Unique Solutions
... changes into reddish brown. This is due to: a combination reaction b decomposition reaction c neutralization reaction d displacement reaction Hint : Turmeric present in curry is an indicator. It will turn reddish brown in basic solution (soap is a basic solution). Silver ornaments become dark on pro ...
... changes into reddish brown. This is due to: a combination reaction b decomposition reaction c neutralization reaction d displacement reaction Hint : Turmeric present in curry is an indicator. It will turn reddish brown in basic solution (soap is a basic solution). Silver ornaments become dark on pro ...
CHEM102 Chemistry II Spring 10-11 Mid
... C) One mole of methane reacts with two moles of oxygen to produce one mole of carbon dioxide and 2 moles of water. D) A, B and C are correct. E) A and C are correct. 45) A reaction that is spontaneous can be described as 45) E A) having the same rate in both the forward and reverse directions. B) re ...
... C) One mole of methane reacts with two moles of oxygen to produce one mole of carbon dioxide and 2 moles of water. D) A, B and C are correct. E) A and C are correct. 45) A reaction that is spontaneous can be described as 45) E A) having the same rate in both the forward and reverse directions. B) re ...
Chemical Reactions
... Reactants – the substances undergoing the chemical change Products – the new substances formed as a results of the chemical change In the case of the burning charcoal Reactants are carbon and oxygen and the product is carbon dioxide C + O2 → CO2 ...
... Reactants – the substances undergoing the chemical change Products – the new substances formed as a results of the chemical change In the case of the burning charcoal Reactants are carbon and oxygen and the product is carbon dioxide C + O2 → CO2 ...
High School Physical Science Glossary
... dispersion forces- weak forces between atoms or molecules resulting from the movement of electrons in the electron cloud around the system effervescence- bubbling of a solution due to the escape of a gas either produced by a chemical reaction or a gas coming out of solution as in a carbonated bevera ...
... dispersion forces- weak forces between atoms or molecules resulting from the movement of electrons in the electron cloud around the system effervescence- bubbling of a solution due to the escape of a gas either produced by a chemical reaction or a gas coming out of solution as in a carbonated bevera ...
chemical reaction - MRS. STOTTS CHEMISTRY
... separates from the solution is known as a precipitate. 4. Color change ...
... separates from the solution is known as a precipitate. 4. Color change ...
Chapter 8
... 1.) Solid Sodium oxide is added to water at room temperature and forms sodium hydroxide (dissolved in water). 2.) Solid calcium reacts with solid sulfur to produce solid calcium sulfide (Hint: Solid sulfur’s formula is S8. ...
... 1.) Solid Sodium oxide is added to water at room temperature and forms sodium hydroxide (dissolved in water). 2.) Solid calcium reacts with solid sulfur to produce solid calcium sulfide (Hint: Solid sulfur’s formula is S8. ...
Chemical Reactions
... (BrINClHOF) For example, Oxygen is O2 as an element. In a compound, it can’t be a diatomic element because it’s not an element anymore, it’s a compound! ...
... (BrINClHOF) For example, Oxygen is O2 as an element. In a compound, it can’t be a diatomic element because it’s not an element anymore, it’s a compound! ...
53 word equations
... Plants are able to make glucose from carbon dioxide gas in a reaction called photosynthesis. The other reactant is water, taken in through the roots. Oxygen gas is also formed in the process. Energy from the Sun is required for the reaction. ...
... Plants are able to make glucose from carbon dioxide gas in a reaction called photosynthesis. The other reactant is water, taken in through the roots. Oxygen gas is also formed in the process. Energy from the Sun is required for the reaction. ...
Chemistry (CP) Final Exam Study Guide 1
... ____ 21. All of the following are physical properties of matter EXCEPT ____. a. mass c. melting point b. color d. ability to rust ____ 22. Which of the following is NOT a physical property of water? a. It has a boiling point of 100 C. b. It is a colorless liquid. c. It is composed of hydrogen and ox ...
... ____ 21. All of the following are physical properties of matter EXCEPT ____. a. mass c. melting point b. color d. ability to rust ____ 22. Which of the following is NOT a physical property of water? a. It has a boiling point of 100 C. b. It is a colorless liquid. c. It is composed of hydrogen and ox ...
Final Exam Practice Problems Set 2
... 2) All atoms of a given element are identical; the atoms of different elements are different and have different properties. 3) Atoms of an element are not changed into different types of atoms by chemical reactions; atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. 4) Compounds are form ...
... 2) All atoms of a given element are identical; the atoms of different elements are different and have different properties. 3) Atoms of an element are not changed into different types of atoms by chemical reactions; atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. 4) Compounds are form ...
exam review - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... c) Rubbing alcohol is commonly used as an antiseptic for small cuts. It is sold as a 23% (v/v) solution of isopropyl alcohol in water. What volume of isopropyl alcohol is used to make 570mL of solution? 12. When silver nitrate is added to sodium chromate, a brick-red precipitate forms. Calculate the ...
... c) Rubbing alcohol is commonly used as an antiseptic for small cuts. It is sold as a 23% (v/v) solution of isopropyl alcohol in water. What volume of isopropyl alcohol is used to make 570mL of solution? 12. When silver nitrate is added to sodium chromate, a brick-red precipitate forms. Calculate the ...
Chemical Equations and Reaction Types Lab
... equation for a reaction cannot be written unless the substances that are reacting and being formed are both ...
... equation for a reaction cannot be written unless the substances that are reacting and being formed are both ...
Balancing Chemical Equations
... Introduction: The equation H2 + O2 H2O is unbalanced because there are two oxygen atoms on the reactants side of the equation, and only one on the products side of the equation. To balance the equation, you cannot change the structure of any of the molecules, but you can change the number of molec ...
... Introduction: The equation H2 + O2 H2O is unbalanced because there are two oxygen atoms on the reactants side of the equation, and only one on the products side of the equation. To balance the equation, you cannot change the structure of any of the molecules, but you can change the number of molec ...
Periodic Table
... • When writing isotopes, the atomic number (or number of protons) will appear at the __________ • The mass number (number of protons plus neutrons will appear at the __________ • The element symbol will appear to the __________ • The different number of neutrons has NO bearing on chemical reactivity ...
... • When writing isotopes, the atomic number (or number of protons) will appear at the __________ • The mass number (number of protons plus neutrons will appear at the __________ • The element symbol will appear to the __________ • The different number of neutrons has NO bearing on chemical reactivity ...
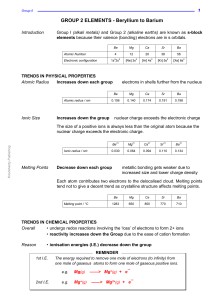
GROUP 2 ELEMENTS - Beryllium to Barium
... basic strength also increases down group this is because the solubility increases the metal ions get larger so charge density decreases there is a lower attraction between the OH¯ ions and larger dipositive ions the ions will split away from each other more easily there will be a greater concentrati ...
... basic strength also increases down group this is because the solubility increases the metal ions get larger so charge density decreases there is a lower attraction between the OH¯ ions and larger dipositive ions the ions will split away from each other more easily there will be a greater concentrati ...
Chemistry EOC Review 2015 Name Per ___ This review is part of
... Describe trends in properties (e.g., ionization energy or reactivity as a function of location on the periodic table, boiling point of organic liquids as a function of molecular weight). Atomic radius is one-half of the distance between the center of identical atoms that are not bonded together. Ion ...
... Describe trends in properties (e.g., ionization energy or reactivity as a function of location on the periodic table, boiling point of organic liquids as a function of molecular weight). Atomic radius is one-half of the distance between the center of identical atoms that are not bonded together. Ion ...
a) air c) milk f) beer
... What is the ratio of oxygen in the two compounds for a fixed amount of nitrogen? ...
... What is the ratio of oxygen in the two compounds for a fixed amount of nitrogen? ...
Total Notes for chem - Catawba County Schools
... Vapor Pressure: - the pressure of a gas above a liquidHenry’s Law: the number of molecules of a gas dissolved in a liquid is directly related to the gas pressure above the liquid(see- blood gases, etc.). Grahams Law: The relative rates at which two gases under identical conditions of temperature and ...
... Vapor Pressure: - the pressure of a gas above a liquidHenry’s Law: the number of molecules of a gas dissolved in a liquid is directly related to the gas pressure above the liquid(see- blood gases, etc.). Grahams Law: The relative rates at which two gases under identical conditions of temperature and ...
CH 301 Practice Test Questions
... at 298 K and 1 atm pressure? The number below each substance is the absolute entropy of the substance at 298 K, 1 atm, in units of J/(mol•K). 19. What is the molarity of a HCl solution if 2.50 L is needed to react with 12.7 g of Al according to the reaction 2 Al + 6 HCl 2 AlCl3 + 3H2 ? 20. Conside ...
... at 298 K and 1 atm pressure? The number below each substance is the absolute entropy of the substance at 298 K, 1 atm, in units of J/(mol•K). 19. What is the molarity of a HCl solution if 2.50 L is needed to react with 12.7 g of Al according to the reaction 2 Al + 6 HCl 2 AlCl3 + 3H2 ? 20. Conside ...
Chemical Reactions
... N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g) C3H6 (g) + Br2 (l) C3H6Br2 (l) 2 Mg (s) + O2 (g) 2 MgO (s) ...
... N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g) C3H6 (g) + Br2 (l) C3H6Br2 (l) 2 Mg (s) + O2 (g) 2 MgO (s) ...
Redox

Redox reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed; in general, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species. The term ""redox"" comes from two concepts involved with electron transfer: reduction and oxidation. It can be explained in simple terms: Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, these are only specific examples of a more general concept of reactions involving electron transfer.Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, have a number of similarities to acid–base reactions. Like acid–base reactions, redox reactions are a matched set, that is, there cannot be an oxidation reaction without a reduction reaction happening simultaneously. The oxidation alone and the reduction alone are each called a half-reaction, because two half-reactions always occur together to form a whole reaction. When writing half-reactions, the gained or lost electrons are typically included explicitly in order that the half-reaction be balanced with respect to electric charge.Though sufficient for many purposes, these descriptions are not precisely correct. Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation state — the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. The oxidation state of an atom is the fictitious charge that an atom would have if all bonds between atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation state, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation state. In practice, the transfer of electrons will always cause a change in oxidation state, but there are many reactions that are classed as ""redox"" even though no electron transfer occurs (such as those involving covalent bonds).There are simple redox processes, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide (CO2) or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), and more complex processes such as the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) in the human body through a series of complex electron transfer processes.