variety of atoms (e.g. carbon dioxide). A gas mixture would contain a variety of pure gases much like the air. What distinguishes a gas from liquids and solids is the vast separation of the individual gas particles. This separation usually makes a colorless gas invisible to the human observer. The interaction of gas particles in the presence of electric and gravitational fields are considered negligible as indicated by the constant velocity vectors in the image. One type of commonly known gas is steam.The gaseous state of matter is found between the liquid and plasma states, the latter of which provides the upper temperature boundary for gases. Bounding the lower end of the temperature scale lie degenerative quantum gases which are gaining increasing attention. High-density atomic gases super cooled to incredibly low temperatures are classified by their statistical behavior as either a Bose gas or a Fermi gas. For a comprehensive listing of these exotic states of matter see list of states of matter.