Heat of reaction
... their standard state produce products in their standard state is called the standard enthalpy of reaction (ΔH°). • The standard state of a substance is its pure and most stable form at 1 atmosphere pressure and at 25°C. • The enthalpy change for the formation of one mole of a compound in its standar ...
... their standard state produce products in their standard state is called the standard enthalpy of reaction (ΔH°). • The standard state of a substance is its pure and most stable form at 1 atmosphere pressure and at 25°C. • The enthalpy change for the formation of one mole of a compound in its standar ...
Self-Test Worksheet for Thermodynamics Section (Quiz
... As the temperature is increased, what is the effect on ∆G° for the reaction? How does this affect the spontaneity of the reaction? 3. After a winter cold spell, a swimming pool has a surface layer of ice. By measuring the thickness of the ice, and the area of the pool, and the depth of the water und ...
... As the temperature is increased, what is the effect on ∆G° for the reaction? How does this affect the spontaneity of the reaction? 3. After a winter cold spell, a swimming pool has a surface layer of ice. By measuring the thickness of the ice, and the area of the pool, and the depth of the water und ...
Make Your Own Summary 1. single displacement reaction 2
... which prevents the reaction from being a double displacement reaction. The products are two compounds, which prevent the reaction from being a single displacement reaction. ...
... which prevents the reaction from being a double displacement reaction. The products are two compounds, which prevent the reaction from being a single displacement reaction. ...
Midterm Review Packet - Mrs. McKenzie`s Chemistry and ICP Classes
... 2. The measurement of the amount of matter in an object is called ___________________. ...
... 2. The measurement of the amount of matter in an object is called ___________________. ...
Day 72 TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... Release of energy as heat Release of energy as light Change in colour ...
... Release of energy as heat Release of energy as light Change in colour ...
Chemistry Midterm Review Sheet
... e) Hg(NO3)2 (aq) and HBr (aq) f) HF(aq) and NaOH (aq) 1) Write balanced equations, with states for the following reactions. If indicated, write down what kind of reaction occurred. a) Solid copper(I) oxide is heated to decompose it into its elements. ...
... e) Hg(NO3)2 (aq) and HBr (aq) f) HF(aq) and NaOH (aq) 1) Write balanced equations, with states for the following reactions. If indicated, write down what kind of reaction occurred. a) Solid copper(I) oxide is heated to decompose it into its elements. ...
Chapter 07 and 08 Chemical Bonding and Molecular
... K21+O2-. There are two electrons lost and two electrons gained. ...
... K21+O2-. There are two electrons lost and two electrons gained. ...
Title - Iowa State University
... d) none of these 4) Which of the following is a strong electrolyte? a) CH3OH b) HCOOH c)KNO3 d) all of these 5) Which of the following would be insoluble? a) CaS b) KOH c) Pb(NO3)2 d) SrSO4 e)both a and d 6) Which of the following are insoluble? I.Ag2SO4 II. Ni3PO4 III. NaI a) I only b) II only c) I ...
... d) none of these 4) Which of the following is a strong electrolyte? a) CH3OH b) HCOOH c)KNO3 d) all of these 5) Which of the following would be insoluble? a) CaS b) KOH c) Pb(NO3)2 d) SrSO4 e)both a and d 6) Which of the following are insoluble? I.Ag2SO4 II. Ni3PO4 III. NaI a) I only b) II only c) I ...
A.P. Chemistry Writing Chemical Reactions Generally students do
... this has more to do with potential questions about reactions than with balancing techniques for nontrivial redox reactions. For example, some reactions students have been asked to write in the past are things they would never have seen. Whether this will remain the case is not known, but if it does, ...
... this has more to do with potential questions about reactions than with balancing techniques for nontrivial redox reactions. For example, some reactions students have been asked to write in the past are things they would never have seen. Whether this will remain the case is not known, but if it does, ...
$doc.title
... with one oxygen atom to form one molecule of water. On the atomic scale, we never see an example of one and a half hydrogen atoms combining with an oxygen atom. This was one of the first observations of the early chemists who explored the properties of chemical elements. This observation is known as ...
... with one oxygen atom to form one molecule of water. On the atomic scale, we never see an example of one and a half hydrogen atoms combining with an oxygen atom. This was one of the first observations of the early chemists who explored the properties of chemical elements. This observation is known as ...
Writing Chemical Reactions
... this has more to do with potential questions about reactions than with balancing techniques for nontrivial redox reactions. For example, some reactions students have been asked to write in the past are things they would never have seen. Whether this will remain the case is not known, but if it does, ...
... this has more to do with potential questions about reactions than with balancing techniques for nontrivial redox reactions. For example, some reactions students have been asked to write in the past are things they would never have seen. Whether this will remain the case is not known, but if it does, ...
syllabus details - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Cross reference with topics 2, 4 and 5. Data for all these properties are listed in the data booklet. Explanations for the first four trends should be given in terms of the balance between the attraction of the nucleus for the electrons and the repulsion between electrons. Explanations based on effe ...
... Cross reference with topics 2, 4 and 5. Data for all these properties are listed in the data booklet. Explanations for the first four trends should be given in terms of the balance between the attraction of the nucleus for the electrons and the repulsion between electrons. Explanations based on effe ...
Copper and Alloys
... neutralisation reaction can be predicted. The first part of the name is ‘ammonium’ if the base used is ammonia. Otherwise, it is the name of the metal in the base. The second part of the name comes from the acid used: chloride, if hydrochloric acid is used nitrate, if nitric acid is used sulph ...
... neutralisation reaction can be predicted. The first part of the name is ‘ammonium’ if the base used is ammonia. Otherwise, it is the name of the metal in the base. The second part of the name comes from the acid used: chloride, if hydrochloric acid is used nitrate, if nitric acid is used sulph ...
Chemistry - Onslow College
... Determine the oxidation number for binary compounds and monatomic ions Oxidation and reduction in terms of change in oxidation number 2. Electron transfer in reactions 3. Oxidants as O2, I2, Cl2, Br2, H+, Fe3+, H2O2, MnO4-(aq)/H+, Cr2O72-(aq)/H+, OCl-, Cu2+, IO3-, conc.HNO3 4. Reductants as ...
... Determine the oxidation number for binary compounds and monatomic ions Oxidation and reduction in terms of change in oxidation number 2. Electron transfer in reactions 3. Oxidants as O2, I2, Cl2, Br2, H+, Fe3+, H2O2, MnO4-(aq)/H+, Cr2O72-(aq)/H+, OCl-, Cu2+, IO3-, conc.HNO3 4. Reductants as ...
Chemistry 12 is an intensive course, covering a great deal of
... – a chemical equation that includes the energy term (thermochemical equation) – a chemical equation using ΔH notation A5 apply collision theory to explain how reaction rates can be changed use collision theory to explain the effect of the following factors on reaction rate: – nature of reactants – c ...
... – a chemical equation that includes the energy term (thermochemical equation) – a chemical equation using ΔH notation A5 apply collision theory to explain how reaction rates can be changed use collision theory to explain the effect of the following factors on reaction rate: – nature of reactants – c ...
HERE
... D) Zinc 15) Which property is an example of a chemical property? A) the ability to burn B) the ability to melt C) the ability to dissolve D) the ability to evaporate 16) During a physical science lab investigating chemical reactions, several students placed an antacid tablet in a zip-lock bag. They ...
... D) Zinc 15) Which property is an example of a chemical property? A) the ability to burn B) the ability to melt C) the ability to dissolve D) the ability to evaporate 16) During a physical science lab investigating chemical reactions, several students placed an antacid tablet in a zip-lock bag. They ...
Chapter 8: Periodic Properties of the Elements
... Chapter 8: Periodic Properties of the Elements Homework: Read Chapter 8. Work out sample/practice exercises Suggested Chapter 8 Problems: 43, 45, 51, 55, 59, 63, 67, 71, 75, 79, 83, 99 Check for the MasteringChemistry.com assignment and complete before due date The Periodic Table: 1869 Dmitri Mendel ...
... Chapter 8: Periodic Properties of the Elements Homework: Read Chapter 8. Work out sample/practice exercises Suggested Chapter 8 Problems: 43, 45, 51, 55, 59, 63, 67, 71, 75, 79, 83, 99 Check for the MasteringChemistry.com assignment and complete before due date The Periodic Table: 1869 Dmitri Mendel ...
THERMOCHEMISTRY ENERGETICS/ENTHALPY
... Atoms may gain or lose electrons to get full outer shells of electrons. Chemical reactions may give out heat – exothermic reactions. Chemical reactions may take in heat from their surroundings – endothermic reactions. ...
... Atoms may gain or lose electrons to get full outer shells of electrons. Chemical reactions may give out heat – exothermic reactions. Chemical reactions may take in heat from their surroundings – endothermic reactions. ...
CHEM 30
... A precipitate forms in a sample of drinking water when SO42- (sulfate) ions are added, but not when Cl- (chloride) ions are added. A cation which could cause this effect is: A. Ca2+ B. Ag+ C. Na+ D. Mg2+ ...
... A precipitate forms in a sample of drinking water when SO42- (sulfate) ions are added, but not when Cl- (chloride) ions are added. A cation which could cause this effect is: A. Ca2+ B. Ag+ C. Na+ D. Mg2+ ...
Organometallic Compounds and Catalysis: Synthesis
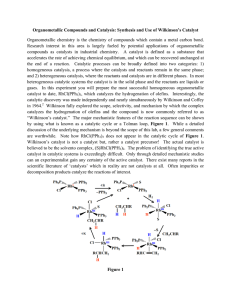
... Organometallic Compounds and Catalysis: Synthesis and Use of Wilkinson’s Catalyst Organometallic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds which contain a metal carbon bond. Research interest in this area is largely fueled by potential applications of organometallic compounds as catalysts in industria ...
... Organometallic Compounds and Catalysis: Synthesis and Use of Wilkinson’s Catalyst Organometallic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds which contain a metal carbon bond. Research interest in this area is largely fueled by potential applications of organometallic compounds as catalysts in industria ...
Chemistry- CST Review
... 1. What causes gas pressure in terms of kinetic theory? Gas pressure is caused by the random motion of the gas molecules. 2. If someone sprays perfume at the front of the room, will the people in the back of the room eventually be able to smell it? Why? Explain completely. Yes, the perfume will be s ...
... 1. What causes gas pressure in terms of kinetic theory? Gas pressure is caused by the random motion of the gas molecules. 2. If someone sprays perfume at the front of the room, will the people in the back of the room eventually be able to smell it? Why? Explain completely. Yes, the perfume will be s ...
Examination 3 Multiple Choice Questions
... One of the postulates of Dalton’s Atomic Theory states: The atoms of a given element are all alike. In what sense is this true? And, how is this false? The atoms of a given element are all alike in the sense that they have the same number of protons. Atoms of a given element can have different numbe ...
... One of the postulates of Dalton’s Atomic Theory states: The atoms of a given element are all alike. In what sense is this true? And, how is this false? The atoms of a given element are all alike in the sense that they have the same number of protons. Atoms of a given element can have different numbe ...
Redox

Redox reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed; in general, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species. The term ""redox"" comes from two concepts involved with electron transfer: reduction and oxidation. It can be explained in simple terms: Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, these are only specific examples of a more general concept of reactions involving electron transfer.Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, have a number of similarities to acid–base reactions. Like acid–base reactions, redox reactions are a matched set, that is, there cannot be an oxidation reaction without a reduction reaction happening simultaneously. The oxidation alone and the reduction alone are each called a half-reaction, because two half-reactions always occur together to form a whole reaction. When writing half-reactions, the gained or lost electrons are typically included explicitly in order that the half-reaction be balanced with respect to electric charge.Though sufficient for many purposes, these descriptions are not precisely correct. Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation state — the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. The oxidation state of an atom is the fictitious charge that an atom would have if all bonds between atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation state, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation state. In practice, the transfer of electrons will always cause a change in oxidation state, but there are many reactions that are classed as ""redox"" even though no electron transfer occurs (such as those involving covalent bonds).There are simple redox processes, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide (CO2) or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), and more complex processes such as the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) in the human body through a series of complex electron transfer processes.