Targets of Opportunity
... According to the article which appeared in today's Corpus Christi Caller Times, a seven block area adjacent to the plant was soon evacuated after winds blew the HF gas in its direction. ...
... According to the article which appeared in today's Corpus Christi Caller Times, a seven block area adjacent to the plant was soon evacuated after winds blew the HF gas in its direction. ...
Lecture Slides - School of Chemical Sciences
... angular momentum, etc. There are “thermodynamic” variables in addition to the standard “mechanical” variables. ...
... angular momentum, etc. There are “thermodynamic” variables in addition to the standard “mechanical” variables. ...
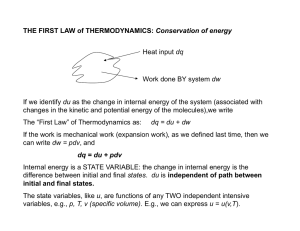
THE FIRST LAW of THERMODYNAMICS: Conservation of energy
... for an Ideal Gas, the internal energy u is a function of T only. Let’s see how to show this: Consider a gas expanding into an evacuated cylinder (vacuum). Since p is zero, no mechanical work is done and dw = 0. Imagine that the process is also adiabatic (perfectly insulated walls), so dq = 0. Since ...
... for an Ideal Gas, the internal energy u is a function of T only. Let’s see how to show this: Consider a gas expanding into an evacuated cylinder (vacuum). Since p is zero, no mechanical work is done and dw = 0. Imagine that the process is also adiabatic (perfectly insulated walls), so dq = 0. Since ...
List Definition Chemistry - A Level / Secondary Chemistry Tuition
... change when 1 mole of an ionic compound is dissolved in a large excess of water under standard conditions 25C and 1 atm. Entropy (S) measures the degree of disorder in a system. The entropy of a system increases when the matter or energy in the system becomes more random in its arrangement. A syste ...
... change when 1 mole of an ionic compound is dissolved in a large excess of water under standard conditions 25C and 1 atm. Entropy (S) measures the degree of disorder in a system. The entropy of a system increases when the matter or energy in the system becomes more random in its arrangement. A syste ...
Solutions Exercises Lecture 2
... the help of the first law of thermodynamics the work can be determined recalling that the process is adiabatic (dq=0) dU = dq + dw = dw and dU = dw ⇒ ∆U = w But how can the work be computed from this? Therefore, we assume that the volume of the water and the pressure in the water stay constant for t ...
... the help of the first law of thermodynamics the work can be determined recalling that the process is adiabatic (dq=0) dU = dq + dw = dw and dU = dw ⇒ ∆U = w But how can the work be computed from this? Therefore, we assume that the volume of the water and the pressure in the water stay constant for t ...
PPT
... extensive parameters are called “equations of state.” Early lab studies determined that p, V, and T could be related by an “equation of state.” ...
... extensive parameters are called “equations of state.” Early lab studies determined that p, V, and T could be related by an “equation of state.” ...
Test 1
... 8. (12 points) I am going to drop a 500 gram block of aluminum that is at 99oC into 500 mLs of water that is at 1oC. Assuming adiabatic conditions, what is the final temperature of the system? (The specific heat capacity of aluminum is .83 J/mol@K, the specific heat capacity of water is 4.184 J/mol@ ...
... 8. (12 points) I am going to drop a 500 gram block of aluminum that is at 99oC into 500 mLs of water that is at 1oC. Assuming adiabatic conditions, what is the final temperature of the system? (The specific heat capacity of aluminum is .83 J/mol@K, the specific heat capacity of water is 4.184 J/mol@ ...
ppt - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Le Châtelier’s Principle: A system in equilibrium that is subjected to a stress will react in a way that tends to counteract the stress At equilibrium, the macroscopic properties of a system remain constant When you perturb the equilibrium, the system will counteract the ...
... Le Châtelier’s Principle: A system in equilibrium that is subjected to a stress will react in a way that tends to counteract the stress At equilibrium, the macroscopic properties of a system remain constant When you perturb the equilibrium, the system will counteract the ...
4-Energy Analysis of Closed Systems
... Specific heat (C): Energy required to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by one degree It is defined when there is no phase change i.e. only solid, only liquid or only vapor 2 types ...
... Specific heat (C): Energy required to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by one degree It is defined when there is no phase change i.e. only solid, only liquid or only vapor 2 types ...
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING CHE
... R: Open only to students in the Department of Chemical Engineering. Applications of chemical engineering principles in design calculations. Selection of optimum design. Influence of design on capital investment, operating cost, product loss and quality. Mathematical programming methods for optimizat ...
... R: Open only to students in the Department of Chemical Engineering. Applications of chemical engineering principles in design calculations. Selection of optimum design. Influence of design on capital investment, operating cost, product loss and quality. Mathematical programming methods for optimizat ...
Ch 4 Sect 2
... Mass is made up of smaller parts called atoms Atoms can be joined or broken apart to produce energy ...
... Mass is made up of smaller parts called atoms Atoms can be joined or broken apart to produce energy ...
Chemistry EOC Review 2015 Name Per ___ This review is part of
... The Law of Conservation of Mass says that mass cannot be created or destroyed. In a chemical reaction, this means that the number of each type of atom must be the same on each side of the equation. It also means that you must have the same type of atoms on each side of the reaction. The coefficients ...
... The Law of Conservation of Mass says that mass cannot be created or destroyed. In a chemical reaction, this means that the number of each type of atom must be the same on each side of the equation. It also means that you must have the same type of atoms on each side of the reaction. The coefficients ...
Thermodynamics: Heat and Work
... transferred as both heat and work to some extent. • However, in most cases one type of energy transfer dwarfs the other. • Therefore, we can use ideal processes to approximate real life ones. ...
... transferred as both heat and work to some extent. • However, in most cases one type of energy transfer dwarfs the other. • Therefore, we can use ideal processes to approximate real life ones. ...
19-Oct
... the mole proportions of chemical reactions. Stoichiometric ratio: The ratio of any two species (reactants or products) in a balanced chemical reaction. ...
... the mole proportions of chemical reactions. Stoichiometric ratio: The ratio of any two species (reactants or products) in a balanced chemical reaction. ...
U / ∂V
... ▪ Methods for work production used are: 1. Rotating paddle wheel immersed in water. 2. Electric motor driving current through coil immersed in water. 3. Compressing a cylinder of gas immersed in water. 4. Rubbing together two metal blocks immersed in water. ...
... ▪ Methods for work production used are: 1. Rotating paddle wheel immersed in water. 2. Electric motor driving current through coil immersed in water. 3. Compressing a cylinder of gas immersed in water. 4. Rubbing together two metal blocks immersed in water. ...
What is an Enzym
... The role of enzymes as catalysts that lower the activation energy of biochemical reactions. Identify factors, such as pH and temperature, and their effect on enzyme activity. Appropriateness for Middle/High School Students Students will be able to observe a chemical reaction, identify the substrate ...
... The role of enzymes as catalysts that lower the activation energy of biochemical reactions. Identify factors, such as pH and temperature, and their effect on enzyme activity. Appropriateness for Middle/High School Students Students will be able to observe a chemical reaction, identify the substrate ...
Notation for states and processes, significance of the word
... 1 bar. The standard-state pressure in general is symbolized as p°. Hitherto p° has customarily been taken as 1 atm. For the future it is recommended that p° should customarily be taken as 10 Pa (1 bar). It should be understood that the present recommended change in the standard-state pressure carrie ...
... 1 bar. The standard-state pressure in general is symbolized as p°. Hitherto p° has customarily been taken as 1 atm. For the future it is recommended that p° should customarily be taken as 10 Pa (1 bar). It should be understood that the present recommended change in the standard-state pressure carrie ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.