On the Evolution of Chemical Organizations
... In order to study such complex dynamics new methods are required that can deal with constructive systems [11], i.e. systems where new components (molecular species) appear, which may change the present network topology. In this paper we study how chemical organization theory [22, 4] can help to expl ...
... In order to study such complex dynamics new methods are required that can deal with constructive systems [11], i.e. systems where new components (molecular species) appear, which may change the present network topology. In this paper we study how chemical organization theory [22, 4] can help to expl ...
2013 8th Grade Physical Science End of Year Exam Study Guide
... 2. Know that the difference between transparent, translucent, and opaque objects. 3. Know that the color of an opaque object is the color of light that is reflected back to you. Atoms and Elements – Chapter 8 (pages 304 – 337) 1. Know the four scientists that have contributed most to the model of an ...
... 2. Know that the difference between transparent, translucent, and opaque objects. 3. Know that the color of an opaque object is the color of light that is reflected back to you. Atoms and Elements – Chapter 8 (pages 304 – 337) 1. Know the four scientists that have contributed most to the model of an ...
UNIT III - Photochemistry
... In the presence of light and chlorophyll Go becomes negative; thereby the reaction proceeds and produces glucose. But in the absence of chlorophyll, the Go for this reaction is +2875 kJ. Since Go is positive, the above reaction is not possible. PHOTOPHYSICAL PROCESS: Generally atoms or molecules ...
... In the presence of light and chlorophyll Go becomes negative; thereby the reaction proceeds and produces glucose. But in the absence of chlorophyll, the Go for this reaction is +2875 kJ. Since Go is positive, the above reaction is not possible. PHOTOPHYSICAL PROCESS: Generally atoms or molecules ...
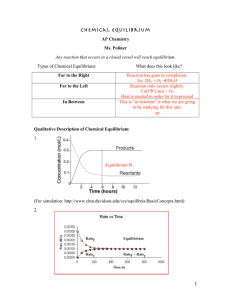
7.1 CHEMICAL SYSTEMS IN EQUILIBRIUM: Dynamic Equilibrium in
... According to Le Chatelier's Principle, if you increase the pressure the system will respond by favouring the reaction which produces fewer molecules. That will cause the pressure to fall again. In order to get as much ammonia as possible in the equilibrium mixture, you need as high a pressure as pos ...
... According to Le Chatelier's Principle, if you increase the pressure the system will respond by favouring the reaction which produces fewer molecules. That will cause the pressure to fall again. In order to get as much ammonia as possible in the equilibrium mixture, you need as high a pressure as pos ...
The Wizard Test Maker
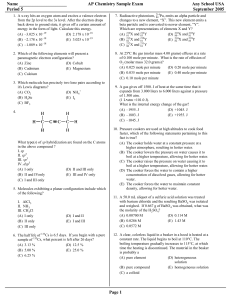
... What is the internal energy change of the gas? (A) –1955. J (D) +1045. J (B) –1803. J (E) +1955. J (C) –1045. J 10. Pressure cookers are used at high altitudes to cook food faster, which of the following statements pertaining to this fact is true? (A) The cooker holds water at a constant pressure at ...
... What is the internal energy change of the gas? (A) –1955. J (D) +1045. J (B) –1803. J (E) +1955. J (C) –1045. J 10. Pressure cookers are used at high altitudes to cook food faster, which of the following statements pertaining to this fact is true? (A) The cooker holds water at a constant pressure at ...
PDF
... systems, which are mainly hardware driven, the microprocessor is the brain of the system which detects input and in turn actuates output. A human chemical interaction, on the other hand, is driven by a twocomponent system: the active component senses input (e.g., environmental pollutants), whereas t ...
... systems, which are mainly hardware driven, the microprocessor is the brain of the system which detects input and in turn actuates output. A human chemical interaction, on the other hand, is driven by a twocomponent system: the active component senses input (e.g., environmental pollutants), whereas t ...
Problem 14. MAGNESIUM DETERMINATION
... applied to macrosystems. To illustrate this idea, E. Schrödinger proposed the following mental experiment. Consider the Geiger counter which detects the entering electrons. The counter is connected to a device which breaks the glass with the poison when the particle enters the counter. Near the glas ...
... applied to macrosystems. To illustrate this idea, E. Schrödinger proposed the following mental experiment. Consider the Geiger counter which detects the entering electrons. The counter is connected to a device which breaks the glass with the poison when the particle enters the counter. Near the glas ...
Properties of Systems in Equilibrium - Le
... where Qsp is called the solubility product reaction quotient. Note that, upon mixing two solutions, one containing A+ and the other containing B-, if Qsp < Ksp the system is not at equilibrium, but since no solid AxBy is present the reaction cannot shift to the right and therefore no reaction will b ...
... where Qsp is called the solubility product reaction quotient. Note that, upon mixing two solutions, one containing A+ and the other containing B-, if Qsp < Ksp the system is not at equilibrium, but since no solid AxBy is present the reaction cannot shift to the right and therefore no reaction will b ...
Chapter 20: Electrochemistry
... V = 0 when two charged objects are separated by infinity We are interested in DV between Anode and Cathode ...
... V = 0 when two charged objects are separated by infinity We are interested in DV between Anode and Cathode ...
Chapter 4 Packet
... molecular and net ionic equations for them. I will also be able identify spectator ions. 6. be able to choose which type of equation is most appropriate (molecular, ionic or net ionic) equation for specific situations. 7. recognize reactions which produce either CO2, H2S, or NH3 gases. 8. determine ...
... molecular and net ionic equations for them. I will also be able identify spectator ions. 6. be able to choose which type of equation is most appropriate (molecular, ionic or net ionic) equation for specific situations. 7. recognize reactions which produce either CO2, H2S, or NH3 gases. 8. determine ...
Balancing Chemical Reactions
... Converting an unbalanced chemical reaction into one that is balanced is mostly a “trial and error” process. There are, however, some important things that you can’t do, some common conventions, and some strategies that help simplify the process. Things That You Can’t Do When Balancing a Chemical Rea ...
... Converting an unbalanced chemical reaction into one that is balanced is mostly a “trial and error” process. There are, however, some important things that you can’t do, some common conventions, and some strategies that help simplify the process. Things That You Can’t Do When Balancing a Chemical Rea ...
Unit 10: Chemical Reactions
... The substances that undergo a chemical reaction are the reactants. The new substances formed are the products. Special symbols are written after formulas in equations to show a substance’s state. The designations for solid, liquid, or gas, are (s), (l), and (g), respectively. A substance dissolv ...
... The substances that undergo a chemical reaction are the reactants. The new substances formed are the products. Special symbols are written after formulas in equations to show a substance’s state. The designations for solid, liquid, or gas, are (s), (l), and (g), respectively. A substance dissolv ...
(a) From , 2012 General Chemistry I
... Suppose that 1.00 mol of ideal gas molecules maintained at 292 K and 3.00 atm expands from 8.00 L to 20.00 L and a final pressure of 1.20 atm by two different paths. (a) Path A is an isothermal, reversible expansion. (b) Path B has two parts. In step 1, the gas is cooled at constant volume until its ...
... Suppose that 1.00 mol of ideal gas molecules maintained at 292 K and 3.00 atm expands from 8.00 L to 20.00 L and a final pressure of 1.20 atm by two different paths. (a) Path A is an isothermal, reversible expansion. (b) Path B has two parts. In step 1, the gas is cooled at constant volume until its ...
Chemistry Section 2
... statements is NOT true of this process? A) The reaction must be spontaneous because it is both exothermic and has a favorable entropy change. B) The reaction could be spontaneous or non-spontaneous depending on the temperature at which the reaction is run. C) The products of the reaction have greate ...
... statements is NOT true of this process? A) The reaction must be spontaneous because it is both exothermic and has a favorable entropy change. B) The reaction could be spontaneous or non-spontaneous depending on the temperature at which the reaction is run. C) The products of the reaction have greate ...
MT 3 Practice
... 10. For the following reaction at 25°C I2(g) + Cl2(g) 2ICl(g) DH° = -26.9 kJ and DS° = 11.3 J/K. Calculate DG° for the reaction in kilojoules. [A] -50.6 kJ [B] 102 kJ [C] 50.6 kJ [D] -30.3 kJ 11. Given the following Fe2O3(s) + 3CO(g) 2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g) 3Fe2O3(s) + CO(g) 2Fe3O4(s) + CO2(g) calculate DG ...
... 10. For the following reaction at 25°C I2(g) + Cl2(g) 2ICl(g) DH° = -26.9 kJ and DS° = 11.3 J/K. Calculate DG° for the reaction in kilojoules. [A] -50.6 kJ [B] 102 kJ [C] 50.6 kJ [D] -30.3 kJ 11. Given the following Fe2O3(s) + 3CO(g) 2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g) 3Fe2O3(s) + CO(g) 2Fe3O4(s) + CO2(g) calculate DG ...
template
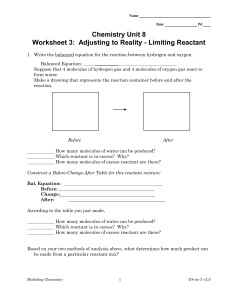
... Construct a Before-Change-After Table for this reactant mixture: Bal. Equation: Before: __________________________________________ Change:__________________________________________ After: ___________________________________________ According to the table you just made, How many molecules of ammonia ...
... Construct a Before-Change-After Table for this reactant mixture: Bal. Equation: Before: __________________________________________ Change:__________________________________________ After: ___________________________________________ According to the table you just made, How many molecules of ammonia ...
Chp 5 Circle the correct answer Consider three 1
... a) Yes, ΔE = 0 at all times, which is why q = -w. b) No, ΔE does not always equal zero but this is only due to factors like friction and heat. c) No, ΔE does not always equal zero because it refers to the system’s internal energy which is affected by heat and work. d) No, ΔE never equals zero becaus ...
... a) Yes, ΔE = 0 at all times, which is why q = -w. b) No, ΔE does not always equal zero but this is only due to factors like friction and heat. c) No, ΔE does not always equal zero because it refers to the system’s internal energy which is affected by heat and work. d) No, ΔE never equals zero becaus ...
thermodynamics
... surroundings, with fixed values of pressure, volume, temperature, mass and composition that do not change with time, is in a state of thermodynamic equilibrium. In general, whether or not a system is in a state of equilibrium depends on the surroundings and the nature of the wall that separates the ...
... surroundings, with fixed values of pressure, volume, temperature, mass and composition that do not change with time, is in a state of thermodynamic equilibrium. In general, whether or not a system is in a state of equilibrium depends on the surroundings and the nature of the wall that separates the ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.