1 Chemistry 201 Name Assignment 2 1. Consider the following
... 1. Consider the following reaction: Al2S3 + 6 H2O 2 Al(OH)3 + 3 H2S If 24.3 g of Al2S3 were reacted with an excess of H2O, then: a) What is the theoretical yield of Al(OH)3? b) What is the theoretical yield of H2S? 2. What mass of O2 is required for the complete combustion of 6.19 g of propane (C3H8 ...
... 1. Consider the following reaction: Al2S3 + 6 H2O 2 Al(OH)3 + 3 H2S If 24.3 g of Al2S3 were reacted with an excess of H2O, then: a) What is the theoretical yield of Al(OH)3? b) What is the theoretical yield of H2S? 2. What mass of O2 is required for the complete combustion of 6.19 g of propane (C3H8 ...
Syllabus - Brooklyn College
... Non-covalent interactions and properties of molecules; Coulombic interaction energy; water, acidbase chemistry (ionic equilibria); pH and buffers (preparation, properties); blood pH regulation; buffer “capacity”; solubility of macromolecules; acid/base titrations. Tools of Biochemistry 2A. Learning ...
... Non-covalent interactions and properties of molecules; Coulombic interaction energy; water, acidbase chemistry (ionic equilibria); pH and buffers (preparation, properties); blood pH regulation; buffer “capacity”; solubility of macromolecules; acid/base titrations. Tools of Biochemistry 2A. Learning ...
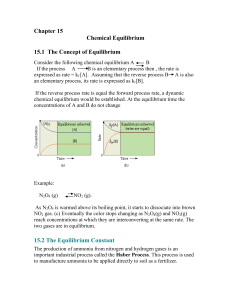
Consider the following chemical equilibrium A B
... Adding H2 will cause the system to shift as to reduce the concentration of H2 to its original value. This will caus the system to produce more of NH3 b. Effect of volume and pressure If a system at equilibrium is disturbed by decreasing the volume (increasing the total pressure), the system respond ...
... Adding H2 will cause the system to shift as to reduce the concentration of H2 to its original value. This will caus the system to produce more of NH3 b. Effect of volume and pressure If a system at equilibrium is disturbed by decreasing the volume (increasing the total pressure), the system respond ...
Current Events #1
... when I first arrived at the scene. I would be sure to mark where every item was located upon my arrival. Next, I would collect and bag any evidence. Finally, I would take pictures of both the inmate and the officer to document any injuries that were sustained during the fight. In this particular cas ...
... when I first arrived at the scene. I would be sure to mark where every item was located upon my arrival. Next, I would collect and bag any evidence. Finally, I would take pictures of both the inmate and the officer to document any injuries that were sustained during the fight. In this particular cas ...
Class01 Intro Units
... Review of Thermodynamics • Extensive variables – depend on total mass of the system, e.g. M, E, S, V • Intensive variables – do not depend on total mass of the system, e.g. p, T, s, (1/v) • Equilibrium (state of maximum disorder) – bodies that are at the same temperature are called in thermal equ ...
... Review of Thermodynamics • Extensive variables – depend on total mass of the system, e.g. M, E, S, V • Intensive variables – do not depend on total mass of the system, e.g. p, T, s, (1/v) • Equilibrium (state of maximum disorder) – bodies that are at the same temperature are called in thermal equ ...
Chapter 5 ENERGY AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... Work Usually in an open container the only work done is by a gas pushing on the surroundings (or by the surroundings pushing on the gas). w = -PV ...
... Work Usually in an open container the only work done is by a gas pushing on the surroundings (or by the surroundings pushing on the gas). w = -PV ...
A Guide to Rate of Reactions
... Equilibrium. This is because the underlying theory of each of these is very different. Rate of reaction is also called Chemical Kinetics and deals with how fast a reaction happens. Chemical equilibrium is based on thermodynamics and answers the question: ‘How far does the reaction go?’ Learners are ...
... Equilibrium. This is because the underlying theory of each of these is very different. Rate of reaction is also called Chemical Kinetics and deals with how fast a reaction happens. Chemical equilibrium is based on thermodynamics and answers the question: ‘How far does the reaction go?’ Learners are ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... [making the parts of the mixture somewhat difficult to distinguish, which is the idea behind “homogenizing” milk - making it the same from the first glass to the last.] Homogeneous mixtures are often also called solutions. The two parts of a solution are the solute (thing being dissolved, or in less ...
... [making the parts of the mixture somewhat difficult to distinguish, which is the idea behind “homogenizing” milk - making it the same from the first glass to the last.] Homogeneous mixtures are often also called solutions. The two parts of a solution are the solute (thing being dissolved, or in less ...
File
... substance to moles of a different substance. (i.e. In the equation: N2 + 3H2 2NH3, 3 mol H2 2 mol NH3) ...
... substance to moles of a different substance. (i.e. In the equation: N2 + 3H2 2NH3, 3 mol H2 2 mol NH3) ...
Thermodynamic Symbols and Constants
... HoT - Ho298 is the enthalpy at the standard state T less the enthalpy at the standard state at 298.15 K. (GoT - Ho298)/T is the Gibbs energy function and is equal to (HoT - Ho298)/T - SoT. This function is tabulated because it shows greater linearity than GoT thus facilitating interpolation between ...
... HoT - Ho298 is the enthalpy at the standard state T less the enthalpy at the standard state at 298.15 K. (GoT - Ho298)/T is the Gibbs energy function and is equal to (HoT - Ho298)/T - SoT. This function is tabulated because it shows greater linearity than GoT thus facilitating interpolation between ...
Conservation of Energy
... If you watch the Weather Channel, you will frequently hear the meteorologist say “There is a lot of energy associated with this system”, or “Most of the energy is concentrated to the north of the frontal boundary”. Are they referring to the winds? Probably not. Usually they are alluding to an area w ...
... If you watch the Weather Channel, you will frequently hear the meteorologist say “There is a lot of energy associated with this system”, or “Most of the energy is concentrated to the north of the frontal boundary”. Are they referring to the winds? Probably not. Usually they are alluding to an area w ...
Chapter 3 - Bruder Chemistry
... It is important to realize that the stoichiometric ratios are the ideal proportions in which reactants are needed to form products. The number of grams of reactant cannot be directly related to the number of grams of product. • To get grams of product from grams of reactant: • Convert grams of react ...
... It is important to realize that the stoichiometric ratios are the ideal proportions in which reactants are needed to form products. The number of grams of reactant cannot be directly related to the number of grams of product. • To get grams of product from grams of reactant: • Convert grams of react ...
BERKELEY HEIGHTS PUBLIC SCHOOLS
... problems involving heats of reaction for exothermic & endothermic reactions with the aid of Hess’s Law D. state & explain entropy & enthalpy of chemical reactions in terms of Gibbs free energy XI. Rates of Chemical Reaction A. state the basic principles of collision theory B. measure rates of chemic ...
... problems involving heats of reaction for exothermic & endothermic reactions with the aid of Hess’s Law D. state & explain entropy & enthalpy of chemical reactions in terms of Gibbs free energy XI. Rates of Chemical Reaction A. state the basic principles of collision theory B. measure rates of chemic ...
- gst boces
... 126. Equilibrium (solution, phase, chemical) *RATES of forward and reverse processes EQUAL *CONCENTRATIONS CONSTANT (constant volume, constant mass) 127. Equilibrium shifted by stress (Le Chatelier’s) *Shifts away from increased temp, concentration *Shifts toward decreases temp, concentration *Shift ...
... 126. Equilibrium (solution, phase, chemical) *RATES of forward and reverse processes EQUAL *CONCENTRATIONS CONSTANT (constant volume, constant mass) 127. Equilibrium shifted by stress (Le Chatelier’s) *Shifts away from increased temp, concentration *Shifts toward decreases temp, concentration *Shift ...
Lecture 3 Chemistry
... Number of electrons in outer shell determines bonding properties chemical behavior ...
... Number of electrons in outer shell determines bonding properties chemical behavior ...
Chapter 14…Kinetic Theory
... How many grams of NaNO3 will dissolve at 30C? Which substance is least soluble at 10C? Which two substances have the same solubility at 72C? 80 grams of KBr placed in 60C creates a (saturated/unsaturated/supersaturated) solution. When Be(NO3)2 (aq) and NaOH (aq) are mixed together, the resulting ...
... How many grams of NaNO3 will dissolve at 30C? Which substance is least soluble at 10C? Which two substances have the same solubility at 72C? 80 grams of KBr placed in 60C creates a (saturated/unsaturated/supersaturated) solution. When Be(NO3)2 (aq) and NaOH (aq) are mixed together, the resulting ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.