... Due to the continuously increasing high energy demands of society and the finite nature of fossil fuels, alternative energy sources are becoming exceedingly important. Hydrogen is a promising alternative fuel because of its clean, renewable and high energy content of 122 kJ g – 1 which is 2.75 times ...
Stable nitrogen isotopic fractionation associated with transamination
... metabolism during transamination or deamination in heterotrophic animals. However, few studies have investigated the isotopic fractionation factor (α) in this process, even though knowledge of this factor is critical in quantitatively evaluating the flux of amino acid metabolism in animals. In this ...
... metabolism during transamination or deamination in heterotrophic animals. However, few studies have investigated the isotopic fractionation factor (α) in this process, even though knowledge of this factor is critical in quantitatively evaluating the flux of amino acid metabolism in animals. In this ...
Chapter 3: The Chemical Basis for Life Lesson 2: Organic Compounds
... Types of carbon compounds in organisms include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. The elements found in each type are listed in the table below. Elements other than carbon and hydrogen usually occur within organic compounds in smaller groups of elements called functional groups. Whe ...
... Types of carbon compounds in organisms include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. The elements found in each type are listed in the table below. Elements other than carbon and hydrogen usually occur within organic compounds in smaller groups of elements called functional groups. Whe ...
Unit 3 - Salina USD 305
... a reaction card. Complete the Find Someone Who Activity in your notebooklet on p. 11 by finding students who match up with the different reaction ...
... a reaction card. Complete the Find Someone Who Activity in your notebooklet on p. 11 by finding students who match up with the different reaction ...
Metabolism: An Overview
... Basic concepts and principles governing all of metabolism need to be discussed, before we venture forth into the study of specific metabolic pathways. First some definitions: METABOLISM is the sum total of all of the chemical reactions that occur within a living cell. Depending upon the cell type, t ...
... Basic concepts and principles governing all of metabolism need to be discussed, before we venture forth into the study of specific metabolic pathways. First some definitions: METABOLISM is the sum total of all of the chemical reactions that occur within a living cell. Depending upon the cell type, t ...
Here
... Write the balanced equation for glucose reacting with oxygen. (Respiration) Calculate the mass of water produced. ...
... Write the balanced equation for glucose reacting with oxygen. (Respiration) Calculate the mass of water produced. ...
9.1-10.5 Organic Chemistry
... Remember Lewis Dot Diagrams from Chem 20?? This means carbon can bond extensively and can bond together to form chains effectively = called Polymerism Carbon covalently bonds by sharing 4 pairs of electrons. These bonds may be single, double or triple, all producing stable compounds Compound ...
... Remember Lewis Dot Diagrams from Chem 20?? This means carbon can bond extensively and can bond together to form chains effectively = called Polymerism Carbon covalently bonds by sharing 4 pairs of electrons. These bonds may be single, double or triple, all producing stable compounds Compound ...
Chemistry
... - Microscopic interpretation in terms of atoms CO2 – 1 C and 2 O - Macroscopic interpretation in terms of moles - CO2 – 1 mol of C (6.02e23 carbon atoms) and - 2 moles of O or 2 x (6.02e23 oxygen atoms) or 1.20e24 oxygen atoms - An empirical formula may or may not be the same as the molecular formul ...
... - Microscopic interpretation in terms of atoms CO2 – 1 C and 2 O - Macroscopic interpretation in terms of moles - CO2 – 1 mol of C (6.02e23 carbon atoms) and - 2 moles of O or 2 x (6.02e23 oxygen atoms) or 1.20e24 oxygen atoms - An empirical formula may or may not be the same as the molecular formul ...
1 - PetyaPisanScienceAQ
... 2) What is the test for the presence of carbon dioxide? Why does it work? (1 K/U, 1 I) Baking soda consists of the chemical compound sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3). Compounds containing carbonate (CO3) react with acids such as vinegar (acetic acid) to produce carbon dioxide gas (CO2). The equation for ...
... 2) What is the test for the presence of carbon dioxide? Why does it work? (1 K/U, 1 I) Baking soda consists of the chemical compound sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3). Compounds containing carbonate (CO3) react with acids such as vinegar (acetic acid) to produce carbon dioxide gas (CO2). The equation for ...
Chapter 2 3EPchanges
... completing the comparison chart of the 4 organic molecules (given by the teacher). ...
... completing the comparison chart of the 4 organic molecules (given by the teacher). ...
Bose-Einstein Condensation in Cold Atoms: a New State of Matter
... matter waves - at ultracold temperatures and atomic scales, quantum mechanics dominates physical phenomena. Bose-Einstein condensation actually serves as an example of having the capacity to observe quantum mechanics and wave-particle duality on a macroscopic scale. The theoretical condition for Bos ...
... matter waves - at ultracold temperatures and atomic scales, quantum mechanics dominates physical phenomena. Bose-Einstein condensation actually serves as an example of having the capacity to observe quantum mechanics and wave-particle duality on a macroscopic scale. The theoretical condition for Bos ...
Camp 1 - drjosephryan.com Home Page
... But while it tells us what the reactants and products are and the physical state of each, it is incomplete because it is not balanced ...
... But while it tells us what the reactants and products are and the physical state of each, it is incomplete because it is not balanced ...
CLASS X carbon and its compound
... called branched chain hydrocarbons. 13. Isomerism : The phenomenon due to which there can exist two or more organic compounds, with different physical and chemical properties, due to the difference in arrangement of carbon atoms in their structure, but have same chemical formula is called isomerism. ...
... called branched chain hydrocarbons. 13. Isomerism : The phenomenon due to which there can exist two or more organic compounds, with different physical and chemical properties, due to the difference in arrangement of carbon atoms in their structure, but have same chemical formula is called isomerism. ...
CHAPTER 2 ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS Questions
... Law of definite proportion: A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by mass. For example, water is always 1 g H for every 8 g oxygen. Law of multiple proportions: When two elements form a series of compounds, the ratios of the mass of the second element that combine ...
... Law of definite proportion: A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by mass. For example, water is always 1 g H for every 8 g oxygen. Law of multiple proportions: When two elements form a series of compounds, the ratios of the mass of the second element that combine ...
CHAPTER 2 ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS Questions
... Law of definite proportion: A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by mass. For example, water is always 1 g H for every 8 g oxygen. Law of multiple proportions: When two elements form a series of compounds, the ratios of the mass of the second element that combine ...
... Law of definite proportion: A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by mass. For example, water is always 1 g H for every 8 g oxygen. Law of multiple proportions: When two elements form a series of compounds, the ratios of the mass of the second element that combine ...
FREE Sample Here - We can offer most test bank and
... d. When two molecules combine, they do so in definite proportions by weight e. When two different elements combine to form a mixture, they do so in definite proportions by weight Section 2.1 3. The relative number of atoms of each element in a particular compound a. b. c. * d. e. ...
... d. When two molecules combine, they do so in definite proportions by weight e. When two different elements combine to form a mixture, they do so in definite proportions by weight Section 2.1 3. The relative number of atoms of each element in a particular compound a. b. c. * d. e. ...
FREE Sample Here
... d. When two molecules combine, they do so in definite proportions by weight e. When two different elements combine to form a mixture, they do so in definite proportions by weight Section 2.1 3. The relative number of atoms of each element in a particular compound a. b. c. * d. e. ...
... d. When two molecules combine, they do so in definite proportions by weight e. When two different elements combine to form a mixture, they do so in definite proportions by weight Section 2.1 3. The relative number of atoms of each element in a particular compound a. b. c. * d. e. ...
NMR SPectroscopy
... As a result of this, the energy of these particles can only exist at discrete energies – we say these energy levels are quantized It is easy to understand if we visualize the “wave” property of matter as an oscillating string in a box—only certain “energy levels” can exist as the string is bound at ...
... As a result of this, the energy of these particles can only exist at discrete energies – we say these energy levels are quantized It is easy to understand if we visualize the “wave” property of matter as an oscillating string in a box—only certain “energy levels” can exist as the string is bound at ...
Chemistry Lesson Plans #07 - Chemical Reactions
... of Conservation of Mass? o In describing a chemical reaction you use statements such as Iron reacts with oxygen to produce iron(III) oxide which is called rust Or it could be written iron + oxygen iron(III) oxide • Note that the reactants are on the left of the arrow and the product is on the right ...
... of Conservation of Mass? o In describing a chemical reaction you use statements such as Iron reacts with oxygen to produce iron(III) oxide which is called rust Or it could be written iron + oxygen iron(III) oxide • Note that the reactants are on the left of the arrow and the product is on the right ...
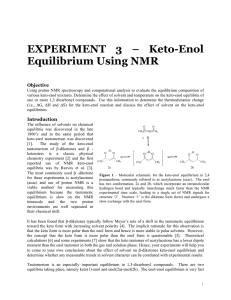
EXPERIMENT 3 – Keto-Enol Equilibrium Using NMR
... However, NMR can be used to provide much more detail than just the molecular structure of small organic and organometallic complexes. It can also be used for connectivity, spatial and dynamic information about a wide variety of materials. There are many books that describe the basics of NMR spectros ...
... However, NMR can be used to provide much more detail than just the molecular structure of small organic and organometallic complexes. It can also be used for connectivity, spatial and dynamic information about a wide variety of materials. There are many books that describe the basics of NMR spectros ...
Chapter One
... what it isn ' t. In 1921, a group from the American M useum of Natural History began excavations at an archaeological site on Dragon-Bone Hill, near the town of Chou-k'outien, 34 miles southwest of Beijing, China. Fos ils found at this site were assigned to a new species, Homo erectus pekinensis, co ...
... what it isn ' t. In 1921, a group from the American M useum of Natural History began excavations at an archaeological site on Dragon-Bone Hill, near the town of Chou-k'outien, 34 miles southwest of Beijing, China. Fos ils found at this site were assigned to a new species, Homo erectus pekinensis, co ...
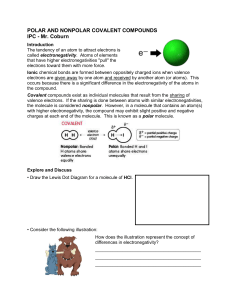
Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Compounds
... IPC - Mr. Coburn Introduction The tendency of an atom to attract electrons is called electronegativity. Atoms of elements that have higher electronegativities "pull" the electrons toward them with more force. Ionic chemical bonds are formed between oppositely charged ions when valence electrons are ...
... IPC - Mr. Coburn Introduction The tendency of an atom to attract electrons is called electronegativity. Atoms of elements that have higher electronegativities "pull" the electrons toward them with more force. Ionic chemical bonds are formed between oppositely charged ions when valence electrons are ...
... INTRODUCTION The major bottleneck in metabolite identification is data processing because it is still mainly a manual process. The biggest challenge for automated data processing is the large number of false positives which may be generated. A powerful tool to help for the removal of these false pos ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.