Lecture28
... important for long-term movements. • change in m (currency ratio c) is important for short-term movements. ...
... important for long-term movements. • change in m (currency ratio c) is important for short-term movements. ...
Dollar steady versus euro, yen amid lower US yields
... rope's largest economy and reinforced a case for more action by the European ...
... rope's largest economy and reinforced a case for more action by the European ...
Chapter 20
... revaluations: with free flows of financial assets, capital flight and speculation could occur in an EMS with separate currencies, but it would be more difficult for them to occur in an EMS with a single currency. ...
... revaluations: with free flows of financial assets, capital flight and speculation could occur in an EMS with separate currencies, but it would be more difficult for them to occur in an EMS with a single currency. ...
Exchange Rate Gap Effect on Economic Growth in Iran
... 3-2-2. Trend of Exchange Rate Gap Prior to Islamic Revolution, the official exchange rate was approximately 70 Rials per US Dollar. At that time, the gap between the official and black market exchange rate was about 7 Rials which has gradually increased until 2001. The trend and fluctuation of this ...
... 3-2-2. Trend of Exchange Rate Gap Prior to Islamic Revolution, the official exchange rate was approximately 70 Rials per US Dollar. At that time, the gap between the official and black market exchange rate was about 7 Rials which has gradually increased until 2001. The trend and fluctuation of this ...
Chapter20
... • In a closed economy, an increase in G causes the interest rate to rise and output to increase. • In a small, open economy, the fact that the domestic interest rate, r2 is greater than the world interest rate, rw, means there must be further adjustment. Canadian and foreign savers find the Canadian ...
... • In a closed economy, an increase in G causes the interest rate to rise and output to increase. • In a small, open economy, the fact that the domestic interest rate, r2 is greater than the world interest rate, rw, means there must be further adjustment. Canadian and foreign savers find the Canadian ...
Full Text
... strategy thus lies in re-balancing Chinese growth in favour of domestic demand, which would involve reducing current-account surpluses and gradually appreciating the renminbi at the same time. Gradually eliminating the Sino-American imbalance in this way would reduce the risk of a fall in the dollar ...
... strategy thus lies in re-balancing Chinese growth in favour of domestic demand, which would involve reducing current-account surpluses and gradually appreciating the renminbi at the same time. Gradually eliminating the Sino-American imbalance in this way would reduce the risk of a fall in the dollar ...
EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL OF SWAZILAND
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
(2)_EN
... relate to goods or securities located in Mozambican territory and to rights to such goods or monetary instruments or refer to activities undertaken in Mozambique; ...
... relate to goods or securities located in Mozambican territory and to rights to such goods or monetary instruments or refer to activities undertaken in Mozambique; ...
Classical Economics & Relative Prices
... Suppose that trade is initially balanced. A rise in productivity increases investment demand In a closed economy, interest rates would rise In an open economy, the trade deficit would increase. In the case, the deficit increases from zero to $15,000 Do interest rates rise at all? ...
... Suppose that trade is initially balanced. A rise in productivity increases investment demand In a closed economy, interest rates would rise In an open economy, the trade deficit would increase. In the case, the deficit increases from zero to $15,000 Do interest rates rise at all? ...
Ch. 18
... equilibrium real fed funds rate + 1/2 (inflation gap) + 1/2 (output gap) Taylor has assumed that equilibrium real fed funds rates (consistent with full employment in the long run) is 2% and that an appropriate target for inflation would be also 2%, with equal weights of ½ on the inflation and output ...
... equilibrium real fed funds rate + 1/2 (inflation gap) + 1/2 (output gap) Taylor has assumed that equilibrium real fed funds rates (consistent with full employment in the long run) is 2% and that an appropriate target for inflation would be also 2%, with equal weights of ½ on the inflation and output ...
An Empirical Study on the Management of China's Sovereign Wealth Funds
... Normally, according to demand of different motive, foreign exchange reserves can be divided into three parts: liquidity demand, security demand and profitable demand [1]. Liquidity demand is the first level of foreign exchange reserves management; it mainly includes trade demand, external debt payme ...
... Normally, according to demand of different motive, foreign exchange reserves can be divided into three parts: liquidity demand, security demand and profitable demand [1]. Liquidity demand is the first level of foreign exchange reserves management; it mainly includes trade demand, external debt payme ...
An exchange-rate-centred monetary policy system
... Second, MAS operates a managed float regime for the Singapore dollar. The trade-weighted exchange rate is allowed to fluctuate within a policy band, which provides a mechanism to accommodate short-term fluctuations in the foreign exchange markets and permits flexibility in managing the exchange rate ...
... Second, MAS operates a managed float regime for the Singapore dollar. The trade-weighted exchange rate is allowed to fluctuate within a policy band, which provides a mechanism to accommodate short-term fluctuations in the foreign exchange markets and permits flexibility in managing the exchange rate ...
Sudden stops, external debt and the exchange rate
... (2009)).7 Britain could presumably have allowed the pound ...
... (2009)).7 Britain could presumably have allowed the pound ...
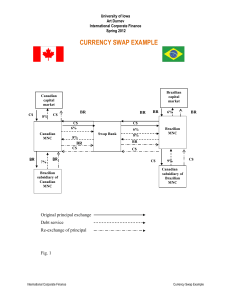
E4 - Art Durnev
... A Canadian MNC desires to finance a capital expenditure of its Brazilian subsidiary. The project has economic life of five years. The cost of the projects is BR40,000,000. At the current exchange rate of BR1.60/C$1.00, the parent firm could raise C$25,000,000 in Canadian capital market by issuing fi ...
... A Canadian MNC desires to finance a capital expenditure of its Brazilian subsidiary. The project has economic life of five years. The cost of the projects is BR40,000,000. At the current exchange rate of BR1.60/C$1.00, the parent firm could raise C$25,000,000 in Canadian capital market by issuing fi ...
Faculty Research Working Papers Series
... largest in terms of output and trade. By such measures, Japan should be number 2, ahead of Germany. Alarmist fears of the early 1990s, notwithstanding, it was never very likely that Japan, a country with half the population and far less land area or natural resources, would surpass the United States ...
... largest in terms of output and trade. By such measures, Japan should be number 2, ahead of Germany. Alarmist fears of the early 1990s, notwithstanding, it was never very likely that Japan, a country with half the population and far less land area or natural resources, would surpass the United States ...
FRBSF E L CONOMIC ETTER
... Banks and other depository institutions (for convenience, we’ll refer to all of these as “banks”) keep a certain amount of funds in reserve to meet unexpected outflows. Banks can keep these reserves as cash in their vaults or as deposits with the Fed. In fact, banks are required to hold a certain am ...
... Banks and other depository institutions (for convenience, we’ll refer to all of these as “banks”) keep a certain amount of funds in reserve to meet unexpected outflows. Banks can keep these reserves as cash in their vaults or as deposits with the Fed. In fact, banks are required to hold a certain am ...
Homework 5
... and demand curve would shift in response to these events. What would happen to the money market interest rate and money supply? When nominal GDP declines the demand for money declines which would put downward pressure on the money market interest rate. But if the central bank wants to stabilize the ...
... and demand curve would shift in response to these events. What would happen to the money market interest rate and money supply? When nominal GDP declines the demand for money declines which would put downward pressure on the money market interest rate. But if the central bank wants to stabilize the ...
The euro in the currency war - Conseil d`Analyse Economique
... in the cases of Italy and Spain, rather than to finance businesses. This outcome has made both banks and sovereigns more vulnerable to each other.7 The bank’s reluctance to extend loans to the private sector can be partly explained by the capital constraints faced by the banks as part of the current ...
... in the cases of Italy and Spain, rather than to finance businesses. This outcome has made both banks and sovereigns more vulnerable to each other.7 The bank’s reluctance to extend loans to the private sector can be partly explained by the capital constraints faced by the banks as part of the current ...
IOSR Journal Of Humanities And Social Science (IOSR-JHSS)
... expensive for the rest of world because foreign currency automatically gains value and hence, exports are expected to rise. In the same vein, imports are expected to reduce as the rest of the world’s commodities become more costly for domestic residents. To this end, favourable balance of trade shou ...
... expensive for the rest of world because foreign currency automatically gains value and hence, exports are expected to rise. In the same vein, imports are expected to reduce as the rest of the world’s commodities become more costly for domestic residents. To this end, favourable balance of trade shou ...
Rate Debt Sustainability and
... further weakens the currency. It is therefore important that this chain of events be analysed in the short run, because it could rapidly lead to the unsustainability of a country's foreign debt (i.e. within some weeks). This could lead a country into bankruptcy even if the GDP rate of growth remains ...
... further weakens the currency. It is therefore important that this chain of events be analysed in the short run, because it could rapidly lead to the unsustainability of a country's foreign debt (i.e. within some weeks). This could lead a country into bankruptcy even if the GDP rate of growth remains ...
balance of payments
... reserves rise by $15,000, therefore, this transaction results in a negative $15,000 entry in the German financial account.(and a positive $15,000 entry in the U.S. financial account) ...
... reserves rise by $15,000, therefore, this transaction results in a negative $15,000 entry in the German financial account.(and a positive $15,000 entry in the U.S. financial account) ...
International Monetary Reform and the Stabilization Problem J. Marcus Fleming
... effectiveness of international control over reserve supply would have continued to be threatened from another side, namely, from changes in the effective currency-equivalent of existing gold reserves. Though it has not proved possible to agree on any solution to the sproblem of gold valuation, all o ...
... effectiveness of international control over reserve supply would have continued to be threatened from another side, namely, from changes in the effective currency-equivalent of existing gold reserves. Though it has not proved possible to agree on any solution to the sproblem of gold valuation, all o ...
Jacob A. Frenkel and Morris Goldstein THE INTERNATIONAL MONETARY SYSTEM: Introduction
... in countries with either relatively low or relatively high inflation rates. In the former, there is a worry about repetition of the latter days of Bretton Woods when disequilibrium exchange rates, heavy exchange market intervention, and massive capital flows combined to wrestle control of the money ...
... in countries with either relatively low or relatively high inflation rates. In the former, there is a worry about repetition of the latter days of Bretton Woods when disequilibrium exchange rates, heavy exchange market intervention, and massive capital flows combined to wrestle control of the money ...
Exchange Rate Theories
... growth rate of the money supply in the short run, although long-run money growth must be consistent with money-demand requirements. So far, we have discussed sterilization in the context of fixed exchange rates. Now, let’s consider how a sterilization operation might occur in a floating exchange rat ...
... growth rate of the money supply in the short run, although long-run money growth must be consistent with money-demand requirements. So far, we have discussed sterilization in the context of fixed exchange rates. Now, let’s consider how a sterilization operation might occur in a floating exchange rat ...
Should Mexico Adopt the US Dollar? A Preliminary Index
... of lenders’ deposits and transactions. From this perspective, it would be desirable to make a thorough evaluation of investment finance in Mexico. Finally, a third alternative would be for domestic banks to elaborate private insurance schemes (see the experience of Argentina). Alternative lenders of ...
... of lenders’ deposits and transactions. From this perspective, it would be desirable to make a thorough evaluation of investment finance in Mexico. Finally, a third alternative would be for domestic banks to elaborate private insurance schemes (see the experience of Argentina). Alternative lenders of ...