physical setting chemistry
... and particle size. These properties can be used to (1) separate the substances (2) chemically combine the substances (3) determine the freezing point of the mixture (4) predict the electrical conductivity of the mixture P.S./Chem.–Jan. ’15 ...
... and particle size. These properties can be used to (1) separate the substances (2) chemically combine the substances (3) determine the freezing point of the mixture (4) predict the electrical conductivity of the mixture P.S./Chem.–Jan. ’15 ...
High School Knowledge Exam – Study Guide
... Chemical Change examples: Reactions between chemicals, burning (fire reacts with something), color change (caused by reaction b/w chemicals) Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1) All matter is made up of very small, discrete particles called atoms 2) All atoms of a given element are identical, and the atoms of ...
... Chemical Change examples: Reactions between chemicals, burning (fire reacts with something), color change (caused by reaction b/w chemicals) Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1) All matter is made up of very small, discrete particles called atoms 2) All atoms of a given element are identical, and the atoms of ...
chemistry
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
PRACTICE – Naming and Writing Ionic Compounds
... Na2S2O3(aq) + 4Cl2(g) + 5H2O(aq) 2NaHSO4(aq) + 8HCl(aq) a. How many moles of Na2S2O3 are needed to react with 0.12mol of Cl2? ...
... Na2S2O3(aq) + 4Cl2(g) + 5H2O(aq) 2NaHSO4(aq) + 8HCl(aq) a. How many moles of Na2S2O3 are needed to react with 0.12mol of Cl2? ...
U3 Student Workbook - The Connected Chemistry Curriculum
... combustion reactions). In the Connecting Activity, students apply the Law of Conservation of Mass to chemical equations by learning how to balance them. Following a teacher demonstration of the simulation and procedures, students will use the simulations to look at ten different reactions. In each o ...
... combustion reactions). In the Connecting Activity, students apply the Law of Conservation of Mass to chemical equations by learning how to balance them. Following a teacher demonstration of the simulation and procedures, students will use the simulations to look at ten different reactions. In each o ...
TEKS Presentation Properties of Matter
... oxygen gas using an electric current. When water molecules change chemically into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas, we say that a chemical change has occurred. Hydrogen gas and oxygen gas each have a different set of properties. Substances change into different substances through TAKS Need to Know chemic ...
... oxygen gas using an electric current. When water molecules change chemically into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas, we say that a chemical change has occurred. Hydrogen gas and oxygen gas each have a different set of properties. Substances change into different substances through TAKS Need to Know chemic ...
Chapter 9
... in the production of many important chemicals, such as aspirin, and disinfectants. One industrial method of preparing chlorobenzene is to react benzene, C6H6, with chlorine, which is represented by the following equation. ...
... in the production of many important chemicals, such as aspirin, and disinfectants. One industrial method of preparing chlorobenzene is to react benzene, C6H6, with chlorine, which is represented by the following equation. ...
Complete Solution Manual
... while G orxn is negative. The negative sign is necessary to convert the positive E ocell value for a spontaneous reaction into a negative G orxn . The superscript indicates standard conditions. These are T = 25C, solute concentrations of 1.0 M, and gas partial pressures of ...
... while G orxn is negative. The negative sign is necessary to convert the positive E ocell value for a spontaneous reaction into a negative G orxn . The superscript indicates standard conditions. These are T = 25C, solute concentrations of 1.0 M, and gas partial pressures of ...
Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
... A compound contains two or more different atoms joined together. A mixture contains two or more different substances that are only physically joined together, not chemically. A mixture can contain both elements and compounds. ...
... A compound contains two or more different atoms joined together. A mixture contains two or more different substances that are only physically joined together, not chemically. A mixture can contain both elements and compounds. ...
Chem G 9
... mechanics came about because scientists found that the tiny particles in an atom did not obey the classical laws of physics postulated by Sir Isaac Newton. Students should appreciate that in the quantum mechanics atomic model: • Electrons are located in orbitals • An orbital is a volume of space ins ...
... mechanics came about because scientists found that the tiny particles in an atom did not obey the classical laws of physics postulated by Sir Isaac Newton. Students should appreciate that in the quantum mechanics atomic model: • Electrons are located in orbitals • An orbital is a volume of space ins ...
Complete Solution Manual
... while G orxn is negative. The negative sign is necessary to convert the positive E ocell value for a spontaneous reaction into a negative G orxn . The superscript indicates standard conditions. These are T = 25C, solute concentrations of 1.0 M, and gas partial pressures of ...
... while G orxn is negative. The negative sign is necessary to convert the positive E ocell value for a spontaneous reaction into a negative G orxn . The superscript indicates standard conditions. These are T = 25C, solute concentrations of 1.0 M, and gas partial pressures of ...
Chemistry-Maths-Student-Guide
... Standard states are the most stable states under standard conditions, e.g. H2O(l), CO2(g), Na(s). However, note that for carbon, the most stable state is C(graphite). Solutions are aqueous and concentrations are 1 mol dm-3. ...
... Standard states are the most stable states under standard conditions, e.g. H2O(l), CO2(g), Na(s). However, note that for carbon, the most stable state is C(graphite). Solutions are aqueous and concentrations are 1 mol dm-3. ...
UN1001: Section 11: Hydrogen Effects
... up hydrogen (or deuterium in heavy water ) by general corrosion. The hydrogen (D) migrates through the metal lattice to cool regions and to regions of high tensile stress - can precipitate as a separate phase - zirconium hydride. These hydrides are themselves brittle, and crack, and the crack can pr ...
... up hydrogen (or deuterium in heavy water ) by general corrosion. The hydrogen (D) migrates through the metal lattice to cool regions and to regions of high tensile stress - can precipitate as a separate phase - zirconium hydride. These hydrides are themselves brittle, and crack, and the crack can pr ...
Learning Outcomes
... to deduce their properties (c) compare the bonding and structures of diamond and graphite in order to deduce their properties such as electrical conductivity, lubricating or cutting action (candidates will not be required to draw the structures) ...................................................... ...
... to deduce their properties (c) compare the bonding and structures of diamond and graphite in order to deduce their properties such as electrical conductivity, lubricating or cutting action (candidates will not be required to draw the structures) ...................................................... ...
Document
... Example Calculation of the amount of graphite to produce a mole of hydrogen at constant temperature. The reaction of heated coal with superheated steam absorbs heat. This heat is usually provided by burning some of the coal. Calculate ΔrH º(500 K) for both reactions? a. C(graphite) + H2O(g) = CO(g) ...
... Example Calculation of the amount of graphite to produce a mole of hydrogen at constant temperature. The reaction of heated coal with superheated steam absorbs heat. This heat is usually provided by burning some of the coal. Calculate ΔrH º(500 K) for both reactions? a. C(graphite) + H2O(g) = CO(g) ...
Gr. 11 Chemistry Student Workbook (Spring 2016)
... The most basic piece of personal protective equipment is a pair of goggles, and these will always be made available to students. Like a calculator for mathematics, and running shoes for physical education goggles are personal pieces of equipment best owned by students. When students own their own go ...
... The most basic piece of personal protective equipment is a pair of goggles, and these will always be made available to students. Like a calculator for mathematics, and running shoes for physical education goggles are personal pieces of equipment best owned by students. When students own their own go ...
Multiple-choice questions : 1. The following graph shows the volume
... Each question below consists of two separate statements. Decide whether each of the two statements is true or false; if both are true, then decide whether or not the second statement is a correct explanation of the first statement. Then select one option from A to D according to the following table: ...
... Each question below consists of two separate statements. Decide whether each of the two statements is true or false; if both are true, then decide whether or not the second statement is a correct explanation of the first statement. Then select one option from A to D according to the following table: ...
2 - TEST BANK 360
... that the atom was a solid, impenetrable mass. Keep in mind that this is in direct contrast to what was observed in the actual experiments, where the majority of the alpha particles passed through without being deflected. ...
... that the atom was a solid, impenetrable mass. Keep in mind that this is in direct contrast to what was observed in the actual experiments, where the majority of the alpha particles passed through without being deflected. ...
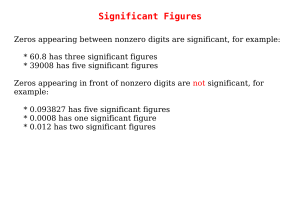
Significant Figures
... Summary of empirical formula determination steps: 1. Use the given % composition, or determine what the %composition is and then find the mass of each element in a 100 g sample of the substance. 2. For each elemental mass, determine the number of mols of the element in the 100 g sample using the cor ...
... Summary of empirical formula determination steps: 1. Use the given % composition, or determine what the %composition is and then find the mass of each element in a 100 g sample of the substance. 2. For each elemental mass, determine the number of mols of the element in the 100 g sample using the cor ...
KEY + + - UIC Department of Chemistry
... When a solution containing 0.634 g of XCl3 was allowed to react with an excess of aqueous AgNO3 , 1.68 g of solid AgCl was formed. What is the identity of the atom X? (10 points) moles AgCl = (1.68 g)(1 mol AgCl/143.3212 g) = 0.011722 mol AgCl moles XCl 3 = (0.011722 mol AgCl)(1 XCl3 / 3 AgCl) = 0.0 ...
... When a solution containing 0.634 g of XCl3 was allowed to react with an excess of aqueous AgNO3 , 1.68 g of solid AgCl was formed. What is the identity of the atom X? (10 points) moles AgCl = (1.68 g)(1 mol AgCl/143.3212 g) = 0.011722 mol AgCl moles XCl 3 = (0.011722 mol AgCl)(1 XCl3 / 3 AgCl) = 0.0 ...
Lipid Hydroperoxide Activation of N-Hydroxy-N
... resolve the hyperfine structure. The g value and splitting constant (1.7 to 2.0 gauss) fit the properties of the ascor bate radical (18). The nitroxyl radical of N-OH-AAF was monitored on a kinetic basis (Chart 6, Trace D) in the LAHP/ hematin/N-OH-AAF systems. Analysis of the time course of the nit ...
... resolve the hyperfine structure. The g value and splitting constant (1.7 to 2.0 gauss) fit the properties of the ascor bate radical (18). The nitroxyl radical of N-OH-AAF was monitored on a kinetic basis (Chart 6, Trace D) in the LAHP/ hematin/N-OH-AAF systems. Analysis of the time course of the nit ...
Unit 3 - High School Chemistry
... 3. Hydrogen usually loses an electron to become a H+ ion. However, it can sometimes gain an electron to become H− (Hydride). 4. The last column of the Table of Elements does not usually form ions. These elements are called the Noble Gases (Helium, Neon, Argon, Krypton, Xenon, and Radon). The number ...
... 3. Hydrogen usually loses an electron to become a H+ ion. However, it can sometimes gain an electron to become H− (Hydride). 4. The last column of the Table of Elements does not usually form ions. These elements are called the Noble Gases (Helium, Neon, Argon, Krypton, Xenon, and Radon). The number ...
QUESTION BANK CHEMISTRY-XII THE SOLID STATE CHAPTER
... 41. Explain the term electrolysis .Write the reactions at cathode and anode when following substances are electrolysed :‐ (i) Molten NaCl (ii) Aqueous solution of NaCl 42. What is meant by electrochemical series? How does it help in :‐ (i) comparing the relative oxidizing or reduci ...
... 41. Explain the term electrolysis .Write the reactions at cathode and anode when following substances are electrolysed :‐ (i) Molten NaCl (ii) Aqueous solution of NaCl 42. What is meant by electrochemical series? How does it help in :‐ (i) comparing the relative oxidizing or reduci ...
Tro Chemistry a Molecular Approach, 3E
... The temperature outside my office today is a cool 48 °F, lower than normal for this time of year on the California coast. However, today’s “chill” pales in comparison with how cold it would be without the presence of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases act like the glass of a greenhouse, ...
... The temperature outside my office today is a cool 48 °F, lower than normal for this time of year on the California coast. However, today’s “chill” pales in comparison with how cold it would be without the presence of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases act like the glass of a greenhouse, ...
Redox

Redox reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed; in general, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species. The term ""redox"" comes from two concepts involved with electron transfer: reduction and oxidation. It can be explained in simple terms: Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, these are only specific examples of a more general concept of reactions involving electron transfer.Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, have a number of similarities to acid–base reactions. Like acid–base reactions, redox reactions are a matched set, that is, there cannot be an oxidation reaction without a reduction reaction happening simultaneously. The oxidation alone and the reduction alone are each called a half-reaction, because two half-reactions always occur together to form a whole reaction. When writing half-reactions, the gained or lost electrons are typically included explicitly in order that the half-reaction be balanced with respect to electric charge.Though sufficient for many purposes, these descriptions are not precisely correct. Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation state — the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. The oxidation state of an atom is the fictitious charge that an atom would have if all bonds between atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation state, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation state. In practice, the transfer of electrons will always cause a change in oxidation state, but there are many reactions that are classed as ""redox"" even though no electron transfer occurs (such as those involving covalent bonds).There are simple redox processes, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide (CO2) or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), and more complex processes such as the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) in the human body through a series of complex electron transfer processes.