Equilibrium - chemmybear.com
... (c) CO will decrease. A decrease in volume will result in an increase in pressure, the equilibrium will shift to the side with fewer gas molecules to decrease the pressure, , a shift to the left. (d) CO will remain the same. Once at equilibrium, the size of the solid will affect neither the reactio ...
... (c) CO will decrease. A decrease in volume will result in an increase in pressure, the equilibrium will shift to the side with fewer gas molecules to decrease the pressure, , a shift to the left. (d) CO will remain the same. Once at equilibrium, the size of the solid will affect neither the reactio ...
Chemistry Skills Practice Assignments
... 2. For which substance, A or B, does the freezing point decrease as the pressure is increased? 3. One of the substances behaves more like most other substances. Which substance and what property allows you to tell? 4. Assuming that the temperature scales for both phase diagrams are the same, which c ...
... 2. For which substance, A or B, does the freezing point decrease as the pressure is increased? 3. One of the substances behaves more like most other substances. Which substance and what property allows you to tell? 4. Assuming that the temperature scales for both phase diagrams are the same, which c ...
apch04 test review_ans
... blue dye in a solution. Our calorimeters have three options for wavelengths: Red - 620 nm, Green - 550 nm, Blue - 470 nm. Based on the absorption spectrum for the three dyes in the figure below, which settings is the best setting for a lab measuring the concentration of each? Absorbance measurements ...
... blue dye in a solution. Our calorimeters have three options for wavelengths: Red - 620 nm, Green - 550 nm, Blue - 470 nm. Based on the absorption spectrum for the three dyes in the figure below, which settings is the best setting for a lab measuring the concentration of each? Absorbance measurements ...
lecture slides file
... The physical state in which the matter exists depends on the nature of the matter (i.e. attractive forces in the atoms or molecules of the matter), and external factors (pressure, temperature). Physical transformations: (solid – liquid) freezing / melting, liquid-gas: vaporization / condensation, an ...
... The physical state in which the matter exists depends on the nature of the matter (i.e. attractive forces in the atoms or molecules of the matter), and external factors (pressure, temperature). Physical transformations: (solid – liquid) freezing / melting, liquid-gas: vaporization / condensation, an ...
the chemical and physical properties of condensed
... phosphate of 35 phosphorus atoms is very similar to a phosphate of 36 phosphorus atoms, etc. The low molecular weight polyphosphates and the very high molecular weight polyphosphates can be easily crystallized as the alkali metal salts, but the polyphosphates with a large diversity of properties in ...
... phosphate of 35 phosphorus atoms is very similar to a phosphate of 36 phosphorus atoms, etc. The low molecular weight polyphosphates and the very high molecular weight polyphosphates can be easily crystallized as the alkali metal salts, but the polyphosphates with a large diversity of properties in ...
Review Unit 8 Test (Chp 15,17)
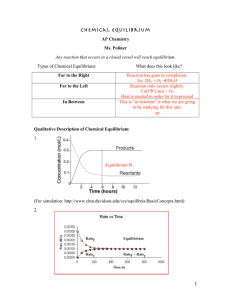
... increases until it becomes the same as the reverse reaction rate at equilibrium. stays constant before and after equilibrium is reached. A is half true, but “decreases”, decreases to become a constant nonzero rate at equilibrium. not “increases.” decreases to become zero at equilibrium. Greater pres ...
... increases until it becomes the same as the reverse reaction rate at equilibrium. stays constant before and after equilibrium is reached. A is half true, but “decreases”, decreases to become a constant nonzero rate at equilibrium. not “increases.” decreases to become zero at equilibrium. Greater pres ...
- Kendriya Vidyalaya NKJ Katni
... 11. The rate for a reaction between the substance A and B is given by Rate= k[A]n [B]m On doubling the conc. of A and halving the conc. of B, find out the ratio of new rate to that of earlier rate of reaction . ...
... 11. The rate for a reaction between the substance A and B is given by Rate= k[A]n [B]m On doubling the conc. of A and halving the conc. of B, find out the ratio of new rate to that of earlier rate of reaction . ...
Biological X-ray absorption spectroscopy (BioXAS): a valuable tool
... Current Opinion in Structural Biology 2008, 18:1–8 This review comes from a themed issue on ...
... Current Opinion in Structural Biology 2008, 18:1–8 This review comes from a themed issue on ...
SOLUBILITY RULES FOR IONIC COMPOUNDS IN WATER
... 2. Ammonia decomposes according to the reaction: 2NH3 (g) ⇆ N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) A 2.00 liter tank is originally charged with 0.500 moles of ammonia, and at equilibrium it is found that the ammonia is 16.5% decomposed. Calculate the numerical value of the Kc for the above reaction. 3. A tank of O2 has a ...
... 2. Ammonia decomposes according to the reaction: 2NH3 (g) ⇆ N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) A 2.00 liter tank is originally charged with 0.500 moles of ammonia, and at equilibrium it is found that the ammonia is 16.5% decomposed. Calculate the numerical value of the Kc for the above reaction. 3. A tank of O2 has a ...
entropy - KFUPM Faculty List
... The second law of thermodynamics says that for a process to be spontaneous as written (in the for- ward direction), Suniv must be positive. An equilibrium process is one that does not occur spontaneously in either the net forward or net reverse direction but can be made to occur by the addition or ...
... The second law of thermodynamics says that for a process to be spontaneous as written (in the for- ward direction), Suniv must be positive. An equilibrium process is one that does not occur spontaneously in either the net forward or net reverse direction but can be made to occur by the addition or ...
F: Chapter 1: Minerals - Jenkins Independent Schools
... dimensions in their crystal structure. Only one right angle forms where crystal surfaces meet. The other angles are oblique, which means they don’t form 90º angles where they intersect. ...
... dimensions in their crystal structure. Only one right angle forms where crystal surfaces meet. The other angles are oblique, which means they don’t form 90º angles where they intersect. ...
Chemical Equilibrium - Department of Chemistry
... If we increase the total pressure at constant volume by adding an inert gas or another gas not involved in the equilibrium, the partial pressure of each species in the equilibrium will not change…therefore the reaction quotient will not change. The system will not respond to changes in total pressur ...
... If we increase the total pressure at constant volume by adding an inert gas or another gas not involved in the equilibrium, the partial pressure of each species in the equilibrium will not change…therefore the reaction quotient will not change. The system will not respond to changes in total pressur ...
Cryo-trapping the Six-coordinate, Distorted
... OH2 (Figure 2(c)). Residue Glu170 (not shown) of one monomer stretches across the dimer interface, forms a hydrogen bond with His171 of the other monomer, and thereby links the two active sites. ...
... OH2 (Figure 2(c)). Residue Glu170 (not shown) of one monomer stretches across the dimer interface, forms a hydrogen bond with His171 of the other monomer, and thereby links the two active sites. ...
Ch. 9 Minerals - Muskegon Area ISD
... • A. Isoloated tetrahedral silicates and ring silicates • B. Single-chain silicates, double-chain silicates, sheet silicates, and framework silicates ...
... • A. Isoloated tetrahedral silicates and ring silicates • B. Single-chain silicates, double-chain silicates, sheet silicates, and framework silicates ...
Chemical Equilibrium - Chemistry with Mrs. Caruso Let the Bonding
... Ex. A solution contains 1.0 x 10-4 M Cu+ and 2.0 x 10-3 M Pb2+. If a source of I- is added to this solution gradually, will PbI2 (Ksp= 1.4 x 10-8) or CuI (Ksp= 5.3x 10-12) precipitate first? What concentrations of I- are necessary to begin precipitation? PbI2 2Cl- + Pb2+ 1.4 x 10-8 = (2.0 x 10-3) ...
... Ex. A solution contains 1.0 x 10-4 M Cu+ and 2.0 x 10-3 M Pb2+. If a source of I- is added to this solution gradually, will PbI2 (Ksp= 1.4 x 10-8) or CuI (Ksp= 5.3x 10-12) precipitate first? What concentrations of I- are necessary to begin precipitation? PbI2 2Cl- + Pb2+ 1.4 x 10-8 = (2.0 x 10-3) ...
Interdiffusion in the systems (Nickel(X)-Oxide) - (Cobalt(X)
... motion of k diffusing species, and which is not restricted to a single diffusional coordinate, is given by ...
... motion of k diffusing species, and which is not restricted to a single diffusional coordinate, is given by ...
CHEMISTRY
... A mixture of substances is considered homogeneous if the mixture has the same physical and chemical properties throughout it. A homogeneous mixture is also called a solution. An element is a substance that contains only one kind of atom. A compound is a substance with two or more kinds of atoms comb ...
... A mixture of substances is considered homogeneous if the mixture has the same physical and chemical properties throughout it. A homogeneous mixture is also called a solution. An element is a substance that contains only one kind of atom. A compound is a substance with two or more kinds of atoms comb ...
Crystal Structures, Thermal Analysis, and
... particularly insoluble in water. It is known that in order to maintain the concentration of active substance in the blood above the therapeutic threshold, arbidol should be taken by one dose every 3–4 h for several days, including night time, which makes effective treatment more difficult [19]. Ther ...
... particularly insoluble in water. It is known that in order to maintain the concentration of active substance in the blood above the therapeutic threshold, arbidol should be taken by one dose every 3–4 h for several days, including night time, which makes effective treatment more difficult [19]. Ther ...
Crystalline Solids: Diffraction
... nineteenth century, the systematic study of the external shapes of such natural crystals led scientists to conclude that this regularity of the outer faces must be due to structural regularities on the microscopic scale. The molecules or atoms had to be assembled in a periodic manner to make a cryst ...
... nineteenth century, the systematic study of the external shapes of such natural crystals led scientists to conclude that this regularity of the outer faces must be due to structural regularities on the microscopic scale. The molecules or atoms had to be assembled in a periodic manner to make a cryst ...
Manual Physical Chemistry III
... Experimental 1: Determination of Surface Tension of Liquids by drop weight Method ............................................ 2 Experimental 2: Determination of Surface Tension Liquids by Capillary Rise Method ............................................... 8 Experimental 3: To find out the partiti ...
... Experimental 1: Determination of Surface Tension of Liquids by drop weight Method ............................................ 2 Experimental 2: Determination of Surface Tension Liquids by Capillary Rise Method ............................................... 8 Experimental 3: To find out the partiti ...
EMISSION, KINETIC AND MAGNETIC PHENOMENA IN
... potential, for the deep donors or acceptors energy levels are defined by the core’s short range potential. Usually shallow impurity levels differ less than hundred meV from the allowed band edges, while deep levels are placed closer to the middle of the bandgap. Thus, semiconductor is a material wit ...
... potential, for the deep donors or acceptors energy levels are defined by the core’s short range potential. Usually shallow impurity levels differ less than hundred meV from the allowed band edges, while deep levels are placed closer to the middle of the bandgap. Thus, semiconductor is a material wit ...
mole concept type 1 - teko classes bhopal
... which gasesous reactants are reacting and products are formed at same temperature and pressure. The volume of gases produced is often given by mentioning certain solvent which absorb contain gases. Solvent gas (es) absorb KOH CO2, SO2, Cl2 Ammon Cu2Cl2 CO Turpentine oil O3 Alkaline pyrogallol O2 wat ...
... which gasesous reactants are reacting and products are formed at same temperature and pressure. The volume of gases produced is often given by mentioning certain solvent which absorb contain gases. Solvent gas (es) absorb KOH CO2, SO2, Cl2 Ammon Cu2Cl2 CO Turpentine oil O3 Alkaline pyrogallol O2 wat ...
AP® Chemistry
... Many students wonder whether or not to guess the answers to the multiple-choice questions about which they are not certain. It is improbable that mere guessing will improve a score. However, if a student has some knowledge of the question and is able to eliminate one or more answer choices as wrong, ...
... Many students wonder whether or not to guess the answers to the multiple-choice questions about which they are not certain. It is improbable that mere guessing will improve a score. However, if a student has some knowledge of the question and is able to eliminate one or more answer choices as wrong, ...
AP® Chemistry
... Many students wonder whether or not to guess the answers to the multiple-choice questions about which they are not certain. It is improbable that mere guessing will improve a score. However, if a student has some knowledge of the question and is able to eliminate one or more answer choices as wrong, ...
... Many students wonder whether or not to guess the answers to the multiple-choice questions about which they are not certain. It is improbable that mere guessing will improve a score. However, if a student has some knowledge of the question and is able to eliminate one or more answer choices as wrong, ...
A flask contains 0
... If you have time after you did the starred () questions, go to the circle questions and look at them again…maybe a second time through will jog your memory. REMEMBER every time you turn the page…make sure that you have bubbled the correct number on the answer. This way if you get off track on b ...
... If you have time after you did the starred () questions, go to the circle questions and look at them again…maybe a second time through will jog your memory. REMEMBER every time you turn the page…make sure that you have bubbled the correct number on the answer. This way if you get off track on b ...
Crystallization

Crystallization is the (natural or artificial) process of formation of solid crystals precipitating from a solution, melt or more rarely deposited directly from a gas. Crystallization is also a chemical solid–liquid separation technique, in which mass transfer of a solute from the liquid solution to a pure solid crystalline phase occurs. In chemical engineering crystallization occurs in a crystallizer. Crystallization is therefore an aspect of precipitation, obtained through a variation of the solubility conditions of the solute in the solvent, as compared to precipitation due to chemical reaction.