GRAMMATICAL
... Not all these labels may be familiar, but your intuitions alone should be enough to convince you of the multiple functions that nouns fulfill. Another fact worth knowing about nouns is that there are three types. By far the most frequent in occurrence are common nouns, or nouns referring to a kind o ...
... Not all these labels may be familiar, but your intuitions alone should be enough to convince you of the multiple functions that nouns fulfill. Another fact worth knowing about nouns is that there are three types. By far the most frequent in occurrence are common nouns, or nouns referring to a kind o ...
Grammar Notes - Holly High School
... of the preposition and includes any adjectives or articles that modify the object of the preposition. o Prepositional phrases can act as adjectives or adverbs. o Prepositional phrases often tell direction. o Look for phrases that begin with words such as: in, between, on, under, around, inside, etc. ...
... of the preposition and includes any adjectives or articles that modify the object of the preposition. o Prepositional phrases can act as adjectives or adverbs. o Prepositional phrases often tell direction. o Look for phrases that begin with words such as: in, between, on, under, around, inside, etc. ...
DICTIONARY OF TERMS
... Some adjectives of two syllables and ALL adjectives of three or more syllables have their comparative and superlative degrees of comparison formed by using the words more and most or less and least. A few adjectives are IRREGULAR and use different words for their comparative and superlative degrees. ...
... Some adjectives of two syllables and ALL adjectives of three or more syllables have their comparative and superlative degrees of comparison formed by using the words more and most or less and least. A few adjectives are IRREGULAR and use different words for their comparative and superlative degrees. ...
Meet the Sentence Structure Family
... Let’s practice! What types of sentences are these? What are the patterns you notice in each sentence? When I was at school today, Mrs. Mann threw Jake across the ...
... Let’s practice! What types of sentences are these? What are the patterns you notice in each sentence? When I was at school today, Mrs. Mann threw Jake across the ...
Study Advice Service
... Some modern grammarians say that the Complement also includes the two Objects. They call the Complement to a copular verb the Complement (C); they call the Direct Object the Complement (Object Direct) (COd); and they call the Indirect Object the COi. It seems easier, as well as more traditional, to ...
... Some modern grammarians say that the Complement also includes the two Objects. They call the Complement to a copular verb the Complement (C); they call the Direct Object the Complement (Object Direct) (COd); and they call the Indirect Object the COi. It seems easier, as well as more traditional, to ...
Study Advice Service
... Some modern grammarians say that the Complement also includes the two Objects. They call the Complement to a copular verb the Complement (C); they call the Direct Object the Complement (Object Direct) (COd); and they call the Indirect Object the COi. It seems easier, as well as more traditional, to ...
... Some modern grammarians say that the Complement also includes the two Objects. They call the Complement to a copular verb the Complement (C); they call the Direct Object the Complement (Object Direct) (COd); and they call the Indirect Object the COi. It seems easier, as well as more traditional, to ...
Study Advice Service Grammar series – 2 UNITS OF LANGUAGE (B
... Some modern grammarians say that the Complement also includes the two Objects. They call the Complement to a copular verb the Complement (C); they call the Direct Object the Complement (Object Direct) (COd); and they call the Indirect Object the COi. It seems easier, as well as more traditional, to ...
... Some modern grammarians say that the Complement also includes the two Objects. They call the Complement to a copular verb the Complement (C); they call the Direct Object the Complement (Object Direct) (COd); and they call the Indirect Object the COi. It seems easier, as well as more traditional, to ...
SENTENCE STRUCTURE
... Dependent Clause — This clause has a subject and a verb, but it cannot stand alone as a sentence. A dependent clause will begin with a subordinating conjunction, such as if, when, that, unless. They make the clause they are added to less important than an independent clause. The dependent clause dep ...
... Dependent Clause — This clause has a subject and a verb, but it cannot stand alone as a sentence. A dependent clause will begin with a subordinating conjunction, such as if, when, that, unless. They make the clause they are added to less important than an independent clause. The dependent clause dep ...
NOUN
... Pronouns: infl. categories: number, gender, case, negation; person – much like nouns (syntactic usage also similar) – (pro)noun ~ “stands for” a noun – classification (mostly syntactic/semantic): • personal: I, you, she, she, it, we, you, they • demonstrative: this, that • possessive: my, your, her, ...
... Pronouns: infl. categories: number, gender, case, negation; person – much like nouns (syntactic usage also similar) – (pro)noun ~ “stands for” a noun – classification (mostly syntactic/semantic): • personal: I, you, she, she, it, we, you, they • demonstrative: this, that • possessive: my, your, her, ...
Chapter 3 Grammar Phrases
... Chapter 3 Grammar: Phrases Notes Phrase – A group of related words that is used as a single part of speech and that does not contain both a verb and its subject. (Considered a single part of speech) Prepositional Phrase – Includes a preposition, the object of the preposition, and any modifiers of th ...
... Chapter 3 Grammar: Phrases Notes Phrase – A group of related words that is used as a single part of speech and that does not contain both a verb and its subject. (Considered a single part of speech) Prepositional Phrase – Includes a preposition, the object of the preposition, and any modifiers of th ...
NOUN
... Pronouns: infl. categories: number, gender, case, negation; person – much like nouns (syntactic usage also similar) – (pro)noun ~ “stands for” a noun – classification (mostly syntactic/semantic): • personal: I, you, she, she, it, we, you, they • demonstrative: this, that • possessive: my, your, her, ...
... Pronouns: infl. categories: number, gender, case, negation; person – much like nouns (syntactic usage also similar) – (pro)noun ~ “stands for” a noun – classification (mostly syntactic/semantic): • personal: I, you, she, she, it, we, you, they • demonstrative: this, that • possessive: my, your, her, ...
Noun Clauses
... In English, there are four nonfinite verbs (i.e. they have no tense and take no subject). Usually they're referred to as verbals: The infinitive: Simple Infinitive: to eat Continuous Infinitive: to be eating Perfect Infinitive: to have eaten The gerund: Simple gerund: eating Perfect Gerund: having e ...
... In English, there are four nonfinite verbs (i.e. they have no tense and take no subject). Usually they're referred to as verbals: The infinitive: Simple Infinitive: to eat Continuous Infinitive: to be eating Perfect Infinitive: to have eaten The gerund: Simple gerund: eating Perfect Gerund: having e ...
Grammar - UTS Library - University of Technology Sydney
... Articles – (the/a/an) – identify things. They introduce nouns and show what the noun is referring to: • things that both writer and reader know – definite article (the) or • things that are not known – indefinite article (a/an). • there are some nouns that don’t need an article – the Zero article – ...
... Articles – (the/a/an) – identify things. They introduce nouns and show what the noun is referring to: • things that both writer and reader know – definite article (the) or • things that are not known – indefinite article (a/an). • there are some nouns that don’t need an article – the Zero article – ...
Parts of Speech, Phrases, and Clauses
... This noun clause is working as the subject of the entire independent clause: That Raul kicks the ball pleases his coach. (3) adjective clause—a group of words containing a subject and a predicate working together to modify some noun or pronoun. It answers the question what kind of? (person, place, t ...
... This noun clause is working as the subject of the entire independent clause: That Raul kicks the ball pleases his coach. (3) adjective clause—a group of words containing a subject and a predicate working together to modify some noun or pronoun. It answers the question what kind of? (person, place, t ...
Dear Students,
... If it answers how? or when? or where? or why? or under what conditions? or to what degree? it is an adverb prepositional phrase. In the sentence above, “at the goalie” is answering the question where? (does he kick the ball). It is modifying the verb kicks so that it is an adverb prepositional phra ...
... If it answers how? or when? or where? or why? or under what conditions? or to what degree? it is an adverb prepositional phrase. In the sentence above, “at the goalie” is answering the question where? (does he kick the ball). It is modifying the verb kicks so that it is an adverb prepositional phra ...
GERUNDIVE AND GERUND
... • Can be used in a noun phrase with a noun in the accusative in place of a gerundive phrase but this tends to happen only when gerundive and noun both have long endings (especially genitive plural): – dē amīcīs dēfendendīs (with gerundive) is better than dē amīcōs dēfendendō (with gerund) – amīcōs d ...
... • Can be used in a noun phrase with a noun in the accusative in place of a gerundive phrase but this tends to happen only when gerundive and noun both have long endings (especially genitive plural): – dē amīcīs dēfendendīs (with gerundive) is better than dē amīcōs dēfendendō (with gerund) – amīcōs d ...
Grammar Rules for Corrections
... 1. A verb must agree in number with its subject (singular or plural). 2. The subject of a sentence CANNOT be part of a prepositional phrase or an appositive (a phrase between commas that can be removed from the sentence.) 3. A verb must match in tense with other surrounding verbs. 4. Present tense m ...
... 1. A verb must agree in number with its subject (singular or plural). 2. The subject of a sentence CANNOT be part of a prepositional phrase or an appositive (a phrase between commas that can be removed from the sentence.) 3. A verb must match in tense with other surrounding verbs. 4. Present tense m ...
Spring Themed Grammar Review
... Pronouns—Underline the pronouns. 1. I was careful on the muddy pathway. 2. She gave her boots to Susan. 3. The baby bird had a worm in its mouth. 4. They were excited to see the first cherry blossoms. 5. Yesterday, we walked to the park. 6. The flowers are pretty as they blow in the breeze. Rewrite ...
... Pronouns—Underline the pronouns. 1. I was careful on the muddy pathway. 2. She gave her boots to Susan. 3. The baby bird had a worm in its mouth. 4. They were excited to see the first cherry blossoms. 5. Yesterday, we walked to the park. 6. The flowers are pretty as they blow in the breeze. Rewrite ...
1. Genitive singular
... objects will appear in the dative case. For first declension nouns, these endings = –ae or –is depending on whether the noun is singular or plural. For second declension, the singular = –o and plural = –is. *Notice that the dative plural for both declensions = –is. puerī laetīs puellīs multōs flōrēs ...
... objects will appear in the dative case. For first declension nouns, these endings = –ae or –is depending on whether the noun is singular or plural. For second declension, the singular = –o and plural = –is. *Notice that the dative plural for both declensions = –is. puerī laetīs puellīs multōs flōrēs ...
ACT practice
... A complete sentence must have a subject and a verb, and stand alone. In other words it must be, or contain, an independent clause (independent = it can stand alone). Melissa picked her nose. We can change the above independent clause (complete sentence) into a dependent clause (incomplete sentence) ...
... A complete sentence must have a subject and a verb, and stand alone. In other words it must be, or contain, an independent clause (independent = it can stand alone). Melissa picked her nose. We can change the above independent clause (complete sentence) into a dependent clause (incomplete sentence) ...
A closer look at long sentences-Unit 3 Text 2
... English language has three clauses: Adjective, Noun and Adverb Clauses, and these clauses have different types and functions. If you can detect them when reading long sentences, you can divide the sentences into chunks easier; and this may help you understand the sentences better. What is more, iden ...
... English language has three clauses: Adjective, Noun and Adverb Clauses, and these clauses have different types and functions. If you can detect them when reading long sentences, you can divide the sentences into chunks easier; and this may help you understand the sentences better. What is more, iden ...
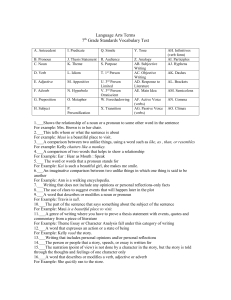
Language Arts Terms
... 3.___A comparison between two unlike things, using a word such as like, as , than, or resembles For example: Kelly chatters like a monkey. 4.___A comparison of two words that helps to show a relationship For Example: Ear : Hear as Mouth : Speak 5.___ The word or words that a pronoun stands for For E ...
... 3.___A comparison between two unlike things, using a word such as like, as , than, or resembles For example: Kelly chatters like a monkey. 4.___A comparison of two words that helps to show a relationship For Example: Ear : Hear as Mouth : Speak 5.___ The word or words that a pronoun stands for For E ...
College Readiness Standards — English
... (e.g., compound sentences containing unnecessary commas and phrases that may or may not be parenthetical) Use an apostrophe to show possession, especially with irregular plural nouns Use a semicolon to indicate a relationship between closely related independent clauses ...
... (e.g., compound sentences containing unnecessary commas and phrases that may or may not be parenthetical) Use an apostrophe to show possession, especially with irregular plural nouns Use a semicolon to indicate a relationship between closely related independent clauses ...
phrases
... A phrase is a group of words that together communicate a meaning to a group of people. Phrases are a very basic way to organize words. When we speak, it is very common to communicate in phrases rather than complete sentences, especially with people we know well. On the other hand, when we write for ...
... A phrase is a group of words that together communicate a meaning to a group of people. Phrases are a very basic way to organize words. When we speak, it is very common to communicate in phrases rather than complete sentences, especially with people we know well. On the other hand, when we write for ...