Chemistry
... Ancient Egyptians pioneered the art of synthetic "wet" chemistry up to 4,000 years ago.[10] By 1000 BC ancient civilizations were using technologies that formed the basis of the various branches of chemistry such as; extracting metal from their ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wi ...
... Ancient Egyptians pioneered the art of synthetic "wet" chemistry up to 4,000 years ago.[10] By 1000 BC ancient civilizations were using technologies that formed the basis of the various branches of chemistry such as; extracting metal from their ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wi ...
Lecture 2
... A rising piston, a rotating shaft, and an electric wire crossing the system boundaries are all associated with work interactions Formal sign convention: Heat transfer to a system and work done by a system are positive; heat transfer from a system and work done on a system are negative. Alterna ...
... A rising piston, a rotating shaft, and an electric wire crossing the system boundaries are all associated with work interactions Formal sign convention: Heat transfer to a system and work done by a system are positive; heat transfer from a system and work done on a system are negative. Alterna ...
13AP General Equilibrium FR worksheet (missing 1988)
... AP* General Equilibrium Free Response Questions ...
... AP* General Equilibrium Free Response Questions ...
Chapter 5
... U < 0 therefore q is negative (–) The sign of q is a “convention”, it designates the direction of heat flow between the system and ...
... U < 0 therefore q is negative (–) The sign of q is a “convention”, it designates the direction of heat flow between the system and ...
Department of Chemistry Course Description
... Chemistry for Nonchemistry majors Prerequisite: (0303233 or concurrently) The course involves separation, purification of and identification organic compounds through their physical properties: melting point, distillation, crystallization, extraction, and chromatography; preparation of simple organi ...
... Chemistry for Nonchemistry majors Prerequisite: (0303233 or concurrently) The course involves separation, purification of and identification organic compounds through their physical properties: melting point, distillation, crystallization, extraction, and chromatography; preparation of simple organi ...
chapter 5 - chemical reactions
... 1. Pb(NO3)2(aq) + K2C rO4(aq) PbCrO4(s) + 2 KNO3(aq) 2. AgNO3(aq) + KBr(aq) AgBr(s) + KNO3(aq) 3. BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl(aq) The products, PbCrO4, AgBr, and BaSO4 are only slightly soluble or insoluble in water. B. Acid-base (or Neutralization) reactions are reactions in aqueo ...
... 1. Pb(NO3)2(aq) + K2C rO4(aq) PbCrO4(s) + 2 KNO3(aq) 2. AgNO3(aq) + KBr(aq) AgBr(s) + KNO3(aq) 3. BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl(aq) The products, PbCrO4, AgBr, and BaSO4 are only slightly soluble or insoluble in water. B. Acid-base (or Neutralization) reactions are reactions in aqueo ...
Chapter 17
... • Achieving the maximum work available from a spontaneous process can occur only via a hypothetical pathway. Any real pathway wastes energy. • All real processes are irreversible. • First law: You can’t win, you can only break even. • Second law: You can’t break even. ...
... • Achieving the maximum work available from a spontaneous process can occur only via a hypothetical pathway. Any real pathway wastes energy. • All real processes are irreversible. • First law: You can’t win, you can only break even. • Second law: You can’t break even. ...
Gill_chapter4
... Energy increases because of (i) agitation (molecules) d, and (ii) compression dvs < 0. We assume no phase change and salinity is fixed – i.e. the fluid is of fixed composition; so = (p, T). Tdchange in heat content per unit mass pdvs = work done by p in compressing fluid’s volume per unit ma ...
... Energy increases because of (i) agitation (molecules) d, and (ii) compression dvs < 0. We assume no phase change and salinity is fixed – i.e. the fluid is of fixed composition; so = (p, T). Tdchange in heat content per unit mass pdvs = work done by p in compressing fluid’s volume per unit ma ...
Chap. 17 - Lemon Bay High School
... • Achieving the maximum work available from a spontaneous process can occur only via a hypothetical pathway. Any real pathway wastes energy. • All real processes are irreversible. • First law: You can’t win, you can only break even. • Second law: You can’t break even. ...
... • Achieving the maximum work available from a spontaneous process can occur only via a hypothetical pathway. Any real pathway wastes energy. • All real processes are irreversible. • First law: You can’t win, you can only break even. • Second law: You can’t break even. ...
Introduction to Soft Matter Physics
... dU dq dw TdS PdV dU dPV dq PdV dPV dU PV dH dq PdV VdP PdV dq VdP Hence the enthalpy change is equal to the heat transferred to the surroundings if the system is kept at constant pressure: dSsur ...
... dU dq dw TdS PdV dU dPV dq PdV dPV dU PV dH dq PdV VdP PdV dq VdP Hence the enthalpy change is equal to the heat transferred to the surroundings if the system is kept at constant pressure: dSsur ...
Chapter 1: Fundamental Concepts
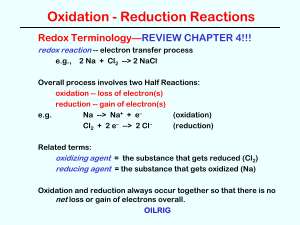
... • The transfer of electrons between species, meaning that one species is oxidized and one is reduced. The two processes will always occur together. • When has a redox reaction occurred? – If there is a change in the oxidation state of any element in the reaction, a redox reaction has happened. – Rem ...
... • The transfer of electrons between species, meaning that one species is oxidized and one is reduced. The two processes will always occur together. • When has a redox reaction occurred? – If there is a change in the oxidation state of any element in the reaction, a redox reaction has happened. – Rem ...
Chemistry 2008 Multiple Choice
... pressure in the laboratory is measured to be 772 torr. Before measuring the volume of gas collected in the tube, what step, if any, must be taken to make it possible to determine the total gas pressure inside the tube? (A) Tilt the tube to the side enough to let some air in to break the partial vacu ...
... pressure in the laboratory is measured to be 772 torr. Before measuring the volume of gas collected in the tube, what step, if any, must be taken to make it possible to determine the total gas pressure inside the tube? (A) Tilt the tube to the side enough to let some air in to break the partial vacu ...
do not - wwphs
... How do enzymes work? 1) Enzymes act upon a substance called a substrate 2) The enzyme has an indent in it called the active site where the substrate can fit into, kind of like a lock and a key ...
... How do enzymes work? 1) Enzymes act upon a substance called a substrate 2) The enzyme has an indent in it called the active site where the substrate can fit into, kind of like a lock and a key ...
Energetics - chemistryatdulwich
... 15.2 U1 Entropy (S) refers to the distribution of available energy among the particles. The more ways the energy can be distributed the higher the entropy. 15.2 U2 Gibbs free energy (G) relates the energy that can be obtained from a chemical reaction to the change in enthalpy (ΔH), change in ent ...
... 15.2 U1 Entropy (S) refers to the distribution of available energy among the particles. The more ways the energy can be distributed the higher the entropy. 15.2 U2 Gibbs free energy (G) relates the energy that can be obtained from a chemical reaction to the change in enthalpy (ΔH), change in ent ...
ACS Practice Test 1
... Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s), (A) metallic zinc is the reducing agent. (B) metallic zinc in reduced. (C) copper ion is oxidized. (D) sulfate ion is the oxidizing agent. 63. In this reaction, which substance behaves as the oxidizing agent? ...
... Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s), (A) metallic zinc is the reducing agent. (B) metallic zinc in reduced. (C) copper ion is oxidized. (D) sulfate ion is the oxidizing agent. 63. In this reaction, which substance behaves as the oxidizing agent? ...
The adiabatic flame temperature
... limit of infinitely fast reaction rates only. In most combustion cases, however, chemical reactions occur on time scales comparable with that of the flow and the molecular transport processes. Only for hydrogen diffusion flames complete ...
... limit of infinitely fast reaction rates only. In most combustion cases, however, chemical reactions occur on time scales comparable with that of the flow and the molecular transport processes. Only for hydrogen diffusion flames complete ...
Chemistry - StudyTime NZ
... Neither Oxygen nor Magnesium have full valence electron shells. Because of this, they must each lose or gain electrons in order to become stable. Oxygen has 8 electrons and hence an electron arrangement ...
... Neither Oxygen nor Magnesium have full valence electron shells. Because of this, they must each lose or gain electrons in order to become stable. Oxygen has 8 electrons and hence an electron arrangement ...
Chm 118
... 4.64 Reference or Standard State A second issue we need to address is that changes in chemical reactions depend upon the conditions of the reagents and products, their pressures, temperatures, etc. Generally, it has been agreed that in the standard state all materials are pure, gases are at one atmo ...
... 4.64 Reference or Standard State A second issue we need to address is that changes in chemical reactions depend upon the conditions of the reagents and products, their pressures, temperatures, etc. Generally, it has been agreed that in the standard state all materials are pure, gases are at one atmo ...
Thermal Cycles - Rankine Cycle with Reheat - plaza
... a. A cyclic machine that will experience no other interaction than to produce energy through a work interaction, while transferring energy from a high-temperature reservoir to a low-temperature reservoir through heat interactions. b. A cyclic machine that will experience no other interaction than to ...
... a. A cyclic machine that will experience no other interaction than to produce energy through a work interaction, while transferring energy from a high-temperature reservoir to a low-temperature reservoir through heat interactions. b. A cyclic machine that will experience no other interaction than to ...
John Dalton and Atomic Theory — www.boundless.com — Readability
... The main points of his theory are: 1. Everything is composed of atoms, which are the indivisible building blocks of matter and cannot be destroyed. 2. All atoms of an element are identical. 3. The atoms of different elements differ in size and mass. 4. Compounds are produced through different whole- ...
... The main points of his theory are: 1. Everything is composed of atoms, which are the indivisible building blocks of matter and cannot be destroyed. 2. All atoms of an element are identical. 3. The atoms of different elements differ in size and mass. 4. Compounds are produced through different whole- ...
EoS - BAS
... The model is able to reproduce the results of the microscopic calculations of both nuclear and neutron-rich matter T=0. The model can be extended to finite temperature. The model is flexible to reproduce a variety of density dependent behaviors of the nuclear symmetry energy and symmetry free ener ...
... The model is able to reproduce the results of the microscopic calculations of both nuclear and neutron-rich matter T=0. The model can be extended to finite temperature. The model is flexible to reproduce a variety of density dependent behaviors of the nuclear symmetry energy and symmetry free ener ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.