Notes Set 1
... Follow- up Questions : In order to see if there will be a reaction between two chemical species, we must ask ourselves the following questions : 1. Is there one species gaining electrons and one losing ? If not, there will not be a reaction. 2. Is the one gaining the electrons a better oxidizing age ...
... Follow- up Questions : In order to see if there will be a reaction between two chemical species, we must ask ourselves the following questions : 1. Is there one species gaining electrons and one losing ? If not, there will not be a reaction. 2. Is the one gaining the electrons a better oxidizing age ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... (3) Energy is released as bonds are formed. (4) Energy is released as bonds are broken. ...
... (3) Energy is released as bonds are formed. (4) Energy is released as bonds are broken. ...
Basic Thermodynamics - Alpha College of Engineering
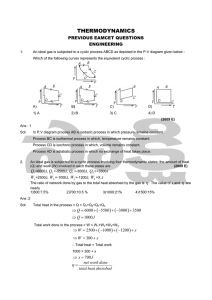
... determine the additional power that must be delivered by the engine. [04 Marks, Jun-2015] 4. A centrifugal pump delivers 50 kg of water per second. The inlet and outlet pressure are 1 bar and 4.2 bar respectively. The suction is 2.2m below the centre of the pump and delivery is 8.5m above the centre ...
... determine the additional power that must be delivered by the engine. [04 Marks, Jun-2015] 4. A centrifugal pump delivers 50 kg of water per second. The inlet and outlet pressure are 1 bar and 4.2 bar respectively. The suction is 2.2m below the centre of the pump and delivery is 8.5m above the centre ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... Stoichiometry: the study of quantities of substances used and produced in a chemical equation. Stoichiometry is based on… chemical equations represent chemical reactions Law of Conservation of Matter: Matter (mass) cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. The atoms are only re-arra ...
... Stoichiometry: the study of quantities of substances used and produced in a chemical equation. Stoichiometry is based on… chemical equations represent chemical reactions Law of Conservation of Matter: Matter (mass) cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. The atoms are only re-arra ...
PDF of Chapter 6 Foundations of Chemistry
... Before you read, decide if you agree or disagree with each of these statements. As you read this chapter, see if you change your mind about any of the statements. 1 The atoms in all objects are the same. 2 You cannot always tell by an object’s appearance whether it is made of more than one type of a ...
... Before you read, decide if you agree or disagree with each of these statements. As you read this chapter, see if you change your mind about any of the statements. 1 The atoms in all objects are the same. 2 You cannot always tell by an object’s appearance whether it is made of more than one type of a ...
C:\Documents and Settings\mrh70950\My Documents
... CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter 1: Electrons, Bonds, and Molecular Properties I. Isomerism: The existence of molecules that have the same molecular formulas but differ in chemical or physical properties A. Constitutional isomers (also called structural isomers) differ ...
... CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter 1: Electrons, Bonds, and Molecular Properties I. Isomerism: The existence of molecules that have the same molecular formulas but differ in chemical or physical properties A. Constitutional isomers (also called structural isomers) differ ...
纳米结构体系物理化学性质的理论研究方法与实例
... 9.1.4 Parallel reactions • Parallel reactions are defined as two or more processes in which the same species participate in each reaction step. • The most common cases of parallel reactions are: (1) those in which the initial reactant decomposes into several different products; (2) those in which t ...
... 9.1.4 Parallel reactions • Parallel reactions are defined as two or more processes in which the same species participate in each reaction step. • The most common cases of parallel reactions are: (1) those in which the initial reactant decomposes into several different products; (2) those in which t ...
Kinetic study on carbonation of crude Li2CO3 with CO2
... single crystal industries in the world, the demand for it has been dramatically growing in recent years, but its supply is to some degree insufficient. Therefore, improving the production of high purity Li2CO3 is extremely necessary nowadays. Attempts to produce high purity Li2CO3 were made by Brown ...
... single crystal industries in the world, the demand for it has been dramatically growing in recent years, but its supply is to some degree insufficient. Therefore, improving the production of high purity Li2CO3 is extremely necessary nowadays. Attempts to produce high purity Li2CO3 were made by Brown ...
derivation of some new distributions in statistical mechanics using
... theory). A fundamental step in using entropy in the new contexts unrelated to thermodynamics was provided by Shannon (1948), who realized that entropy could be used to measure types of disorder other than those of thermodynamic micro-states. Shannon was interested in information theory, particularly ...
... theory). A fundamental step in using entropy in the new contexts unrelated to thermodynamics was provided by Shannon (1948), who realized that entropy could be used to measure types of disorder other than those of thermodynamic micro-states. Shannon was interested in information theory, particularly ...
- Vijay Education Academy
... Many metals occur in the earth‟s crust as sulphides. To extract metals, the sulphide ores are first roasted in reverberatory furnace in excess of air when metal oxide is formed and sulphur dioxide is released. Chemical engineer suggested the management not to release SO 2 into the atmosphere. He sug ...
... Many metals occur in the earth‟s crust as sulphides. To extract metals, the sulphide ores are first roasted in reverberatory furnace in excess of air when metal oxide is formed and sulphur dioxide is released. Chemical engineer suggested the management not to release SO 2 into the atmosphere. He sug ...
20. Chemical Equilibrium
... a given temperature in such a way as to allow the products to accumulate in the reaction container. After a period of time, the reaction will reach equilibrium. At this point, it may be possible to experimentally determine the concentrations of the reactants and products in the container. The concen ...
... a given temperature in such a way as to allow the products to accumulate in the reaction container. After a period of time, the reaction will reach equilibrium. At this point, it may be possible to experimentally determine the concentrations of the reactants and products in the container. The concen ...
Synthesis of Aliphatic Nitro Compounds1i2 A simple new
... Preparation of %nitrooctane from b-iodo~ctane.~2-Iodooctane (71.2 g., 0.30 mole) was poured into a stirred solution of 225 ml. dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and 36 g. of sodium nitrite (0.52 mole) contained in a 500 ml. flask immersed in a water bath held a t room temperature. Stirring was continued for ...
... Preparation of %nitrooctane from b-iodo~ctane.~2-Iodooctane (71.2 g., 0.30 mole) was poured into a stirred solution of 225 ml. dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and 36 g. of sodium nitrite (0.52 mole) contained in a 500 ml. flask immersed in a water bath held a t room temperature. Stirring was continued for ...
Test bank questions
... A. At equilibrium the total concentration of products equals the total concentration of reactants, that is, [products] = [reactants]. B. Equilibrium is the result of the cessation of all chemical change. C. There is only one set of equilibrium concentrations that equals the K c value. D. At equilibr ...
... A. At equilibrium the total concentration of products equals the total concentration of reactants, that is, [products] = [reactants]. B. Equilibrium is the result of the cessation of all chemical change. C. There is only one set of equilibrium concentrations that equals the K c value. D. At equilibr ...
Behavior of the chemical potential/molar free energy in single
... In addition to these fundamental states of aggregation, liquids and solids may have multiple structural forms that are stable under different conditions of temperature and pressure. In solids, this is the stability of different crystal structures. Such structural variants (that have the same composi ...
... In addition to these fundamental states of aggregation, liquids and solids may have multiple structural forms that are stable under different conditions of temperature and pressure. In solids, this is the stability of different crystal structures. Such structural variants (that have the same composi ...
15. Thermodynamics
... 11. Two identical containers A and B with frictionless pistons contain the same ideal gas at the same temperature and same volume V. The mass of the gas in A is mA and that in B is mB . The gas in each cylinder is now allowed to expand isothermally to the final volume2V. The changes in the pressure ...
... 11. Two identical containers A and B with frictionless pistons contain the same ideal gas at the same temperature and same volume V. The mass of the gas in A is mA and that in B is mB . The gas in each cylinder is now allowed to expand isothermally to the final volume2V. The changes in the pressure ...
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER SIR.S.M.TAHIR CHEMISTRY Mob: 9557076999
... Explain, why does the atomic radii increases considerably from N to P but very little increase is observed from As to Bi. ...
... Explain, why does the atomic radii increases considerably from N to P but very little increase is observed from As to Bi. ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.