File
... 89. The ability to conduct electricity in the solid state is a characteristic of metallic bonding. This characteristic is best explained by the presence of A) high ionization energies B) high electronegativities C) mobile electrons D) mobile protons 90. Which formula represents a nonpolar molecule c ...
... 89. The ability to conduct electricity in the solid state is a characteristic of metallic bonding. This characteristic is best explained by the presence of A) high ionization energies B) high electronegativities C) mobile electrons D) mobile protons 90. Which formula represents a nonpolar molecule c ...
Chemistry2 Midterm Review 2012 – Tuesday
... c. the system absorbs 77.5 kJ of heat while doing 63.5 kJ of work on the surroundings 52. What is specific heat capacity? Water has a high specific heat capacity of 4.884 J/g·C. What does that mean about water? 53. Draw a potential energy diagram for the following reaction: N2 + 3H2 2NH3 ΔH = -91. ...
... c. the system absorbs 77.5 kJ of heat while doing 63.5 kJ of work on the surroundings 52. What is specific heat capacity? Water has a high specific heat capacity of 4.884 J/g·C. What does that mean about water? 53. Draw a potential energy diagram for the following reaction: N2 + 3H2 2NH3 ΔH = -91. ...
SAT - mvhs-fuhsd.org
... • The number of unpaired valence electrons in a nonmetal tells you how many covalent bonds that atom can form with other nonmetals or how many electrons it wants to gain from metals to form an ion. • The number of valence electrons in a metal tells you how many electrons the metal will lose to nonme ...
... • The number of unpaired valence electrons in a nonmetal tells you how many covalent bonds that atom can form with other nonmetals or how many electrons it wants to gain from metals to form an ion. • The number of valence electrons in a metal tells you how many electrons the metal will lose to nonme ...
Review - Final Exam
... 41. Which has the stronger ionic bonds, BeF2 or LiF? Give two reasons. 42. Why can’t ionic compounds conduct an electric current in the solid state? 43. Why can ionic compounds conduct electricity when dissolved in water? 44. Describe a small experiment that could be done to determine whether a comp ...
... 41. Which has the stronger ionic bonds, BeF2 or LiF? Give two reasons. 42. Why can’t ionic compounds conduct an electric current in the solid state? 43. Why can ionic compounds conduct electricity when dissolved in water? 44. Describe a small experiment that could be done to determine whether a comp ...
Chapter 11: The rise of oxygen and ozone – ppt
... Fe2+ is soluble in water Fe3+ is not soluble During times when O2 is present, iron will preferentially be in the Fe3+ state, which will not dissolve in water, not be transported by the oceans large distances, and therefore not end up in sediments. So, at times when the sediments have iron (the iron ...
... Fe2+ is soluble in water Fe3+ is not soluble During times when O2 is present, iron will preferentially be in the Fe3+ state, which will not dissolve in water, not be transported by the oceans large distances, and therefore not end up in sediments. So, at times when the sediments have iron (the iron ...
FINAL REVIEW
... 13. Determine the percent composition for Na2CO3 43.38% Na 11.33% C 45.285% O 14. What is the percent composition for a compound that contains 1.30 g of aluminum and 1.15 g of oxygen? 53.1% Al 46.9% O 15. An unknown compound is analyzed and found to contain 40.0% carbon, 6.67 % hydrogen, and 53.3% o ...
... 13. Determine the percent composition for Na2CO3 43.38% Na 11.33% C 45.285% O 14. What is the percent composition for a compound that contains 1.30 g of aluminum and 1.15 g of oxygen? 53.1% Al 46.9% O 15. An unknown compound is analyzed and found to contain 40.0% carbon, 6.67 % hydrogen, and 53.3% o ...
Elements Elements (cont.) Elements (cont.)
... • Cations: ions that have a positive charge – Form when an atom loses electrons ...
... • Cations: ions that have a positive charge – Form when an atom loses electrons ...
Halogens - Cronodon
... The chlorine has displaced the bromide because chlorine is a stronger oxidising agent than bromine (equivalently bromide is a stronger reducing agent than chloride). The oxidising power of the halogens decreases in the order: F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 (oxidising strength) Q.16. When a halogen oxidises ano ...
... The chlorine has displaced the bromide because chlorine is a stronger oxidising agent than bromine (equivalently bromide is a stronger reducing agent than chloride). The oxidising power of the halogens decreases in the order: F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 (oxidising strength) Q.16. When a halogen oxidises ano ...
What are atoms? Notes - Riverdale Middle School
... What refers to an area around an atomic nucleus where an electron is most likely to be? Electron cloud Most of the atom is empty space. The nucleus in the center of the atom has most of the mass. ...
... What refers to an area around an atomic nucleus where an electron is most likely to be? Electron cloud Most of the atom is empty space. The nucleus in the center of the atom has most of the mass. ...
Introduction(s)
... periodic table in terms of number of valence electrons, number of shells(main energy levels) and net nuclear force(kernel charge). ...
... periodic table in terms of number of valence electrons, number of shells(main energy levels) and net nuclear force(kernel charge). ...
Memorization?
... periodic table in terms of number of valence electrons, number of shells(main energy levels) and net nuclear force(kernel charge). ...
... periodic table in terms of number of valence electrons, number of shells(main energy levels) and net nuclear force(kernel charge). ...
electron configuration
... Filling Patterns of Atomic Orbitals • Atomic Orbitals are filled from lowest energy to highest energy • Full/half full atomic orbitals – Adding electrons until all orbitals are full is a lower energy state (usually) – Paired electrons are higher energy than unpaired (Hund’s Rule) – Half full orbita ...
... Filling Patterns of Atomic Orbitals • Atomic Orbitals are filled from lowest energy to highest energy • Full/half full atomic orbitals – Adding electrons until all orbitals are full is a lower energy state (usually) – Paired electrons are higher energy than unpaired (Hund’s Rule) – Half full orbita ...
Chem Bonding Notes
... 4. What occurs when an atom of chlorine and an atom of hydrogen become a molecule of hydrogen chloride? (1) A chemical bond is broken and energy is released. (2) A chemical bond is broken and energy is absorbed. (3) A chemical bond is formed and energy is released. (4) A chemical bond is formed and ...
... 4. What occurs when an atom of chlorine and an atom of hydrogen become a molecule of hydrogen chloride? (1) A chemical bond is broken and energy is released. (2) A chemical bond is broken and energy is absorbed. (3) A chemical bond is formed and energy is released. (4) A chemical bond is formed and ...
Chemical Reactions - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 2. Balance and read the following equations: a. b. c. d. ...
... 2. Balance and read the following equations: a. b. c. d. ...
Practice Test 2
... What volume (in liters) of hydrogen gas at STP is released by mixing 5.34 g of iron with 5.00 mL of 1.250 M HCl? (15 pts) ...
... What volume (in liters) of hydrogen gas at STP is released by mixing 5.34 g of iron with 5.00 mL of 1.250 M HCl? (15 pts) ...
File
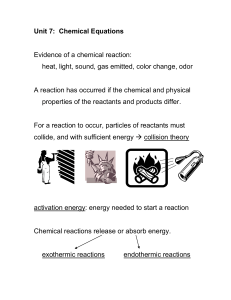
... The properties of a compound are unique and differ from the elements that make up the compound. A chemical equation is a written representation of the process that occurs in a chemical reaction. A chemical equation is written with the reactants on the left side of an arrow (yield symbol) and the pro ...
... The properties of a compound are unique and differ from the elements that make up the compound. A chemical equation is a written representation of the process that occurs in a chemical reaction. A chemical equation is written with the reactants on the left side of an arrow (yield symbol) and the pro ...
L1 – CHEMISTRY FINAL REVIEW
... 2 Na3PO4 + 3 Li2SO3 3 Na2SO3 + 2 Li3PO4 f. nitric acid + copper (II) Hydrogen ( ) + Copper II nitrate (single replacement) *according to our rules, this would not work but in nitric acid is very strong so it does work. No worries, exam will not have exceptions 2 HNO3 + Cu H2 + Cu(NO3)2 g. deco ...
... 2 Na3PO4 + 3 Li2SO3 3 Na2SO3 + 2 Li3PO4 f. nitric acid + copper (II) Hydrogen ( ) + Copper II nitrate (single replacement) *according to our rules, this would not work but in nitric acid is very strong so it does work. No worries, exam will not have exceptions 2 HNO3 + Cu H2 + Cu(NO3)2 g. deco ...
chapter-2 - HCC Learning Web
... • The periodic table of the elements shows the electron distribution for each element ...
... • The periodic table of the elements shows the electron distribution for each element ...
Chapter 7. CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... When solutions are involved in a reaction, only some of the ions present are usually involved. Other ions may be present, but they are still in the solution at the end of the reaction, unchanged by the chemical process. These ions are called spectator ions and are best left out of the balanced equat ...
... When solutions are involved in a reaction, only some of the ions present are usually involved. Other ions may be present, but they are still in the solution at the end of the reaction, unchanged by the chemical process. These ions are called spectator ions and are best left out of the balanced equat ...
NAME UNIT 7: NOTES: REDOX (PART 1): OXIDATION #`S, An
... For instance, the sodium ion of NaCl is given an oxidation state of +1, compared to the original Na0. This +1 value indicates that 1 electron was involved in the bonding process to the Cl, (that's the "1") and that the electron has been lost (that's the "+") to the chloride. Thus, that simple symbol ...
... For instance, the sodium ion of NaCl is given an oxidation state of +1, compared to the original Na0. This +1 value indicates that 1 electron was involved in the bonding process to the Cl, (that's the "1") and that the electron has been lost (that's the "+") to the chloride. Thus, that simple symbol ...
Topic 4: Classifying Elements What did the early chemists use to
... We usually refer to compounds containing HYDROGEN by their COMMON name. All compounds containing hydrogen are MOLECULAR compounds. How do we indicate the physical state of a compound? (something is writte ...
... We usually refer to compounds containing HYDROGEN by their COMMON name. All compounds containing hydrogen are MOLECULAR compounds. How do we indicate the physical state of a compound? (something is writte ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... Ex: Bubbles of CO2 form when baking soda and vinegar are mixed ...
... Ex: Bubbles of CO2 form when baking soda and vinegar are mixed ...
chemeqohnotes18f2005
... Examples: enzymes catalyze biochemical reactions catalytic converters convert CO into CO2 ...
... Examples: enzymes catalyze biochemical reactions catalytic converters convert CO into CO2 ...
File - IGCSE STUDY BANK
... The phrase ‘rate of reaction’ means ‘how fast is the reaction’. It can be measured as the 'rate of formation of product' or the 'rate of disappearance of reactant'. o Rusting is a ‘slow’ reaction, you hardly see any change looking at it!, o weathering of rocks is a very slow reaction, o fermentation ...
... The phrase ‘rate of reaction’ means ‘how fast is the reaction’. It can be measured as the 'rate of formation of product' or the 'rate of disappearance of reactant'. o Rusting is a ‘slow’ reaction, you hardly see any change looking at it!, o weathering of rocks is a very slow reaction, o fermentation ...
Redox

Redox reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed; in general, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species. The term ""redox"" comes from two concepts involved with electron transfer: reduction and oxidation. It can be explained in simple terms: Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, these are only specific examples of a more general concept of reactions involving electron transfer.Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, have a number of similarities to acid–base reactions. Like acid–base reactions, redox reactions are a matched set, that is, there cannot be an oxidation reaction without a reduction reaction happening simultaneously. The oxidation alone and the reduction alone are each called a half-reaction, because two half-reactions always occur together to form a whole reaction. When writing half-reactions, the gained or lost electrons are typically included explicitly in order that the half-reaction be balanced with respect to electric charge.Though sufficient for many purposes, these descriptions are not precisely correct. Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation state — the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. The oxidation state of an atom is the fictitious charge that an atom would have if all bonds between atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation state, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation state. In practice, the transfer of electrons will always cause a change in oxidation state, but there are many reactions that are classed as ""redox"" even though no electron transfer occurs (such as those involving covalent bonds).There are simple redox processes, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide (CO2) or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), and more complex processes such as the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) in the human body through a series of complex electron transfer processes.