International Political Economy
... facing a temporary economic crisis – Today provides assistance to developing nations • Conditionality or – Requires countries who barrow money to meet certain conditions = liberalization and privatization of economy ...
... facing a temporary economic crisis – Today provides assistance to developing nations • Conditionality or – Requires countries who barrow money to meet certain conditions = liberalization and privatization of economy ...
Globalization and Capital Markets
... • “Bretton Woods II” worldview: Asia needs a dollar peg to grow, eliminate surplus labor. • They also need FDI for those purposes. • Since they need an export surplus for growth, massive reserve accumulation follows. • U.S. interest rates are kept low, USD high (though not against euro). • Chinese c ...
... • “Bretton Woods II” worldview: Asia needs a dollar peg to grow, eliminate surplus labor. • They also need FDI for those purposes. • Since they need an export surplus for growth, massive reserve accumulation follows. • U.S. interest rates are kept low, USD high (though not against euro). • Chinese c ...
document
... • Destruction of global economy with increasing non-cooperative economic policy-making • Broken credibility on the gold standard and adoption of floating rates • Monetary policy became subject to domestic goals to help finance wartime deficits • Capital controls to protect gold and avoid currency cr ...
... • Destruction of global economy with increasing non-cooperative economic policy-making • Broken credibility on the gold standard and adoption of floating rates • Monetary policy became subject to domestic goals to help finance wartime deficits • Capital controls to protect gold and avoid currency cr ...
Exam 3 with answers
... D) the low-income nations will lose their ability to borrow in international markets. 6. Two nations each own 50% of the capital of the other nation (diversification). What is the situation when labor comprises over 50% of available resources? A) In order to achieve perfect diversification, labor mu ...
... D) the low-income nations will lose their ability to borrow in international markets. 6. Two nations each own 50% of the capital of the other nation (diversification). What is the situation when labor comprises over 50% of available resources? A) In order to achieve perfect diversification, labor mu ...
Trade Protectionism: A Balancing (of Payments)
... could choose to implement policies that increase the national savings rate or make decisions which force capital flows to reverse. A country could also choose to devalue its currency to improve the current account deficit. When U.S. policymakers accused China of "currency manipulation" several years ...
... could choose to implement policies that increase the national savings rate or make decisions which force capital flows to reverse. A country could also choose to devalue its currency to improve the current account deficit. When U.S. policymakers accused China of "currency manipulation" several years ...
The Falling Dollar
... In conclusion, some concern must be felt regarding the value of the Dollar and its decline’s impact on the U.S. economy. Many Americans believe that the U.S. economy is impervious to crises that befall other nations and are inclined to view the declining value of the dollar as a minor inconvenience ...
... In conclusion, some concern must be felt regarding the value of the Dollar and its decline’s impact on the U.S. economy. Many Americans believe that the U.S. economy is impervious to crises that befall other nations and are inclined to view the declining value of the dollar as a minor inconvenience ...
The International Monetary Fund
... of a new reserve asset to supplement both gold and dollar Known as a special drawing right or SDR ...
... of a new reserve asset to supplement both gold and dollar Known as a special drawing right or SDR ...
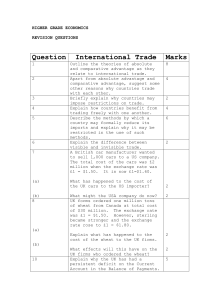
higher grade economics - Bannerman High School
... being a member of the European Union? What is meant by the term Eurozone? Under what circumstances may an economy wish to adopt protectionist policies? What information can be found in the Capital Account section of the UK Balance of Payments? ...
... being a member of the European Union? What is meant by the term Eurozone? Under what circumstances may an economy wish to adopt protectionist policies? What information can be found in the Capital Account section of the UK Balance of Payments? ...
EXCHANGE RATE Chapter13 able
... Exchange rates between the dollar and other currencies normally fluctuate, just as other prices fluctuate in response to demand and supply conditions We will later see that it is possible for countries to fix the rate at which currencies trade (and some countries do fix their exchange rate to anothe ...
... Exchange rates between the dollar and other currencies normally fluctuate, just as other prices fluctuate in response to demand and supply conditions We will later see that it is possible for countries to fix the rate at which currencies trade (and some countries do fix their exchange rate to anothe ...
Balance of payments
... Quota: A limit set on the amounts of particular products that can be imported Dumping: Selling products in other countries at prices below production costs or below typical prices in the home market Embargo: A total ban on importing specific products or a total stop to trading with a particular coun ...
... Quota: A limit set on the amounts of particular products that can be imported Dumping: Selling products in other countries at prices below production costs or below typical prices in the home market Embargo: A total ban on importing specific products or a total stop to trading with a particular coun ...
EC120 week 1 - University of Essex
... heavily upon the policy response to the decline in output and rise in unemployment (see Diagram 1). It took time to adjust the capital stock to the new reality ...
... heavily upon the policy response to the decline in output and rise in unemployment (see Diagram 1). It took time to adjust the capital stock to the new reality ...
1 Counterfactual Histories of the Great Depression Barry
... change in macroeconomic policy to expand the economy. It was the latter component that frightened these veterans of the German hyperinflation. Their fear was that devaluation would be less of a positive influence on prices and demand than a negative shock to confidence (whatever changes in domestic ...
... change in macroeconomic policy to expand the economy. It was the latter component that frightened these veterans of the German hyperinflation. Their fear was that devaluation would be less of a positive influence on prices and demand than a negative shock to confidence (whatever changes in domestic ...
Prospects for Monetary Union in Southern Africa
... A peg can be changed, and frequently is. Even a currency board is not permanent (Argentina). But getting out of a monetary union is hard. Some Italian politicians today would like to, but can’t, legally or economically. Good? ...
... A peg can be changed, and frequently is. Even a currency board is not permanent (Argentina). But getting out of a monetary union is hard. Some Italian politicians today would like to, but can’t, legally or economically. Good? ...
AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Exchange Rate Policy
... How Can an Exchange Rates be Fixed? • Exchange Market Intervention • ie China sells Yuan/buys USD to keep Chinese products cheap to US consumers • Central Banks maintain foreign exchange reserves • Governments may limit ability to exchange currency; ie Korea limits foreigners’ ability to buy Won ...
... How Can an Exchange Rates be Fixed? • Exchange Market Intervention • ie China sells Yuan/buys USD to keep Chinese products cheap to US consumers • Central Banks maintain foreign exchange reserves • Governments may limit ability to exchange currency; ie Korea limits foreigners’ ability to buy Won ...
Slides on International Institutions (Session 3)
... Almost every industry had its “made to order tariff” Foreign response was to impose own barriers Everyone’s exports tumbled ...
... Almost every industry had its “made to order tariff” Foreign response was to impose own barriers Everyone’s exports tumbled ...
Will Failure of the "European Monetary Union" Jeopardise the
... unit of account in the intervention and the credit mechanisms; 2. an Exchange Rate Mechanism (ERM), which allowed a margin of fluctuation of each EC currency of + 2.25% in respect to the central rate, for all currencies, except of the Italian (initially) and the Spanish, British and Portuguese (afte ...
... unit of account in the intervention and the credit mechanisms; 2. an Exchange Rate Mechanism (ERM), which allowed a margin of fluctuation of each EC currency of + 2.25% in respect to the central rate, for all currencies, except of the Italian (initially) and the Spanish, British and Portuguese (afte ...
Real Exchange Rate
... Causes of Higher Long-run Exchange Rates • A decrease in a country’s relative price level (If U.S goods are cheaper than in India, more people will buy U.S goods, and bid up the price of the dollar) • An increase in a country’s relative productivity • (If U.S goods are made more productively, they ...
... Causes of Higher Long-run Exchange Rates • A decrease in a country’s relative price level (If U.S goods are cheaper than in India, more people will buy U.S goods, and bid up the price of the dollar) • An increase in a country’s relative productivity • (If U.S goods are made more productively, they ...
Strong Dollar Weak Dollar: Foreign Exchange Rates and the U.S.
... amount of pounds, lira, yen or d-marks. This idea is not new. Through most of the modern era the world was on a fixed-rate system. The most recent version is referred to as the Bretton Woods System. In 1947, the industrialized countries of the world met in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire, to discuss th ...
... amount of pounds, lira, yen or d-marks. This idea is not new. Through most of the modern era the world was on a fixed-rate system. The most recent version is referred to as the Bretton Woods System. In 1947, the industrialized countries of the world met in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire, to discuss th ...
Working Paper Number 63 The Winner`s Curse: Premature
... 3. USING AN ‘EXTERNAL MONEY’: THE GOLD STANDARD AND CURRENCY BOARDS The ‘classical’ gold standard system that operated between 1870 and 1913 was, for the participating countries, an apparent equivalent to moving to a ‘dollar standard’ today. Participating countries declared parities against gold, wi ...
... 3. USING AN ‘EXTERNAL MONEY’: THE GOLD STANDARD AND CURRENCY BOARDS The ‘classical’ gold standard system that operated between 1870 and 1913 was, for the participating countries, an apparent equivalent to moving to a ‘dollar standard’ today. Participating countries declared parities against gold, wi ...
Chapter 2
... 2. protection shall be afforded domestic industries through customs tariffs, not through such commercial measures as import quotas; and 3. consultation shall be the primary method used to solve global trade problems. ...
... 2. protection shall be afforded domestic industries through customs tariffs, not through such commercial measures as import quotas; and 3. consultation shall be the primary method used to solve global trade problems. ...
Vulnerability Among Emerging Markets
... an international currency war, a general weakening of currency. This threatens us because it takes away our competitiveness” (9/27/2010). • I.e., countries everywhere are trying to push down the value of their currencies, to gain exports & employment, – a goal that is not globally consistent. ...
... an international currency war, a general weakening of currency. This threatens us because it takes away our competitiveness” (9/27/2010). • I.e., countries everywhere are trying to push down the value of their currencies, to gain exports & employment, – a goal that is not globally consistent. ...
International Business Strategy, Management & the New
... International Business: Strategy, Management, and the New Realities ...
... International Business: Strategy, Management, and the New Realities ...
LM Y - Harvard University
... themselves with BoP surpluses during 2003-08 & 2010-13? • Strong economic performance (especially Asia) -- IS shifts right. • Easy monetary policy in US and other major industrialized countries (low i*) -- BP shifts down. ...
... themselves with BoP surpluses during 2003-08 & 2010-13? • Strong economic performance (especially Asia) -- IS shifts right. • Easy monetary policy in US and other major industrialized countries (low i*) -- BP shifts down. ...
AP United States History
... downturn. It drew criticism as tending to favor bankers and lenders--who needed the value of a borrowed dollar to hold steady, or increase, until it was repaid--and detrimental to borrowers and workers. Heirs to the Greenback Party of the 1870s believed that paper money was the solution. In post-war ...
... downturn. It drew criticism as tending to favor bankers and lenders--who needed the value of a borrowed dollar to hold steady, or increase, until it was repaid--and detrimental to borrowers and workers. Heirs to the Greenback Party of the 1870s believed that paper money was the solution. In post-war ...