CST REVIEW Percent Error 1. 2. What is the formula for density?
... 35. Atoms and molecules in liquids move in a random pattern relative to one another because the intermolecular forces are too weak to hold the atoms or molecules in a solid form. Under the same conditions of pressure and temperature, how does a liquid differ from a solid and gas? 36. Draw Lewis dot ...
... 35. Atoms and molecules in liquids move in a random pattern relative to one another because the intermolecular forces are too weak to hold the atoms or molecules in a solid form. Under the same conditions of pressure and temperature, how does a liquid differ from a solid and gas? 36. Draw Lewis dot ...
FoundationsofChemistryppt
... 1. The atoms in all objects are the same. 2. You cannot always tell by an object’s appearance whether it is made of more than one type of atom. 3. The weight of a material never changes, regardless of where it is. 4. Boiling is one method used to separate parts of a mixture. ...
... 1. The atoms in all objects are the same. 2. You cannot always tell by an object’s appearance whether it is made of more than one type of atom. 3. The weight of a material never changes, regardless of where it is. 4. Boiling is one method used to separate parts of a mixture. ...
I Examen I Trim Science
... A solid is the state of matter that has a definite shape and volume. The particles in a solid do not move fast enough to overcome the attraction between them. Each particle vibrates in place and is locked in place by the particles around it. 2 types of solids: Crystalline solids: have a very ...
... A solid is the state of matter that has a definite shape and volume. The particles in a solid do not move fast enough to overcome the attraction between them. Each particle vibrates in place and is locked in place by the particles around it. 2 types of solids: Crystalline solids: have a very ...
stoichiometry - J. Seguin Science
... quantitative study of reactants and products in a chemical reaction. ...
... quantitative study of reactants and products in a chemical reaction. ...
Equilibrium at constant temperature and pressure: Gibbs Free
... at constant (U,V,N) to minimizing free energy of a system at constant (T, V, N). There are multiple ways to arrive at this change of variables, known as a Legendre transformation. (Those of you in 3.16 will recognize this). ...
... at constant (U,V,N) to minimizing free energy of a system at constant (T, V, N). There are multiple ways to arrive at this change of variables, known as a Legendre transformation. (Those of you in 3.16 will recognize this). ...
Spring Benchmark Exam
... 30. A technician prepared a solution by heating 100 milliliters of distilled water while adding KCl crystals until no more KCl would dissolve. She then capped the clear solution and set it aside on the lab bench. After several hours she noticed the solution had become cloudy and some solid had settl ...
... 30. A technician prepared a solution by heating 100 milliliters of distilled water while adding KCl crystals until no more KCl would dissolve. She then capped the clear solution and set it aside on the lab bench. After several hours she noticed the solution had become cloudy and some solid had settl ...
Chapter 12
... and volume are known at each step of the process The work done on a gas that takes it from some initial state to some final state is the negative of the area under the curve on the ...
... and volume are known at each step of the process The work done on a gas that takes it from some initial state to some final state is the negative of the area under the curve on the ...
Chapter 12
... and volume are known at each step of the process The work done on a gas that takes it from some initial state to some final state is the negative of the area under the curve on the ...
... and volume are known at each step of the process The work done on a gas that takes it from some initial state to some final state is the negative of the area under the curve on the ...
exam review - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 19. A mixture of 9.22 moles of A, 10.11 moles of B, and 27.83 moles of C is placed in a one-liter container at a certain temperature. The reaction is allowed to reach equilibrium. At equilibrium the number of moles of B is 18.32. Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction: A (g) + 2 B (g) ↔ ...
... 19. A mixture of 9.22 moles of A, 10.11 moles of B, and 27.83 moles of C is placed in a one-liter container at a certain temperature. The reaction is allowed to reach equilibrium. At equilibrium the number of moles of B is 18.32. Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction: A (g) + 2 B (g) ↔ ...
Chapter 17 - Bakersfield College
... Each set of equilibrium concentration is called an equilibrium position and it depends on the initial concentrations (there are an infinite # of equilibrium positions but only one equilibrium constant). ...
... Each set of equilibrium concentration is called an equilibrium position and it depends on the initial concentrations (there are an infinite # of equilibrium positions but only one equilibrium constant). ...
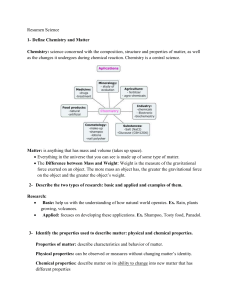
Matter Notes
... Study of Chemistry Chemistry: The study of the properties, composition and behaviour of matter What is matter? Anything that has mass & volume. Eg: wood, oxygen, etc Properties of Matter (physical or chemical) A. Physical Properties: ...
... Study of Chemistry Chemistry: The study of the properties, composition and behaviour of matter What is matter? Anything that has mass & volume. Eg: wood, oxygen, etc Properties of Matter (physical or chemical) A. Physical Properties: ...
Chapter 1
... A state function depends only on the initial and final states of a system. • Example: The altitude difference between Denver and Chicago does not depend on whether you fly or drive, only on the elevation of the two cities above sea level. • Similarly, the internal energy of 50 g of H2O(l) at 25 °C d ...
... A state function depends only on the initial and final states of a system. • Example: The altitude difference between Denver and Chicago does not depend on whether you fly or drive, only on the elevation of the two cities above sea level. • Similarly, the internal energy of 50 g of H2O(l) at 25 °C d ...
In this experiment you will observe examples of the five basic types
... Your lab report should include the purpose of the lab, the completed data and evaluation sheet, and answers (in complete sentences) to the following questions. 1. What are some of the observable changes that are evidence that a chemical reaction has taken place? 2. How did the flaming splint behave ...
... Your lab report should include the purpose of the lab, the completed data and evaluation sheet, and answers (in complete sentences) to the following questions. 1. What are some of the observable changes that are evidence that a chemical reaction has taken place? 2. How did the flaming splint behave ...
chemical reactions
... gauze covering the beaker. Use a document camera, or similar, to project the reaction on a screen. Repeat this using small pieces of Na and K. When cutting Li, Na and K from a larger piece, do that under the document camera to show the silvery surface of the metal. Add one or two drops of phenolphth ...
... gauze covering the beaker. Use a document camera, or similar, to project the reaction on a screen. Repeat this using small pieces of Na and K. When cutting Li, Na and K from a larger piece, do that under the document camera to show the silvery surface of the metal. Add one or two drops of phenolphth ...
Radioactive Reactions
... Radioactive Reactions • When an atom emits part of its NUCLEUS (protons or neutrons) this is called radiation • This happens because the nucleus is unstable. • When an atom emits protons its identity changes • This can happen naturally (sun) or through man made isotopes in a lab ...
... Radioactive Reactions • When an atom emits part of its NUCLEUS (protons or neutrons) this is called radiation • This happens because the nucleus is unstable. • When an atom emits protons its identity changes • This can happen naturally (sun) or through man made isotopes in a lab ...
P340_2011_week10
... possible to slow-down (cool) atoms by passing them through a region with counter-oriented laser beams tuned to just below an optical transition [“optical molassses”; so that atoms moving toward the laser will see photons Doppler shifted onto the resonance and absorb the photon (along with its moment ...
... possible to slow-down (cool) atoms by passing them through a region with counter-oriented laser beams tuned to just below an optical transition [“optical molassses”; so that atoms moving toward the laser will see photons Doppler shifted onto the resonance and absorb the photon (along with its moment ...
entropy - KFUPM Faculty List
... Qualitatively, the entropy (S) of a system is a measure of how spread out or how dispersed the system’s energy is. The simplest interpretation of this is how spread out a system’s energy is in space. In other words, for a given system, the greater the volume it occupies, the greater its entropy. ...
... Qualitatively, the entropy (S) of a system is a measure of how spread out or how dispersed the system’s energy is. The simplest interpretation of this is how spread out a system’s energy is in space. In other words, for a given system, the greater the volume it occupies, the greater its entropy. ...
110 exam i material
... the space shuttle lifting off __________________________ c. Indicate which of the following is a chemical or physical change Burning of a log __________________________ Rusting of a nail __________________________ melting of ice __________________________ The odor of a skunk ________________________ ...
... the space shuttle lifting off __________________________ c. Indicate which of the following is a chemical or physical change Burning of a log __________________________ Rusting of a nail __________________________ melting of ice __________________________ The odor of a skunk ________________________ ...
Predictions of binary mixtures of noble gases and n
... Transferrable force fields, based on the n-6 Lennard Jones potential, are presented for noble gases. By using tuning the repulsive exponent the presented two body potential can predict vapor pressures and saturated liquid densities with a high degree of accuracy [1-2] without the use of blending par ...
... Transferrable force fields, based on the n-6 Lennard Jones potential, are presented for noble gases. By using tuning the repulsive exponent the presented two body potential can predict vapor pressures and saturated liquid densities with a high degree of accuracy [1-2] without the use of blending par ...
Equilibrium Review worksheet
... In a rigid 1.00 L laboratory reaction vessel, a technician places 1.00 mol of each of the four substances involved in this equilibrium. The vessel is heated to 650 °C. Determine the equilibrium amount concentrations of each substance, organizing your values in an ICE table. (Hint: use the value of K ...
... In a rigid 1.00 L laboratory reaction vessel, a technician places 1.00 mol of each of the four substances involved in this equilibrium. The vessel is heated to 650 °C. Determine the equilibrium amount concentrations of each substance, organizing your values in an ICE table. (Hint: use the value of K ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.