Higher Chemistry Resources Guide - Glow Blogs
... attraction that can operate between all atoms and molecules. These forces are much weaker than all other types of bonding. They are formed as a result of electrostatic attraction between temporary dipoles and induced dipoles caused by movement of electrons in atoms and molecules. The strength of Lon ...
... attraction that can operate between all atoms and molecules. These forces are much weaker than all other types of bonding. They are formed as a result of electrostatic attraction between temporary dipoles and induced dipoles caused by movement of electrons in atoms and molecules. The strength of Lon ...
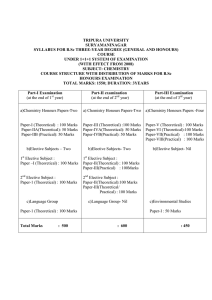
TRIPURA UNIVERSITY SURYAMANINAGAR SYLLABUS FOR B.Sc THREE-YEAR DEGREE (GENERAL AND HONOURS) COURSE
... Chemical Kinetics: Order and molecularity of reaction, rate of reaction, rate laws and rate equations, differential and integral forms of rate equation- zero order, first order and second order reactions, half life and average life, experimental methods for the determination of order of reactions, e ...
... Chemical Kinetics: Order and molecularity of reaction, rate of reaction, rate laws and rate equations, differential and integral forms of rate equation- zero order, first order and second order reactions, half life and average life, experimental methods for the determination of order of reactions, e ...
Higher Chemistry Resources Guide - Glow Blogs
... attraction that can operate between all atoms and molecules. These forces are much weaker than all other types of bonding. They are formed as a result of electrostatic attraction between temporary dipoles and induced dipoles caused by movement of electrons in atoms and molecules. The strength of Lon ...
... attraction that can operate between all atoms and molecules. These forces are much weaker than all other types of bonding. They are formed as a result of electrostatic attraction between temporary dipoles and induced dipoles caused by movement of electrons in atoms and molecules. The strength of Lon ...
Reactors for Measuring Reaction Rates
... benzoquinone. This example illustrates the general procedure used for solving isothermal problems. First, write down the reaction rate expression. Second, formulate the material balance. Third, substitute the reaction rate expression into the material balance and ...
... benzoquinone. This example illustrates the general procedure used for solving isothermal problems. First, write down the reaction rate expression. Second, formulate the material balance. Third, substitute the reaction rate expression into the material balance and ...
Kinetic multi-layer model of aerosol surface and bulk chemistry (KM
... more flexible and requires no assumptions about interfacial transport. As detailed in Appendix B, the ozone concentrations calculated for the near-surface bulk indicate that the assumption of Henry’s law equilibrium is not a realistic boundary layer condition for the PDE method when applied to react ...
... more flexible and requires no assumptions about interfacial transport. As detailed in Appendix B, the ozone concentrations calculated for the near-surface bulk indicate that the assumption of Henry’s law equilibrium is not a realistic boundary layer condition for the PDE method when applied to react ...
Bond Dissociation Energies of Organic Molecules
... ABSTRACT In this Account we have compiled a list of reliable bond energies that are based on a set of critically evaluated experiments. A brief description of the three most important experimental techniques for measuring bond energies is provided. We demonstrate how these experimental data can be a ...
... ABSTRACT In this Account we have compiled a list of reliable bond energies that are based on a set of critically evaluated experiments. A brief description of the three most important experimental techniques for measuring bond energies is provided. We demonstrate how these experimental data can be a ...
Unit 1 - Physical Chemistry REACTION KINETICS
... The rate determing step would be step ① as it is the slow step and only chemicals involved in the rate determining step would effect the rate of reaction. HI is a reaction intermediate and would be used up as fast as it is produced. Proving a mechanism can be very difficult. Detecting intermediates ...
... The rate determing step would be step ① as it is the slow step and only chemicals involved in the rate determining step would effect the rate of reaction. HI is a reaction intermediate and would be used up as fast as it is produced. Proving a mechanism can be very difficult. Detecting intermediates ...
1.02 x 10 = 3 mol lit 3.4 x 10
... (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Answer all questions in Part I and six questions from Part II, choosing tw ...
... (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Answer all questions in Part I and six questions from Part II, choosing tw ...
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II
... this text. It happens that seven primary quantities are needed to completely describe all natural phenomena1. The decision as to which quantities are primary is arbitrary. The units of the primary quantities and their symbols are listed in Table 1.3-1 and are defined arbitrarily as follows: Meter: t ...
... this text. It happens that seven primary quantities are needed to completely describe all natural phenomena1. The decision as to which quantities are primary is arbitrary. The units of the primary quantities and their symbols are listed in Table 1.3-1 and are defined arbitrarily as follows: Meter: t ...
Chemistry - WorkNotes
... Students know the rate of reaction is the decrease in concentration of reactants or the increase in concentration of products with time. ...
... Students know the rate of reaction is the decrease in concentration of reactants or the increase in concentration of products with time. ...
View/Open - Minerva Access
... The search for new types of metal catalyzed C-C bond-coupling reactions continues, with an active research front being the development of alternatives to stoichiometric organometallic cross coupling reagents [1]. Metal catalyzed decarboxylative coupling reactions represent an attractive way of creat ...
... The search for new types of metal catalyzed C-C bond-coupling reactions continues, with an active research front being the development of alternatives to stoichiometric organometallic cross coupling reagents [1]. Metal catalyzed decarboxylative coupling reactions represent an attractive way of creat ...
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY Subject information (overview of syllabus)
... Soil chemistry: composition of soil and chemical reactions that may occur in soil. Atmospheric chemistry: atmospheric physical and chemical processes, particularly the photochemical process, as well as various effects from dispersion of pollutants, sampling and analytical methods relating to atmosph ...
... Soil chemistry: composition of soil and chemical reactions that may occur in soil. Atmospheric chemistry: atmospheric physical and chemical processes, particularly the photochemical process, as well as various effects from dispersion of pollutants, sampling and analytical methods relating to atmosph ...
Continued on Next page
... the given ∆H to find the enthalpy corresponding to the number of moles reacted. Since Qrxn = −Qsoln , state Q as a positive value. Remember to convert kJ to J. Step 3 Rearrange the equation Q = m · c · ∆T to calculate the ∆T of the solution (in J). Use the ∆T to find Tf. Assume that the reaction mix ...
... the given ∆H to find the enthalpy corresponding to the number of moles reacted. Since Qrxn = −Qsoln , state Q as a positive value. Remember to convert kJ to J. Step 3 Rearrange the equation Q = m · c · ∆T to calculate the ∆T of the solution (in J). Use the ∆T to find Tf. Assume that the reaction mix ...
Enthalpy, Entropy, Mollier Diagram and Steam
... this segment, we will introduce the concept of entropy and we will expand on the concept of enthalpy. As we progress through this text, you will notice that the discussion on entropy will be limited, reflecting the somewhat limited role of entropy in practical thermodynamics. On the other hand, our ...
... this segment, we will introduce the concept of entropy and we will expand on the concept of enthalpy. As we progress through this text, you will notice that the discussion on entropy will be limited, reflecting the somewhat limited role of entropy in practical thermodynamics. On the other hand, our ...
Lectures on Chapter 4, Part 2 Powerpoint 97 Document
... SO42-(aq) + 2 e Add water to the reactant side to supply an oxygen and add two protons to the product side that will remain plus the two electrons. SO32-(aq) + H2O(l) SO42-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 e Reduction: MnO4-(aq) + 3 eMnO2 (s) Add water to the product side to take up the extra oxygen from Mn cpds, ...
... SO42-(aq) + 2 e Add water to the reactant side to supply an oxygen and add two protons to the product side that will remain plus the two electrons. SO32-(aq) + H2O(l) SO42-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 e Reduction: MnO4-(aq) + 3 eMnO2 (s) Add water to the product side to take up the extra oxygen from Mn cpds, ...
Chem 171-2-3: Final Exam Review Multiple Choice Problems 1
... Carbon disulfide is a liquid that can be used in the production of rayon and cellophane. It is manufactured from methane and elemental sulfur according to the following chemical equation: CH4 (g) + 4 S (s) Ÿ CS2 (l) + 2 H2S (g) How many moles of CS2 can be formed by the complete reaction of 10.6 mol ...
... Carbon disulfide is a liquid that can be used in the production of rayon and cellophane. It is manufactured from methane and elemental sulfur according to the following chemical equation: CH4 (g) + 4 S (s) Ÿ CS2 (l) + 2 H2S (g) How many moles of CS2 can be formed by the complete reaction of 10.6 mol ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.