AP Chemistry Notes and Worksheets 2014
... Look at the image created for a sample of neon to the right. You can see three “peaks” or bumps on the graph. Each bump represents the amount of particles of that particular mass that were detected, telling us that there are three isotopes of neon in the sample. Example. Use the mass spectrum sh ...
... Look at the image created for a sample of neon to the right. You can see three “peaks” or bumps on the graph. Each bump represents the amount of particles of that particular mass that were detected, telling us that there are three isotopes of neon in the sample. Example. Use the mass spectrum sh ...
CARBANIONS Carbanions are units that contain a negative charge
... changes and formation of new carbon-carbon bonds. Carbanions are very useful intermediates for the formation of new carbon-carbon bonds. Thus carbanions participate in 1) SN2 alkylation reactions, 2) in 1,2 additions to carbonyl functions, and 3) in 1,4-additions such as Michael Reactions. Fluorinat ...
... changes and formation of new carbon-carbon bonds. Carbanions are very useful intermediates for the formation of new carbon-carbon bonds. Thus carbanions participate in 1) SN2 alkylation reactions, 2) in 1,2 additions to carbonyl functions, and 3) in 1,4-additions such as Michael Reactions. Fluorinat ...
THE TEACHING PROGRAM OF CHEMISTRY DEPARTMENT
... Basic concepts: matter, energy, volume, pressure, temperature, system, unit systems, intensive and extensive properties The properties of gases: Ideal gas laws, equation state of ideal gas, mixtures of gases, the kinetic theory of gases, mean values and distributions, deviation of ideality, imperfec ...
... Basic concepts: matter, energy, volume, pressure, temperature, system, unit systems, intensive and extensive properties The properties of gases: Ideal gas laws, equation state of ideal gas, mixtures of gases, the kinetic theory of gases, mean values and distributions, deviation of ideality, imperfec ...
Chemistry - College Catalog
... Enrollment limited to first-year students. Enrollment by placement only. The first two courses in this sequence meet the general education requirement in the physical sciences. Not recommended for students majoring in Chemistry or Biological Chemistry. This three-quarter sequence is a systematic int ...
... Enrollment limited to first-year students. Enrollment by placement only. The first two courses in this sequence meet the general education requirement in the physical sciences. Not recommended for students majoring in Chemistry or Biological Chemistry. This three-quarter sequence is a systematic int ...
this PDF file - University of Pannonia
... The conversion pathway can be demonstrated by reaction mechanism. Unfortunately, reaction mechanism does not contain all necessary information which is needed to design a reactor because it gathers steps of conversion but does not give any information about the reaction rate. To run a reactor under ...
... The conversion pathway can be demonstrated by reaction mechanism. Unfortunately, reaction mechanism does not contain all necessary information which is needed to design a reactor because it gathers steps of conversion but does not give any information about the reaction rate. To run a reactor under ...
Stoichiometry
... • By definition, these are the mass of 1 mol of a substance (i.e., g/mol) – The molar mass of an element is the mass number for the element that we find on the periodic table – The formula weight (in amu’s) will be the same number as the molar mass (in g/mol) Stoichiometry ...
... • By definition, these are the mass of 1 mol of a substance (i.e., g/mol) – The molar mass of an element is the mass number for the element that we find on the periodic table – The formula weight (in amu’s) will be the same number as the molar mass (in g/mol) Stoichiometry ...
Stoichiometry Notes
... an unknown substance and the solute of the standard solution. The completion of the reaction is indicated by the end point of the reaction, which is observed by the colour change either due to the indicator or due to the solute itself. Whether the reactions during the analysis are either between an ...
... an unknown substance and the solute of the standard solution. The completion of the reaction is indicated by the end point of the reaction, which is observed by the colour change either due to the indicator or due to the solute itself. Whether the reactions during the analysis are either between an ...
CHAPTER 14 CHEMICAL KINETICS
... Strategy: The relationship between the concentration of a reactant at different times in a first-order reaction is given by Equations (14.3) and (14.4) of the text. We are asked to determine the time required for 95% of the phosphine to decompose. If we initially have 100% of the compound and 95% ha ...
... Strategy: The relationship between the concentration of a reactant at different times in a first-order reaction is given by Equations (14.3) and (14.4) of the text. We are asked to determine the time required for 95% of the phosphine to decompose. If we initially have 100% of the compound and 95% ha ...
No Slide Title
... Energy as Heat, continued A Substance’s Energy Can Be Measure by Enthalpy, continued • Enthalpy is the sum of the internal energy of a system plus the product of the system’s volume multiplied by the pressure that the system exerts on its surroundings • If pressure remains constant, the enthalpy inc ...
... Energy as Heat, continued A Substance’s Energy Can Be Measure by Enthalpy, continued • Enthalpy is the sum of the internal energy of a system plus the product of the system’s volume multiplied by the pressure that the system exerts on its surroundings • If pressure remains constant, the enthalpy inc ...
Principles of Chemistry 1 and 2 Notes
... (turning it on/off) Generally speaking: Compounds that possess dipole moments are said to be polar and compounds that do not possess dipole moments are said to be non polar. Examples: Diatomic molecules: CO, NO, HCl, HF, etc…. all have dipole moments and hence are polar. Exceptions for the general r ...
... (turning it on/off) Generally speaking: Compounds that possess dipole moments are said to be polar and compounds that do not possess dipole moments are said to be non polar. Examples: Diatomic molecules: CO, NO, HCl, HF, etc…. all have dipole moments and hence are polar. Exceptions for the general r ...
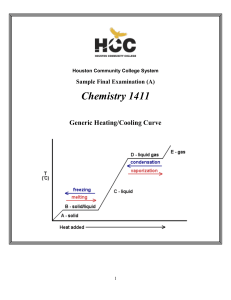
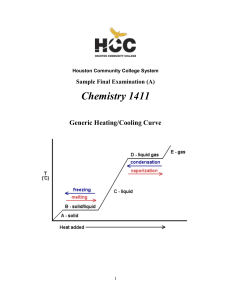
CHEM-1411 Final Practice Exam
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
1411FINALSAMPLE+KEY - Houston Community College
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
A Theoretical and Experimental Approach for Correlating
... entirety using first-principles theory. Of course, there are also problems. For example, such small particles are often unstable and even if they are stable, their native structure may be altered during catalytic reactions. This means that experimental characterization is difficult and best carried out ...
... entirety using first-principles theory. Of course, there are also problems. For example, such small particles are often unstable and even if they are stable, their native structure may be altered during catalytic reactions. This means that experimental characterization is difficult and best carried out ...
CHAPTER
... same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of particles, he may have been thinking of particles rearranging themselves. Individual gas particles are so small that their rearranging cannot be observed, but the volumes of gases can be measured directly. Avogadro's principle is one of the earl ...
... same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of particles, he may have been thinking of particles rearranging themselves. Individual gas particles are so small that their rearranging cannot be observed, but the volumes of gases can be measured directly. Avogadro's principle is one of the earl ...
Exam Edge Digital
... (iii) Bohr’s theory only worked to explain the emission spectrum of hydrogen. When his theory was applied to atoms with more than one electron, it failed to account for many of the lines in the emission spectra of these atoms. ...
... (iii) Bohr’s theory only worked to explain the emission spectrum of hydrogen. When his theory was applied to atoms with more than one electron, it failed to account for many of the lines in the emission spectra of these atoms. ...
Review Study Guide for the Final
... To what volume, in liters, must you dilute a solution containing 4 liters of 0.100 M of Ca(OH)2 to obtain a 0.00100 M solution as calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2)? ...
... To what volume, in liters, must you dilute a solution containing 4 liters of 0.100 M of Ca(OH)2 to obtain a 0.00100 M solution as calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2)? ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.