General and Organic Chemistry: Theory content HT 2016
... Chemical shift. Inductive and anisotropic effects. Magnetically and non-magnetically equivalent protons, how to count protons. Spin-spin coupling, splitting, chemical exchange. Practical interpretation of simple 1H-NMR spectra. 13C-NMR. Lecture: Oxidation, reduction. ...
... Chemical shift. Inductive and anisotropic effects. Magnetically and non-magnetically equivalent protons, how to count protons. Spin-spin coupling, splitting, chemical exchange. Practical interpretation of simple 1H-NMR spectra. 13C-NMR. Lecture: Oxidation, reduction. ...
chemical equation - HCC Learning Web
... Writing and Balancing the Equation for a Chemical Reaction 1. Determine what reaction is occurring. What are the reactants, the products, and the physical states involved? 2. Write the unbalanced equation that summarizes the reaction described in step 1. 3. Balance the equation by inspection, start ...
... Writing and Balancing the Equation for a Chemical Reaction 1. Determine what reaction is occurring. What are the reactants, the products, and the physical states involved? 2. Write the unbalanced equation that summarizes the reaction described in step 1. 3. Balance the equation by inspection, start ...
first test
... 16. Ammonia reacts with diatomic oxygen to form nitric oxide and water vapor: 4NH3 + 5O2 4NO + 6H2O When 40.0 g NH3 and 50.0 g O2 are allowed to react, which is the limiting reagent? A. NH3 B. O2 C. Neither reagent is limiting. ...
... 16. Ammonia reacts with diatomic oxygen to form nitric oxide and water vapor: 4NH3 + 5O2 4NO + 6H2O When 40.0 g NH3 and 50.0 g O2 are allowed to react, which is the limiting reagent? A. NH3 B. O2 C. Neither reagent is limiting. ...
Fundamentals of Chemistry
... • The number of electrons in the valence shell determines the relative activity of an element. • The arrangement of electrons in the outer shell explains why some elements are chemically very active, some are not very active, and others are inert. • Group I has 1 valence electron, which makes it eas ...
... • The number of electrons in the valence shell determines the relative activity of an element. • The arrangement of electrons in the outer shell explains why some elements are chemically very active, some are not very active, and others are inert. • Group I has 1 valence electron, which makes it eas ...
Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. Three
... Law of Conservation of Mass: Matter can be neither created nor destroyed. Law of Definite Proportions: A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by weight. Law of Multiple Proportions: If two elements can combine to form more than one compound, then the masses of one e ...
... Law of Conservation of Mass: Matter can be neither created nor destroyed. Law of Definite Proportions: A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by weight. Law of Multiple Proportions: If two elements can combine to form more than one compound, then the masses of one e ...
Atoms and Molecules
... Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons, whose properties are shown below: ...
... Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons, whose properties are shown below: ...
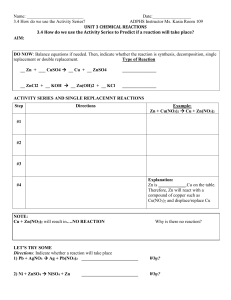
3.4 How do we use the Activity Series
... ADPHS Instructor Ms. Kasia Room 109 UNIT 3 CHEMICAL REACTIONS 3.4 How do we use the Activity Series to Predict if a reaction will take place? AIM: ...
... ADPHS Instructor Ms. Kasia Room 109 UNIT 3 CHEMICAL REACTIONS 3.4 How do we use the Activity Series to Predict if a reaction will take place? AIM: ...
Chemistry Revision Guide - Mr Cartlidge`s Science Blog
... When the liquids being distilled have similar boiling points, normal distillation can’t separate them completely but simply gives a purer mixture. In this case a fractionating column is used. This provides a large surface area for condensation meaning much purer ‘fractions’ are produced. The most im ...
... When the liquids being distilled have similar boiling points, normal distillation can’t separate them completely but simply gives a purer mixture. In this case a fractionating column is used. This provides a large surface area for condensation meaning much purer ‘fractions’ are produced. The most im ...
General and Organic Chemistry: Theory content HT 2016
... Chemical shift. Inductive and anisotropic effects. Magnetically and non-magnetically equivalent protons, how to count protons. Spin-spin coupling, splitting, chemical exchange. Practical interpretation of simple 1H-NMR spectra. 13C-NMR. Lecture: Oxidation, reduction. F&F ch. 7.8A, 7.8C, 10.13, 13.6B ...
... Chemical shift. Inductive and anisotropic effects. Magnetically and non-magnetically equivalent protons, how to count protons. Spin-spin coupling, splitting, chemical exchange. Practical interpretation of simple 1H-NMR spectra. 13C-NMR. Lecture: Oxidation, reduction. F&F ch. 7.8A, 7.8C, 10.13, 13.6B ...
Ch 17- Carboxylic Acids and their derivatives
... – 1) The reaction can proceed through a six membered cyclic transition state to form an enol which tautomerises to the ketone – 2) When the carboxylate anion decarboxylates, it forms a resonance-stabilized enolate anion ...
... – 1) The reaction can proceed through a six membered cyclic transition state to form an enol which tautomerises to the ketone – 2) When the carboxylate anion decarboxylates, it forms a resonance-stabilized enolate anion ...
chemistry in the 8th grade
... configuration. This would be 2 electrons in the first shell and 8 electrons in any shell after the first one. Atoms can undergo chemical reactions by losing, gaining, or sharing electrons to achieve this stable configuration. If atoms have 3 or fewer outer electrons, they can lose these electrons to ...
... configuration. This would be 2 electrons in the first shell and 8 electrons in any shell after the first one. Atoms can undergo chemical reactions by losing, gaining, or sharing electrons to achieve this stable configuration. If atoms have 3 or fewer outer electrons, they can lose these electrons to ...
Molecules of the Cell: The Building Blocks of Life
... neutrons possess most of the mass of an atom and form the core or atomic nucleus, while the electrons orbit the nucleus in regions called “shells” ( Figure 3.2a ). There are some 92 different naturally occurring elements, all of which differ from one another based on the number of protons and neutro ...
... neutrons possess most of the mass of an atom and form the core or atomic nucleus, while the electrons orbit the nucleus in regions called “shells” ( Figure 3.2a ). There are some 92 different naturally occurring elements, all of which differ from one another based on the number of protons and neutro ...
Metabolic-pathway– directed targeted metabolomics
... strategy (trigonelline, N-methyl-nicotinic acid) the subsequent hypothesis-driven targeted data evaluation revealed several novel characteristic metabolites for weak and strong coffee. • A target database can easily be extended to include other compounds of interest to broaden th ...
... strategy (trigonelline, N-methyl-nicotinic acid) the subsequent hypothesis-driven targeted data evaluation revealed several novel characteristic metabolites for weak and strong coffee. • A target database can easily be extended to include other compounds of interest to broaden th ...
Dynamic Modeling of Lactic Acid Fermentation Metabolism with
... from various studies, mainly Hoefnagel et al. [7] and Rizzi et al. [20]. These equations and initial values are shown in Tables 2 and 3. For permease (PERM), the equation suggested by Rizzi et al. [19] was used. Although this equation was developed from the Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain, it is ado ...
... from various studies, mainly Hoefnagel et al. [7] and Rizzi et al. [20]. These equations and initial values are shown in Tables 2 and 3. For permease (PERM), the equation suggested by Rizzi et al. [19] was used. Although this equation was developed from the Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain, it is ado ...
Structure and Properties of Matter
... called molecular formula of the compound. Thus, a molecular formula of a substance tells us how many atoms of each kind are present in one molecule. In Fig. 2.6, you will find that atoms in a molecule are not only connected in definite ways but also exhibit definite spatial arrangements. Properties ...
... called molecular formula of the compound. Thus, a molecular formula of a substance tells us how many atoms of each kind are present in one molecule. In Fig. 2.6, you will find that atoms in a molecule are not only connected in definite ways but also exhibit definite spatial arrangements. Properties ...
Chapter 11 Notes
... An unstable isotope will decay but the exact amount of time until it decays is unknown. ...
... An unstable isotope will decay but the exact amount of time until it decays is unknown. ...
File
... • The following reaction shows table salt production. How many moles of sodium chloride are produced from 0.02 moles of chlorine? ...
... • The following reaction shows table salt production. How many moles of sodium chloride are produced from 0.02 moles of chlorine? ...
Atoms and Molecules
... Each element is composed of atoms – which are incredibly small. All atoms of a given element are identical to one another in mass and other properties, and different from all other atoms. That atoms were indivisible, and were not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. When atoms of different el ...
... Each element is composed of atoms – which are incredibly small. All atoms of a given element are identical to one another in mass and other properties, and different from all other atoms. That atoms were indivisible, and were not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. When atoms of different el ...
CHEMISTRY REVISION GUIDE for CIE IGCSE Coordinated Science
... Paper chromatography is a technique that can be used to separate mixtures of dyes or pigments and is used to test the purity of a mixture or to see what it contains. Firstly a very strong solution of the mixture is prepared which is used to build up a small intense spot on a piece of absorbent paper ...
... Paper chromatography is a technique that can be used to separate mixtures of dyes or pigments and is used to test the purity of a mixture or to see what it contains. Firstly a very strong solution of the mixture is prepared which is used to build up a small intense spot on a piece of absorbent paper ...
Directed Reading
... a. Helium does not react with other substances but does form new substances. b. Helium reacts with other substances but does not form new substances. c. Helium reacts with other substances to form new substances. d. Helium does not react with other substances to form new substances. ______ 9. A subs ...
... a. Helium does not react with other substances but does form new substances. b. Helium reacts with other substances but does not form new substances. c. Helium reacts with other substances to form new substances. d. Helium does not react with other substances to form new substances. ______ 9. A subs ...
February Homework Packet
... 8. How do the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the third shell of an atom compare to the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the first shell of the same atom? (1) In the third shell, an electron has more energy and is closer to the nucleus. (2) In the third ...
... 8. How do the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the third shell of an atom compare to the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the first shell of the same atom? (1) In the third shell, an electron has more energy and is closer to the nucleus. (2) In the third ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.