4. Minerals: rock`s elementary building block 4.1. What is a mineral
... Another class of minerals comprises the carbonates. The most common carbonate mineral is CaCO3 already mentioned above in relation with biological mineralization. The basic structural unit of carbonates is the carbonate anion (CO3)2-. In carbonate minerals, carbonate anions are arranged in sheets a ...
... Another class of minerals comprises the carbonates. The most common carbonate mineral is CaCO3 already mentioned above in relation with biological mineralization. The basic structural unit of carbonates is the carbonate anion (CO3)2-. In carbonate minerals, carbonate anions are arranged in sheets a ...
High-energy x-ray production with pyroelectric crystals
... charges causes a masking charge to rapidly form on the polarized surfaces, preventing the change in the polarization from reaching levels useful for x-ray production. In a vacuum, however, the result of heating a pyroelectric crystal can be the ejection of electrons from the crystal surface2 and the ...
... charges causes a masking charge to rapidly form on the polarized surfaces, preventing the change in the polarization from reaching levels useful for x-ray production. In a vacuum, however, the result of heating a pyroelectric crystal can be the ejection of electrons from the crystal surface2 and the ...
Ultrapure, high mobility organic photoconductors
... program designed to obtain reliable experimental data over wide temperature ranges on charge-cartier transport in organic photoconductors. Naphthalene and perylene were selected, among others, to serve as model substances. Naphthalene is one of the most simple aromatic molecules; very extensive inve ...
... program designed to obtain reliable experimental data over wide temperature ranges on charge-cartier transport in organic photoconductors. Naphthalene and perylene were selected, among others, to serve as model substances. Naphthalene is one of the most simple aromatic molecules; very extensive inve ...
Uric acid sodium salt (U2875) - Product Information - Sigma
... 4. Grover, P. K., et al., Dissolved urate salts out calcium oxalate in undiluted human urine in vitro. Implications for calcium oxalate stone genesis. ...
... 4. Grover, P. K., et al., Dissolved urate salts out calcium oxalate in undiluted human urine in vitro. Implications for calcium oxalate stone genesis. ...
Materials Separation from Waste Liquid Crystal Displays Using
... (Br), and chlorine (Cl), etc., which are potentially harmful to the ecosystem and human health. From the above description, it can be noted that waste LCD is important not only in terms of its quantity but also its toxicity. Many of the materials contained in waste LCDs are highly toxic. If not trea ...
... (Br), and chlorine (Cl), etc., which are potentially harmful to the ecosystem and human health. From the above description, it can be noted that waste LCD is important not only in terms of its quantity but also its toxicity. Many of the materials contained in waste LCDs are highly toxic. If not trea ...
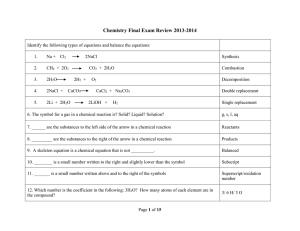
Solution FRQs Practice
... 2003 D Required For each of the following, use appropriate chemical principles to explain the observations. Include chemical equations as appropriate. (a) In areas affected by acid rain, statues and structures made of limestone (calcium carbonate) often show signs of considerable deterioration. (b) ...
... 2003 D Required For each of the following, use appropriate chemical principles to explain the observations. Include chemical equations as appropriate. (a) In areas affected by acid rain, statues and structures made of limestone (calcium carbonate) often show signs of considerable deterioration. (b) ...
Type Of Chemical Reaction
... A strong base is typically a pH of what number? _____14_____ The ion that accounts for Acidity is: _____H+_or H3O+____ The ion that accounts for Basic is: ____OH-____ ...
... A strong base is typically a pH of what number? _____14_____ The ion that accounts for Acidity is: _____H+_or H3O+____ The ion that accounts for Basic is: ____OH-____ ...
1
... hydrogen, instead) did not demonstrate neutron emission above the background level during transition through its particular Curie point (Tc =123 K due to isotopic effect.). In contrast to [1], in the prior experiments [4,5] a deuterium atmosphere was not used because the host-deuterium in ionic form ...
... hydrogen, instead) did not demonstrate neutron emission above the background level during transition through its particular Curie point (Tc =123 K due to isotopic effect.). In contrast to [1], in the prior experiments [4,5] a deuterium atmosphere was not used because the host-deuterium in ionic form ...
CHAPTER 6: Earth science
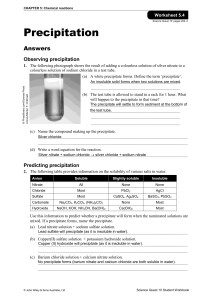
... 1. The following photograph shows the result of adding a colourless solution of silver nitrate to a colourless solution of sodium chloride in a test tube. (a) A white precipitate forms. Define the term ‘precipitate’. An insoluble solid forms when two solutions are mixed. ...
... 1. The following photograph shows the result of adding a colourless solution of silver nitrate to a colourless solution of sodium chloride in a test tube. (a) A white precipitate forms. Define the term ‘precipitate’. An insoluble solid forms when two solutions are mixed. ...
EKSIKA JOINT EVALUATION TEST. Kenya Certificate
... i)Ionic radius of element E is bigger than its atomic radius. Explain (2mks) ...
... i)Ionic radius of element E is bigger than its atomic radius. Explain (2mks) ...
國立嘉義大學九十二學年度
... (E) 0.316 kg/L 4.Which statement is false? (A) The average kinetic energies of molecules from samples of different "ideal" gases is the same at the same temperature. (B) The molecules of an ideal gas are relatively far apart. (C) All molecules of an ideal gas have the same kinetic energy at constant ...
... (E) 0.316 kg/L 4.Which statement is false? (A) The average kinetic energies of molecules from samples of different "ideal" gases is the same at the same temperature. (B) The molecules of an ideal gas are relatively far apart. (C) All molecules of an ideal gas have the same kinetic energy at constant ...
File
... General properties of aqueous solutions Precipitation reactions Oxidation-reduction reactions Concentration of solutions ...
... General properties of aqueous solutions Precipitation reactions Oxidation-reduction reactions Concentration of solutions ...
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY LECTURE NOTES
... When a metal electrode is dipped in a solution, if the rate of formation of ions is equal to the rate of their discharge, the electrode is said to be in equilibrium. The potential acquired by the electrode under such a condition is called the reversible or equilibrium potential. Polarisation: Wh ...
... When a metal electrode is dipped in a solution, if the rate of formation of ions is equal to the rate of their discharge, the electrode is said to be in equilibrium. The potential acquired by the electrode under such a condition is called the reversible or equilibrium potential. Polarisation: Wh ...
Physical properties
... • Distillation is used to purify a compound by separating it from a non-volatile or less-volatile material. When different compounds in a mixture have different boiling points, they separate into individual components when the mixture is carefully distilled. • Distillation is the process of heating ...
... • Distillation is used to purify a compound by separating it from a non-volatile or less-volatile material. When different compounds in a mixture have different boiling points, they separate into individual components when the mixture is carefully distilled. • Distillation is the process of heating ...
Ch.1 Section 1.9 Notes - Effingham County Schools
... Mixtures can be separated into pure substances by physical methods. 1. Distillation: a process that depends on the differences in the volatility (how readily substances become gases) of the components. In simple distillation, a mixture is heated in a device and the most volatile component vaporizes ...
... Mixtures can be separated into pure substances by physical methods. 1. Distillation: a process that depends on the differences in the volatility (how readily substances become gases) of the components. In simple distillation, a mixture is heated in a device and the most volatile component vaporizes ...
Purification and - Jena Bioscience
... obvious advantages, such as rapid growth, well developed methods of protein expression and cheapness of cultivation, E. coli has a range of shortcomings that limit its utility in protein studies. The most prominent problem relates to the inefficiency of E. coli in assisting the folding of eukaryotic ...
... obvious advantages, such as rapid growth, well developed methods of protein expression and cheapness of cultivation, E. coli has a range of shortcomings that limit its utility in protein studies. The most prominent problem relates to the inefficiency of E. coli in assisting the folding of eukaryotic ...
CST REVIEW Percent Error 1. 2. What is the formula for density?
... 34. List the following in order of increasing electronegativity: K, Br, Ca, As 35. Atoms and molecules in liquids move in a random pattern relative to one another because the intermolecular forces are too weak to hold the atoms or molecules in a solid form. Under the same conditions of pressure and ...
... 34. List the following in order of increasing electronegativity: K, Br, Ca, As 35. Atoms and molecules in liquids move in a random pattern relative to one another because the intermolecular forces are too weak to hold the atoms or molecules in a solid form. Under the same conditions of pressure and ...
1 • Welcome to the GIA Junior Gemologist Program
... • Some magma may feed volcanoes on the Earth's surface, but most remains trapped below, where it cools very slowly over thousands or millions of years until it solidifies (hardens) • When magma cools and hardens slowly, the individual minerals in it form large grains (or crystals) that are easy to s ...
... • Some magma may feed volcanoes on the Earth's surface, but most remains trapped below, where it cools very slowly over thousands or millions of years until it solidifies (hardens) • When magma cools and hardens slowly, the individual minerals in it form large grains (or crystals) that are easy to s ...
Chapter 1 Theory and principles of the solid
... well as differences in intermolecular distances. Ultimately these differences will lead to different phases with different energy levels (Cui, 2007). The solid phase is the most common phase within the pharmaceutical industry. It is a well-known fact that the solid phase can present in a multitude o ...
... well as differences in intermolecular distances. Ultimately these differences will lead to different phases with different energy levels (Cui, 2007). The solid phase is the most common phase within the pharmaceutical industry. It is a well-known fact that the solid phase can present in a multitude o ...
The atomic packing factor
... The atomic packing factor [A.P.F]: It can be defined as the ratio between the volume of the basic atoms of the unit cell (which represent the volume of all atoms in one unit cell ) to the volume of the unit cell it self. For cubic crystals, A.P. F its depends on the riadus of atoms and characrtiziat ...
... The atomic packing factor [A.P.F]: It can be defined as the ratio between the volume of the basic atoms of the unit cell (which represent the volume of all atoms in one unit cell ) to the volume of the unit cell it self. For cubic crystals, A.P. F its depends on the riadus of atoms and characrtiziat ...
Liquid crystal display.pdf
... Viewable size: The size of an LCD panel measured on the diagonal (more specifically known as active display area). Response time: The minimum time necessary to change a pixel's color or brightness. Response time is also divided into rise and fall time. For LCD Monitors, this is measured in btb (blac ...
... Viewable size: The size of an LCD panel measured on the diagonal (more specifically known as active display area). Response time: The minimum time necessary to change a pixel's color or brightness. Response time is also divided into rise and fall time. For LCD Monitors, this is measured in btb (blac ...
Crystallization

Crystallization is the (natural or artificial) process of formation of solid crystals precipitating from a solution, melt or more rarely deposited directly from a gas. Crystallization is also a chemical solid–liquid separation technique, in which mass transfer of a solute from the liquid solution to a pure solid crystalline phase occurs. In chemical engineering crystallization occurs in a crystallizer. Crystallization is therefore an aspect of precipitation, obtained through a variation of the solubility conditions of the solute in the solvent, as compared to precipitation due to chemical reaction.