transcript - American Chemical Society
... this device. “When you start to look at work that’s been done with pox viruses you quickly realize that they are unique in the sense that they are invariant irrespective of what the animal host is or even what part of the world they come from. In that respect, they are a good model system to start w ...
... this device. “When you start to look at work that’s been done with pox viruses you quickly realize that they are unique in the sense that they are invariant irrespective of what the animal host is or even what part of the world they come from. In that respect, they are a good model system to start w ...
Name - cloudfront.net
... A 0.12 M solution of an acid that ionizes only slightly in solution would be termed ____. In the reaction: CO32- + H2O ↔ HCO31- + OH1-, the carbonate ion (CO32-) is acting as a(n) ____. What is transferred between a conjugate acid-base pair? What are the acids in the following: CN1- + H2O ↔ HCN + OH ...
... A 0.12 M solution of an acid that ionizes only slightly in solution would be termed ____. In the reaction: CO32- + H2O ↔ HCO31- + OH1-, the carbonate ion (CO32-) is acting as a(n) ____. What is transferred between a conjugate acid-base pair? What are the acids in the following: CN1- + H2O ↔ HCN + OH ...
Kinetic energy
... All organisms on Earth need food to live and grow. These organisms either produce their own food, via photosynthesis, or eat other organisms according to complex food webs. The energy that is transferred through these processes can be traced back to what feature of our universe? A. the Sun B. distan ...
... All organisms on Earth need food to live and grow. These organisms either produce their own food, via photosynthesis, or eat other organisms according to complex food webs. The energy that is transferred through these processes can be traced back to what feature of our universe? A. the Sun B. distan ...
Faith groups call for chemical policy reform for Father`s
... Interfaith Statement for Chemical Policy Reform The Problem: Toxic Chemicals Threaten Life on Earth Toxic chemicals enter and harm our bodies, plants and animals, and natural systems through air and water pollution, and chemicals in household products including cleaners, personal care products, plas ...
... Interfaith Statement for Chemical Policy Reform The Problem: Toxic Chemicals Threaten Life on Earth Toxic chemicals enter and harm our bodies, plants and animals, and natural systems through air and water pollution, and chemicals in household products including cleaners, personal care products, plas ...
Standard Thermodynamic Functions of Reaction
... when ξ = 1 mol for (5.4), 2 mol of H2O is produced; whereas when ξ = 1 mol for (5.5), 1 mol of H2O is produced. ...
... when ξ = 1 mol for (5.4), 2 mol of H2O is produced; whereas when ξ = 1 mol for (5.5), 1 mol of H2O is produced. ...
Entropy
... 2. What are the units for entropy? For specific entropy? 3. Two moles of helium (M = 4 g/mol) are at 15 degrees C and 1000 mb. (a) If 6240 Joules of heat are added while keeping volume constant, what is the final temperature and pressure? (b) The helium is now allowed to expand isothermally to twice ...
... 2. What are the units for entropy? For specific entropy? 3. Two moles of helium (M = 4 g/mol) are at 15 degrees C and 1000 mb. (a) If 6240 Joules of heat are added while keeping volume constant, what is the final temperature and pressure? (b) The helium is now allowed to expand isothermally to twice ...
Standard answers: 1 Basic concepts, Fuels, alkanes and alkenes
... The rate of the forward and reverse reactions are the same 36. Effect of pressure on equilibrium Increasing P moves the eqm to the side with fewer moles of gas (and vice versa) 37. Effect of temperature on equilibrium Increasing temperature moves the eqm to the endothermic side (and vice versa ...
... The rate of the forward and reverse reactions are the same 36. Effect of pressure on equilibrium Increasing P moves the eqm to the side with fewer moles of gas (and vice versa) 37. Effect of temperature on equilibrium Increasing temperature moves the eqm to the endothermic side (and vice versa ...
8 Chemical Equations Chapter Outline Chemical Equations
... 2. Whole number coefficients are placed in front of substances to balance the atoms in the equation. The numbers indicate the units of the substance reacted or formed during the reaction. ...
... 2. Whole number coefficients are placed in front of substances to balance the atoms in the equation. The numbers indicate the units of the substance reacted or formed during the reaction. ...
Lecture 24 (Slides) October 18
... • When Main Group elements react, electrons can be transferred (usually from a metal to a nonmetal) to form ionic bonds. In other cases, pairs of electrons can be shared (usually between nonmetal atoms) to form covalent bonds. In both cases valence electrons are somehow “rearranged” when new chemica ...
... • When Main Group elements react, electrons can be transferred (usually from a metal to a nonmetal) to form ionic bonds. In other cases, pairs of electrons can be shared (usually between nonmetal atoms) to form covalent bonds. In both cases valence electrons are somehow “rearranged” when new chemica ...
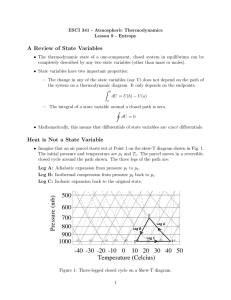
241outline
... 3. Second Law of Thermodynamics (4,5) Text: Primary: Physical Chemistry, 7th ed., P. Atkins and de Paula, Freeman, 2002 (earlier versions of this text will work, but make sure you do the right problems.) Don't forget to look at the appendices. Grading/Exams: Grades will be based on 3 (probably) equa ...
... 3. Second Law of Thermodynamics (4,5) Text: Primary: Physical Chemistry, 7th ed., P. Atkins and de Paula, Freeman, 2002 (earlier versions of this text will work, but make sure you do the right problems.) Don't forget to look at the appendices. Grading/Exams: Grades will be based on 3 (probably) equa ...
Second Semester Review Part 1
... (E) Activated complex à products 126. The gas–phase reaction, A2 + B2 à 2AB, proceeds by bimolecular collisions between A2 and B2 molecules. If the concentrations of both A2 and B2 are doubled, the reaction rate will be changed by a factor of (A) ½ ...
... (E) Activated complex à products 126. The gas–phase reaction, A2 + B2 à 2AB, proceeds by bimolecular collisions between A2 and B2 molecules. If the concentrations of both A2 and B2 are doubled, the reaction rate will be changed by a factor of (A) ½ ...
Chapter 1 and Sections 3.1-3.3
... Chemistry is the study of the composition of matter (substances) and the way in which they interact physically and chemically over time. Energy is involved in every change/transformation of matter. Chemists work to characterize or analyze the composition, structure and properties of matter and the c ...
... Chemistry is the study of the composition of matter (substances) and the way in which they interact physically and chemically over time. Energy is involved in every change/transformation of matter. Chemists work to characterize or analyze the composition, structure and properties of matter and the c ...
Section 1 Describing Chemical Reactions Chapter 8
... • A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances. • In any chemical reaction, the original substances are known as the reactants and the resulting substances are known as the products. • According to the law of conservation of mas ...
... • A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances. • In any chemical reaction, the original substances are known as the reactants and the resulting substances are known as the products. • According to the law of conservation of mas ...
energy
... Each of the properties of a substance in a given state has only one definite value, and these properties always have the same value for a given state, regardless of how the substance arrived at that state. How many? A state can be specified by a certain number of properties. Equilibrium: implies a s ...
... Each of the properties of a substance in a given state has only one definite value, and these properties always have the same value for a given state, regardless of how the substance arrived at that state. How many? A state can be specified by a certain number of properties. Equilibrium: implies a s ...
Kinetics and Equilibrium ___ 1. In a chemical reaction the use of a
... ___ 41. A catalyst can increase the rate of a chemical reaction by (1) increasing the value of the equilibrium constant; (2) increasing the energy of the products; (3) decreasing the energy of the products; (4) decreasing the required activation energy. ___ 42. For a chemical system at equilibrium ...
... ___ 41. A catalyst can increase the rate of a chemical reaction by (1) increasing the value of the equilibrium constant; (2) increasing the energy of the products; (3) decreasing the energy of the products; (4) decreasing the required activation energy. ___ 42. For a chemical system at equilibrium ...
Bioenergy basics miller
... • Renewable fuels and chemicals can be incorporated across the core ChE curriculum – Energy and mass balance calculations – Thermodynamics: physical properties, phase equilibria, reaction equilibria – Reaction engineering: kinetics, reactor design, catalysis – Separations: design separations schemes ...
... • Renewable fuels and chemicals can be incorporated across the core ChE curriculum – Energy and mass balance calculations – Thermodynamics: physical properties, phase equilibria, reaction equilibria – Reaction engineering: kinetics, reactor design, catalysis – Separations: design separations schemes ...
Chapter 11
... • The standard enthalpy of formation (Hfo) is also called the standard heat of formation and is the enthalpy change of the a formation reaction. • A formation reaction is the process of forming 1 mole of a substance in its standard state from its component elements in their standard states. • H2(g) ...
... • The standard enthalpy of formation (Hfo) is also called the standard heat of formation and is the enthalpy change of the a formation reaction. • A formation reaction is the process of forming 1 mole of a substance in its standard state from its component elements in their standard states. • H2(g) ...
The chemical elements are fundamental building materials of matter
... • 1.A: All matter is made of atoms. There are a limited number of types of atoms: these are the elements. • 1.B: The atoms of each element have unique structures arising from interactions between electrons and nuclei. • 1.C: Elements display periodicity in their properties when the elements are orga ...
... • 1.A: All matter is made of atoms. There are a limited number of types of atoms: these are the elements. • 1.B: The atoms of each element have unique structures arising from interactions between electrons and nuclei. • 1.C: Elements display periodicity in their properties when the elements are orga ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.