Chemistry - Plymouth Public Schools
... Chemical Reactions and Stoichiometry Central Concepts: In a chemical reaction, one or more reactants are transformed into one or more new products. Chemical equations represent the reaction and must be balanced. The conservation of atoms in a chemical reaction leads to the ability to calculate the a ...
... Chemical Reactions and Stoichiometry Central Concepts: In a chemical reaction, one or more reactants are transformed into one or more new products. Chemical equations represent the reaction and must be balanced. The conservation of atoms in a chemical reaction leads to the ability to calculate the a ...
2 C2H6 (g)
... The Ostwald process is used commercially to produce nitric acid, which is, in turn, used in many modern chemical processes. In the first step of the Ostwald process, ammonia is reacted with oxygen gas to produce nitric oxide and water. 4 NH3 (g) + 5 O2 (g) 4 NO g + 6 H2O (g) What is the maximum ma ...
... The Ostwald process is used commercially to produce nitric acid, which is, in turn, used in many modern chemical processes. In the first step of the Ostwald process, ammonia is reacted with oxygen gas to produce nitric oxide and water. 4 NH3 (g) + 5 O2 (g) 4 NO g + 6 H2O (g) What is the maximum ma ...
Kinetics and Equilibrium
... Direction: Using the balanced equation below, create a molecular model of this chemical reaction (use 3 different colored pencils) ...
... Direction: Using the balanced equation below, create a molecular model of this chemical reaction (use 3 different colored pencils) ...
1 - Mr. J`s Chemistry 4U
... 52) T / F : Every sample of a given pure substance can have different physical and chemical properties. 53) T / F : Every sample of a given pure substance has exactly the same chemical composition. 54) T / F : A pure substance cannot be separated into other substances without changing its identity. ...
... 52) T / F : Every sample of a given pure substance can have different physical and chemical properties. 53) T / F : Every sample of a given pure substance has exactly the same chemical composition. 54) T / F : A pure substance cannot be separated into other substances without changing its identity. ...
Chapter 3 - Whitwell High School
... N2 + H2 Æ NH3 • We do have one problem; it does not give amounts correctly. • It is not balanced. • In chemical reaction, atoms cannot be created or destroyed. N2 + 3 H2 Æ 2 NH3 ...
... N2 + H2 Æ NH3 • We do have one problem; it does not give amounts correctly. • It is not balanced. • In chemical reaction, atoms cannot be created or destroyed. N2 + 3 H2 Æ 2 NH3 ...
Second Semester Final Review Guide
... When a bond breaks, energy is (released / abosorbed). circle one 1. When a bond forms, energy is (released / abosorbed). circle one 2. When more energy is released than absorbed, the reaction is (exothermic / endothermic). circle one 3. When more energy is absorbed than released, the reaction is (ex ...
... When a bond breaks, energy is (released / abosorbed). circle one 1. When a bond forms, energy is (released / abosorbed). circle one 2. When more energy is released than absorbed, the reaction is (exothermic / endothermic). circle one 3. When more energy is absorbed than released, the reaction is (ex ...
Worksheet Key
... c. The concentrations are no longer changing. _ true _ d. The reaction is not over, but will continue forever if isolated. _ true _ e. The speed at which products are made equals the speed at which reactants form. true 2. What is equal at equilibrium? ____forward and reverse rates_____ 3. What gener ...
... c. The concentrations are no longer changing. _ true _ d. The reaction is not over, but will continue forever if isolated. _ true _ e. The speed at which products are made equals the speed at which reactants form. true 2. What is equal at equilibrium? ____forward and reverse rates_____ 3. What gener ...
Physical Chemistry (SCQF level 7)
... e-assessment must ensure that the national standard is applied to all candidate evidence and that conditions of assessment as specified in the Evidence Requirements are met, regardless of the mode of gathering evidence. Further advice is available in SQA Guidelines on Online Assessment for Further E ...
... e-assessment must ensure that the national standard is applied to all candidate evidence and that conditions of assessment as specified in the Evidence Requirements are met, regardless of the mode of gathering evidence. Further advice is available in SQA Guidelines on Online Assessment for Further E ...
Ghw#8-chapter-17-Tro-F-16
... 1. If DH is negative it helps product to be favored 2. If DS is positive it helps product to be favored 3. If DG is negative reaction is product favored Gibbs free energy change = difference between the enthalpy of a system and the product of its absolute temperature and entropy predictor of spontan ...
... 1. If DH is negative it helps product to be favored 2. If DS is positive it helps product to be favored 3. If DG is negative reaction is product favored Gibbs free energy change = difference between the enthalpy of a system and the product of its absolute temperature and entropy predictor of spontan ...
Analytical Chemistry (II)
... Course Description: An introduction to Electrochemistry and Electroanalytical Techniques. CHEM- 23226 ...
... Course Description: An introduction to Electrochemistry and Electroanalytical Techniques. CHEM- 23226 ...
ESS103A Igneous Petrology - UCLA - Earth, Planetary, and Space
... 2. All assignments must be turned in on time to receive full credit. Extensions will be considered on a case-by-case basis 3. Don’t cheat. (copying from previous years’ assignments or fellow students, sharing answers during exams, etc.) ...
... 2. All assignments must be turned in on time to receive full credit. Extensions will be considered on a case-by-case basis 3. Don’t cheat. (copying from previous years’ assignments or fellow students, sharing answers during exams, etc.) ...
Ch. 16 Study Guide
... can only use equilibrium concentrations in the Kc /Kp expression, (2) initial concentrations should be in molarity if using Kc , (3) changes in concentrations always occur in the same ratio as the coefficients in the balanced equation, and (4) all reactants should change in one direction while all p ...
... can only use equilibrium concentrations in the Kc /Kp expression, (2) initial concentrations should be in molarity if using Kc , (3) changes in concentrations always occur in the same ratio as the coefficients in the balanced equation, and (4) all reactants should change in one direction while all p ...
Electrochemical Fundamentals
... physicist who contributed to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. As a chemist, Faraday discovered benzene, investigated the clathrate hydrate of chlorine, invented an early form of the bunsen burner and the system of oxidation numbers, and popularized terminology such as anode, cath ...
... physicist who contributed to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. As a chemist, Faraday discovered benzene, investigated the clathrate hydrate of chlorine, invented an early form of the bunsen burner and the system of oxidation numbers, and popularized terminology such as anode, cath ...
Chemical Reactions Definitions Air Fuel Ratio
... Therefore, by expressing a mixture in terms of the number of moles we are also expressing it in terms of a volume fraction. During combustion, nitrogen behaves as an inert gas and does not react with other elements. However; N2 greatly affects the outcome of a combustion process, since it enters in ...
... Therefore, by expressing a mixture in terms of the number of moles we are also expressing it in terms of a volume fraction. During combustion, nitrogen behaves as an inert gas and does not react with other elements. However; N2 greatly affects the outcome of a combustion process, since it enters in ...
Thermodynamics
... DH1: enthalpy change (or energy change) – the energy needed to break one mole of O=O bonds + energy needed to break 2 moles of H-H bonds, endothermic: DH1 = (+358 kJ mol-1) + 2 x (+436 kJ mol-1) = +1230 kJ mol-1. DH2: energy evolved or given out when 4 moles of O-H bonds are formed, exothermic: DH2 ...
... DH1: enthalpy change (or energy change) – the energy needed to break one mole of O=O bonds + energy needed to break 2 moles of H-H bonds, endothermic: DH1 = (+358 kJ mol-1) + 2 x (+436 kJ mol-1) = +1230 kJ mol-1. DH2: energy evolved or given out when 4 moles of O-H bonds are formed, exothermic: DH2 ...
Valero2012-ThermodynamicsUpperCrust.pdf
... the reaction involved in the formation of the mineral is zero. This procedure named Helgeson’s algorithm, is useful when either DGf or DHf are known. Once the entropy of the mineral is known, DGf (or DHf) can be calculated with DHf (or DGf) through Eq. (1). The error associated to this approximation ...
... the reaction involved in the formation of the mineral is zero. This procedure named Helgeson’s algorithm, is useful when either DGf or DHf are known. Once the entropy of the mineral is known, DGf (or DHf) can be calculated with DHf (or DGf) through Eq. (1). The error associated to this approximation ...
Thermochemistry - University of Missouri
... calorimeter of negligible heat capacity. The initial temperature of the HCl and NaOH solutions was the same, 22.50°C, and the final temperature of the mixed solution was 25.86°C. Calculate the heat change for the neutralization reaction on a molar basis: ...
... calorimeter of negligible heat capacity. The initial temperature of the HCl and NaOH solutions was the same, 22.50°C, and the final temperature of the mixed solution was 25.86°C. Calculate the heat change for the neutralization reaction on a molar basis: ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... Changing the volume of a reactant container changes the concentration of gaseous reactants and therefore their partial pressures Equilibrium position will therefore move The value of Kc or Kp does NOT change Changing pressure by adding more of an inert gas has no effect of the equilibrium position - ...
... Changing the volume of a reactant container changes the concentration of gaseous reactants and therefore their partial pressures Equilibrium position will therefore move The value of Kc or Kp does NOT change Changing pressure by adding more of an inert gas has no effect of the equilibrium position - ...
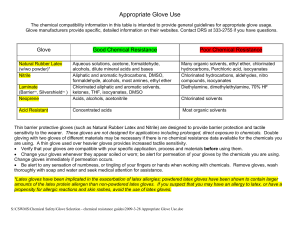
Appropriate Glove Use
... alcohols, dilute mineral acids and bases Aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons, DMSO, ...
... alcohols, dilute mineral acids and bases Aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons, DMSO, ...
Document
... In a chemical reaction • Can be described several ways: 1. In a sentence Copper reacts with chlorine to form copper (II) chloride. ...
... In a chemical reaction • Can be described several ways: 1. In a sentence Copper reacts with chlorine to form copper (II) chloride. ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.