GLOSSARY OF TERMS OF THE SHOP INGOLD
... a clearing unit is derived from gold price. When using the gold standard, the currency is formed either by coins minted from a precisely defined amount of gold or by such notes for whose value the issuer (state) guarantees to pay with gold. The gold standard is perceived as a principle of coverage o ...
... a clearing unit is derived from gold price. When using the gold standard, the currency is formed either by coins minted from a precisely defined amount of gold or by such notes for whose value the issuer (state) guarantees to pay with gold. The gold standard is perceived as a principle of coverage o ...
Vocabulary, Economic terms, page 99
... the difference in value between imports and exports of goods over a particular period: ...
... the difference in value between imports and exports of goods over a particular period: ...
entry task - Issaquah Connect
... THE IMF International Monetary Fund Cooperative organization trying to provide financial stability Helps the expansion of international trade Promotes high levels of employment Promotes exchange stability Maintains orderly exchange arrangements among members Allows for easier repayments ...
... THE IMF International Monetary Fund Cooperative organization trying to provide financial stability Helps the expansion of international trade Promotes high levels of employment Promotes exchange stability Maintains orderly exchange arrangements among members Allows for easier repayments ...
SECTION 8: Open Economy: International Trade & Finance Need to Know The , consists of international transactions that don’t create liabilities.
... There are two main kinds of exchange rate regimes: A country has a Fixed Exchange Rate when the government keeps the exchange rate against some other currency at or near a particular target. For example, Hong Kong has an official policy of setting an exchange rate of HK$7.80 per US$1. o This ...
... There are two main kinds of exchange rate regimes: A country has a Fixed Exchange Rate when the government keeps the exchange rate against some other currency at or near a particular target. For example, Hong Kong has an official policy of setting an exchange rate of HK$7.80 per US$1. o This ...
FEATURES OF ECONOMIC UNION
... of stronger economies such as Germany and France with inflation more difficult to control - fears that because fiscal policy can be be more effectively used in a common monetary zone that it could thereby be used irresponsibly by some governments ...
... of stronger economies such as Germany and France with inflation more difficult to control - fears that because fiscal policy can be be more effectively used in a common monetary zone that it could thereby be used irresponsibly by some governments ...
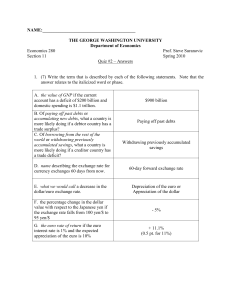
THE GEORGE WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY
... 3. (4) The current dollar/euro exchange rate is 1.35. Suppose you plan to invest $1000 in a simple interest one-year European CD paying an interest rate of 2% per year. A. (3) Calculate the rate of return on this investment if you expect the dollar/euro exchange rate to be 1.25 in one year. Show yo ...
... 3. (4) The current dollar/euro exchange rate is 1.35. Suppose you plan to invest $1000 in a simple interest one-year European CD paying an interest rate of 2% per year. A. (3) Calculate the rate of return on this investment if you expect the dollar/euro exchange rate to be 1.25 in one year. Show yo ...
the international monetary and financial environment
... fixed at a prescribed level, relative to the U.S. dollar and to each other. ■ 1960s (late)- Demise of the Bretton Woods agreement- the U.S. government employed deficit spending to finance both the Vietnam War and expensive government programs. ■ Rising government spending stimulated the economy and ...
... fixed at a prescribed level, relative to the U.S. dollar and to each other. ■ 1960s (late)- Demise of the Bretton Woods agreement- the U.S. government employed deficit spending to finance both the Vietnam War and expensive government programs. ■ Rising government spending stimulated the economy and ...
1 CHAPTER 10 INTERNATIONAL MONETARY SYSTEM 1. Explain
... This forced nations to keep adequate gold reserves on hand. A nation could not let paper currency to grow faster than the value of its gold reserves, which controlled inflation. c. Helped correct a nation’s trade imbalance. i. If a nation imports more than it exports, gold flowed out to pay for impo ...
... This forced nations to keep adequate gold reserves on hand. A nation could not let paper currency to grow faster than the value of its gold reserves, which controlled inflation. c. Helped correct a nation’s trade imbalance. i. If a nation imports more than it exports, gold flowed out to pay for impo ...
Study Guide for Final: Material studied BEFORE the Second Midterm
... Development of world trading system: considerable liberalization after WW II through General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade; further liberalization after 1995 through World Trade Organization ...
... Development of world trading system: considerable liberalization after WW II through General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade; further liberalization after 1995 through World Trade Organization ...
classical gold standard
... “When the exchanges were favourable, gold flowed freely into this country and an increase of legal tender money accompanied the development of trade. When the balance of trade was unfavourable and the exchanges were adverse, it became profitable to export gold. The would-be exporter bought his gold ...
... “When the exchanges were favourable, gold flowed freely into this country and an increase of legal tender money accompanied the development of trade. When the balance of trade was unfavourable and the exchanges were adverse, it became profitable to export gold. The would-be exporter bought his gold ...
IMFC Statement by Steven Mnuchin, Secretary of the Treasury
... languishing below pre-crisis levels amid weak business investment. The economy has gone through periods of disappointing performance before, however, and a continuation of this weak growth is not pre-ordained. In response, the Administration is undertaking an ambitious policy agenda that includes ta ...
... languishing below pre-crisis levels amid weak business investment. The economy has gone through periods of disappointing performance before, however, and a continuation of this weak growth is not pre-ordained. In response, the Administration is undertaking an ambitious policy agenda that includes ta ...
A Model of US Import Flows (1974-1988) Dominick Answini
... as the second independent variable, to smooth the effect of this anomaly. A second reason has already been explored. The US economy was simply growing too fast to let exchange rates stand in the way of it~ demand for foreign goods, many of which Americans had begun to prefer after exposure to them i ...
... as the second independent variable, to smooth the effect of this anomaly. A second reason has already been explored. The US economy was simply growing too fast to let exchange rates stand in the way of it~ demand for foreign goods, many of which Americans had begun to prefer after exposure to them i ...
The analysis
... of its quality, contractual;) a deviation in the smaller party from a currency official rate. f) the percent, raised by banks at the account of bills 2) the percentage income of the buyer of the bill; 3) a difference between the price of the repayment and by placing of the state securities. The acc ...
... of its quality, contractual;) a deviation in the smaller party from a currency official rate. f) the percent, raised by banks at the account of bills 2) the percentage income of the buyer of the bill; 3) a difference between the price of the repayment and by placing of the state securities. The acc ...
Cold War Origins: 1945-1962
... Cold War Origins: Basic Questions • Read Henretta 783-790. Stop before “Containment Militarized: NSC-68”. • What were the major post-war disagreements or tensions that led to the Cold War? • What was the goal of the Marshall Plan, and ...
... Cold War Origins: Basic Questions • Read Henretta 783-790. Stop before “Containment Militarized: NSC-68”. • What were the major post-war disagreements or tensions that led to the Cold War? • What was the goal of the Marshall Plan, and ...
Seminar—Where is Global Finance Heading? Status of the
... currency use to result in a virtuous circle of greater stability and currency use, that is, U.S. treasury securities are perceived as safe in large part because China has decided to hold them. Central banks can simply allocate part of their reserves to new currencies. They could preannounce that the ...
... currency use to result in a virtuous circle of greater stability and currency use, that is, U.S. treasury securities are perceived as safe in large part because China has decided to hold them. Central banks can simply allocate part of their reserves to new currencies. They could preannounce that the ...
1 Recreating the 1940s-Founded Institutions for Today`s Global
... exchange. The government would determine what types of goods could be imported and how much to pay exporters. Exchange controls also involved multiple exchange rates, government licenses to export and import, and even officially conducted barter trade. They deviated from the principles of economic ...
... exchange. The government would determine what types of goods could be imported and how much to pay exporters. Exchange controls also involved multiple exchange rates, government licenses to export and import, and even officially conducted barter trade. They deviated from the principles of economic ...
3.E Money in the European Union Middle School Lesson Plan
... To introduce the idea of the lesson, teacher will ask students if any have ever traveled outside of the United States. If so, teacher will ask that student whether they were able to use dollars to buy things in that other country. The student may explain that they were not able to use US dollars, bu ...
... To introduce the idea of the lesson, teacher will ask students if any have ever traveled outside of the United States. If so, teacher will ask that student whether they were able to use dollars to buy things in that other country. The student may explain that they were not able to use US dollars, bu ...
GDP and Economic Policy
... These transactions, i.e. trade in goods and services, financial transactions including foreign investment and remittances, are captured in the balance of payments. ...
... These transactions, i.e. trade in goods and services, financial transactions including foreign investment and remittances, are captured in the balance of payments. ...
TAKS Remediation Lesson #1
... payments system, and serves as banker for banks and the U.S. government. Conducting the nation’s monetary policy is one of the most important — and often the most visible — functions of the Fed. Prior to 1913, panics were common occurrences, as investors were unsure about the safety of their deposit ...
... payments system, and serves as banker for banks and the U.S. government. Conducting the nation’s monetary policy is one of the most important — and often the most visible — functions of the Fed. Prior to 1913, panics were common occurrences, as investors were unsure about the safety of their deposit ...
Asia Financial Crisis
... Moody’s lowered their credit rating from A1 to B2 Seoul stock exchange dropped 4% on Nov 7, 7% on Nov 8, and 7.2% on Nov 24 ...
... Moody’s lowered their credit rating from A1 to B2 Seoul stock exchange dropped 4% on Nov 7, 7% on Nov 8, and 7.2% on Nov 24 ...
Uruguay Round.
... Redirection of public spending from subsidies ("especially indiscriminate subsidies") toward broad-based provision of key pro-growth, pro-poor services like primary education, primary health care and infrastructure investment; Tax reform – broadening the tax base and adopting moderate marginal t ...
... Redirection of public spending from subsidies ("especially indiscriminate subsidies") toward broad-based provision of key pro-growth, pro-poor services like primary education, primary health care and infrastructure investment; Tax reform – broadening the tax base and adopting moderate marginal t ...
The Role of Exchange Rate
... A rise in U.S. interest rates relative to those abroad will increase demand for U.S. assets. The demand for dollars will increase. The supply of dollars will decrease as fewer Americans sell their dollars to buy foreign assets. ...
... A rise in U.S. interest rates relative to those abroad will increase demand for U.S. assets. The demand for dollars will increase. The supply of dollars will decrease as fewer Americans sell their dollars to buy foreign assets. ...
Lecture Slides Chapter 13
... interest rates o nation with deficit sees decrease in money supply leading to higher interest rates o interest rate differential leads to flow of investment capital from surplus nation to deficit nation o facilitates balance of payments equilibrium ...
... interest rates o nation with deficit sees decrease in money supply leading to higher interest rates o interest rate differential leads to flow of investment capital from surplus nation to deficit nation o facilitates balance of payments equilibrium ...