mnemonic as an innovative approach to creative
... something or (b) as an adjective meaning aiding memory. Iza, & Gil [27] describes mnemonic as memory-enhancing pedagogical methods aimed at improving learning and information recall through the use of imagery. The Wikipedia defines mnemonics as any learning technique that aids information retention. ...
... something or (b) as an adjective meaning aiding memory. Iza, & Gil [27] describes mnemonic as memory-enhancing pedagogical methods aimed at improving learning and information recall through the use of imagery. The Wikipedia defines mnemonics as any learning technique that aids information retention. ...
CBSE Living Science Chemistry Class X
... Take 20 mL of dil. H2SO4 in a conical flask fitted with a cork and a delivery tube having a fine jet. Clamp the conical flask to the clamp stand (Fig. 1.2). Add some pieces of granulated zinc to the conical flask and stopper the flask with a cork fitted with delivery tube having fine jet. There occu ...
... Take 20 mL of dil. H2SO4 in a conical flask fitted with a cork and a delivery tube having a fine jet. Clamp the conical flask to the clamp stand (Fig. 1.2). Add some pieces of granulated zinc to the conical flask and stopper the flask with a cork fitted with delivery tube having fine jet. There occu ...
DOC
... Heterogeneous Equilibria concentrations of pure liquids and solids are effectively constants, they do not appear in K expressions for example: NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq) ...
... Heterogeneous Equilibria concentrations of pure liquids and solids are effectively constants, they do not appear in K expressions for example: NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq) ...
Science
... Acids and Bases 19. Students shall understand the historical development of the acid/base theories. 20. Students shall apply rules of nomenclature to acids, bases and salts. 21. Students shall understand the general properties of acids, bases and salts. 22. Students shall demonstrate an understandin ...
... Acids and Bases 19. Students shall understand the historical development of the acid/base theories. 20. Students shall apply rules of nomenclature to acids, bases and salts. 21. Students shall understand the general properties of acids, bases and salts. 22. Students shall demonstrate an understandin ...
Introductary topics
... neutral. The sum of the positive and negative charges must add up to zero. ...
... neutral. The sum of the positive and negative charges must add up to zero. ...
No Slide Title
... 1.000 atm, and the initial volume occupied by the gas is 2.000 L. 8000. J of heat is added to the gas under conditions of constant applied pressure. The final volume occupied by the gas is 6.000 L. What are q, w, and U for the process? From the first law, U = q + w. Heat is added to the system, so ...
... 1.000 atm, and the initial volume occupied by the gas is 2.000 L. 8000. J of heat is added to the gas under conditions of constant applied pressure. The final volume occupied by the gas is 6.000 L. What are q, w, and U for the process? From the first law, U = q + w. Heat is added to the system, so ...
chemistry
... The catalytic converter in an automobile changes harmful gases produced during fuel combustion to less harmful exhaust gases. In the catalytic converter, nitrogen dioxide reacts with carbon monoxide to produce nitrogen and carbon dioxide. In addition, some carbon monoxide reacts with oxygen, produci ...
... The catalytic converter in an automobile changes harmful gases produced during fuel combustion to less harmful exhaust gases. In the catalytic converter, nitrogen dioxide reacts with carbon monoxide to produce nitrogen and carbon dioxide. In addition, some carbon monoxide reacts with oxygen, produci ...
The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to form water and oxygen
... Section II Directions: Questions 1 through 3 are long constructed response questions that should require about 20 minutes to answer. Questions 4 through 7 are short constructed response questions that should require about 7 minutes each to answer. Read each question carefully and write your response ...
... Section II Directions: Questions 1 through 3 are long constructed response questions that should require about 20 minutes to answer. Questions 4 through 7 are short constructed response questions that should require about 7 minutes each to answer. Read each question carefully and write your response ...
vce chemistry trial exam 1
... Cu2+(aq) + 2e– → Cu(s) (reduction because electrons are being gained) There are 3 electrons being produced in the oxidation of each Al atom and 2 electrons being gained in the reduction of each copper ion. The electrons lost and gained must be balanced in the overall equation. Each half-equation is ...
... Cu2+(aq) + 2e– → Cu(s) (reduction because electrons are being gained) There are 3 electrons being produced in the oxidation of each Al atom and 2 electrons being gained in the reduction of each copper ion. The electrons lost and gained must be balanced in the overall equation. Each half-equation is ...
Determination of the Empirical Formula of an
... The unknown lead oxide (1.012 g) was added to a clean, tared 200 mm ignition tube through a funnel to ensure that all of the lead oxide was located in the lower portion of the tube, and the tube with lead oxide was weighed. A two-holed rubber stopper covered with aluminum foil (to prevent the rubber ...
... The unknown lead oxide (1.012 g) was added to a clean, tared 200 mm ignition tube through a funnel to ensure that all of the lead oxide was located in the lower portion of the tube, and the tube with lead oxide was weighed. A two-holed rubber stopper covered with aluminum foil (to prevent the rubber ...
Biology, 8e (Campbell)
... B) electrons are not symmetrically distributed in a molecule. C) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water. D) two polar covalent bonds react. E) a hydrogen atom loses an electron. Answer: B Topic: Concept 2.3 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 59) A van der Waals interaction is the weak attraction ...
... B) electrons are not symmetrically distributed in a molecule. C) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water. D) two polar covalent bonds react. E) a hydrogen atom loses an electron. Answer: B Topic: Concept 2.3 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 59) A van der Waals interaction is the weak attraction ...
- Career Point Kota
... (ii) Argon : - Non-polar molecular solid which posses dispersion or london forces. (b) zinc oxide is white in colour at room temperature. On heating it loses oxygen & turns yellow ...
... (ii) Argon : - Non-polar molecular solid which posses dispersion or london forces. (b) zinc oxide is white in colour at room temperature. On heating it loses oxygen & turns yellow ...
C:\D\Books\Cambridge University Press\CUP Problems\Problems.wpd
... have the composition C18H19O9N. This waste can be oxidized by aerobic, heterotrophic bacteria in two ways: a without and b with nitrification. Write balanced reaction equations and find the maximum biological oxygen demand for the two cases. 98. Calculate the maximum biological oxygen demand without ...
... have the composition C18H19O9N. This waste can be oxidized by aerobic, heterotrophic bacteria in two ways: a without and b with nitrification. Write balanced reaction equations and find the maximum biological oxygen demand for the two cases. 98. Calculate the maximum biological oxygen demand without ...
all practice examples
... How many millilitres of 5.00 M K2Cr2O7 solution must be diluted to prepare 250. cm3 of 0.100 M solution? ...
... How many millilitres of 5.00 M K2Cr2O7 solution must be diluted to prepare 250. cm3 of 0.100 M solution? ...
UNIT 5 - H-W Science Website
... energy (in which case it will be released) or sometimes not enough energy (in which case it will be absorbed from the surroundings). The change in energy is due mainly to bond rearrangement during a reaction. Whether there is a net absorption or release of energy depends on the number of bonds broke ...
... energy (in which case it will be released) or sometimes not enough energy (in which case it will be absorbed from the surroundings). The change in energy is due mainly to bond rearrangement during a reaction. Whether there is a net absorption or release of energy depends on the number of bonds broke ...
Chapter 8 and 9
... From this information you can calculate the amount of carbon and hydrogen in the sample. However since oxygen is in excess you must find oxygen through indirect means (the mass comes from what is not accounted for by carbon and hydrogen, in a sample that only contains CHO). ...
... From this information you can calculate the amount of carbon and hydrogen in the sample. However since oxygen is in excess you must find oxygen through indirect means (the mass comes from what is not accounted for by carbon and hydrogen, in a sample that only contains CHO). ...
Atomic structure and periodic table
... Copper (I) means Cu+ as in Copper(I)oxide Copper (II) means Cu2+ as in Copper(II)oxide Iron (II) means Fe2+ as in Iron(II)sulphide Iron (III) means Fe3+ as in Iron(III)chloride Sulphur(VI)mean S6+ as in Iron(III)sulphate(VI) Sulphur(VI)mean S6+ as in sulphur(VI)oxide Sulphur(IV)mean S4+ as in sulphu ...
... Copper (I) means Cu+ as in Copper(I)oxide Copper (II) means Cu2+ as in Copper(II)oxide Iron (II) means Fe2+ as in Iron(II)sulphide Iron (III) means Fe3+ as in Iron(III)chloride Sulphur(VI)mean S6+ as in Iron(III)sulphate(VI) Sulphur(VI)mean S6+ as in sulphur(VI)oxide Sulphur(IV)mean S4+ as in sulphu ...
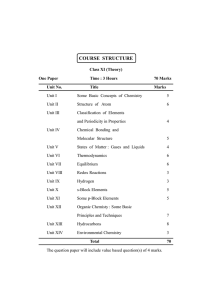
COURSE STRUCTURE
... In all physical and chemical changes, the total mass of reactants is equal to that of products. Law of constant composition : A chemical compound is always found to be made of same elements combined together in the same fixed ratio by mass. Law of multiple proportion : Two elements combined together ...
... In all physical and chemical changes, the total mass of reactants is equal to that of products. Law of constant composition : A chemical compound is always found to be made of same elements combined together in the same fixed ratio by mass. Law of multiple proportion : Two elements combined together ...
NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL CHEMISTRY EXAMINATION (1995
... From these data, she can conclude that a) both Ba(IO 3 ) 2 and Mg(ClO3 ) 2 are insoluble in water. b) both PbCrO4 and Mg(ClO3 ) 2 are insoluble in water. c) Ba(IO 3 ) 2 , Pb(IO 3 ) 2 , and PbCrO4 are insoluble in water. d) all of Ba(IO 3 ) 2 , Mg(ClO 3 ) 2 , Pb(IO 3 ) 2 , PbCrO4 , and CaCrO 4 are in ...
... From these data, she can conclude that a) both Ba(IO 3 ) 2 and Mg(ClO3 ) 2 are insoluble in water. b) both PbCrO4 and Mg(ClO3 ) 2 are insoluble in water. c) Ba(IO 3 ) 2 , Pb(IO 3 ) 2 , and PbCrO4 are insoluble in water. d) all of Ba(IO 3 ) 2 , Mg(ClO 3 ) 2 , Pb(IO 3 ) 2 , PbCrO4 , and CaCrO 4 are in ...
Lecture 1 - Алтайский государственный технический
... The diameters of atomic nuclei are about 10-4A. Thus, the nuclei are about 0.01% the diameter of the atom as a whole. If the nucleus had a diameter equal to that of a pinhead, then the atom itself would have a diameter of some 10 meters (about 39 and a half feet). The nucleus of an atom is therefor ...
... The diameters of atomic nuclei are about 10-4A. Thus, the nuclei are about 0.01% the diameter of the atom as a whole. If the nucleus had a diameter equal to that of a pinhead, then the atom itself would have a diameter of some 10 meters (about 39 and a half feet). The nucleus of an atom is therefor ...
Redox

Redox reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed; in general, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species. The term ""redox"" comes from two concepts involved with electron transfer: reduction and oxidation. It can be explained in simple terms: Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, these are only specific examples of a more general concept of reactions involving electron transfer.Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, have a number of similarities to acid–base reactions. Like acid–base reactions, redox reactions are a matched set, that is, there cannot be an oxidation reaction without a reduction reaction happening simultaneously. The oxidation alone and the reduction alone are each called a half-reaction, because two half-reactions always occur together to form a whole reaction. When writing half-reactions, the gained or lost electrons are typically included explicitly in order that the half-reaction be balanced with respect to electric charge.Though sufficient for many purposes, these descriptions are not precisely correct. Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation state — the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. The oxidation state of an atom is the fictitious charge that an atom would have if all bonds between atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation state, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation state. In practice, the transfer of electrons will always cause a change in oxidation state, but there are many reactions that are classed as ""redox"" even though no electron transfer occurs (such as those involving covalent bonds).There are simple redox processes, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide (CO2) or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), and more complex processes such as the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) in the human body through a series of complex electron transfer processes.